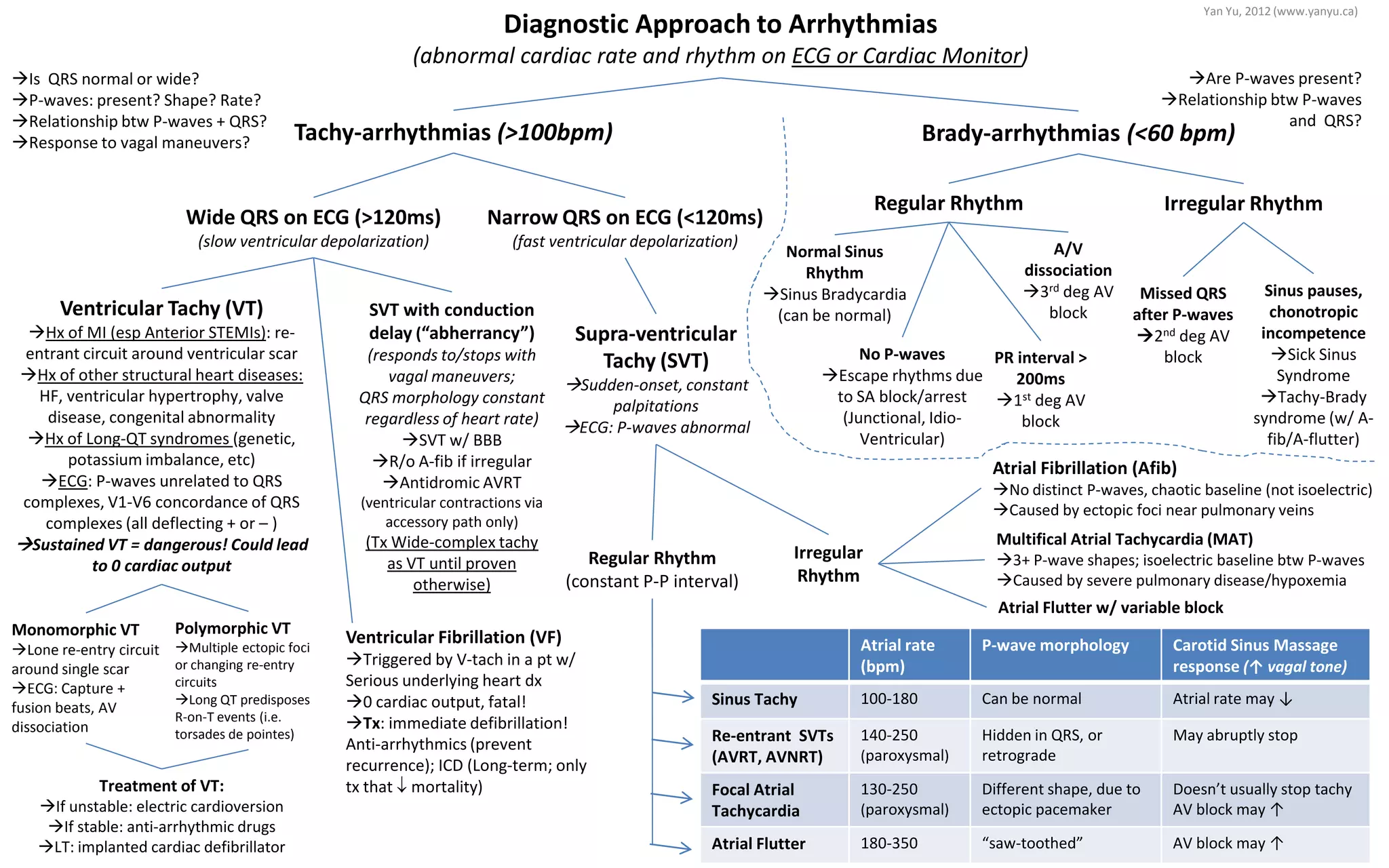
This document provides an overview of the diagnostic approach and treatment for arrhythmias based on ECG findings. It outlines the key characteristics of different types of tachycardias and bradycardias including whether P-waves are present, the relationship between P-waves and QRS complexes, and response to vagal maneuvers. Treatment options are also summarized, such as electric cardioversion for unstable ventricular tachycardia or an implanted cardiac defibrillator for long term management of life-threatening arrhythmias.