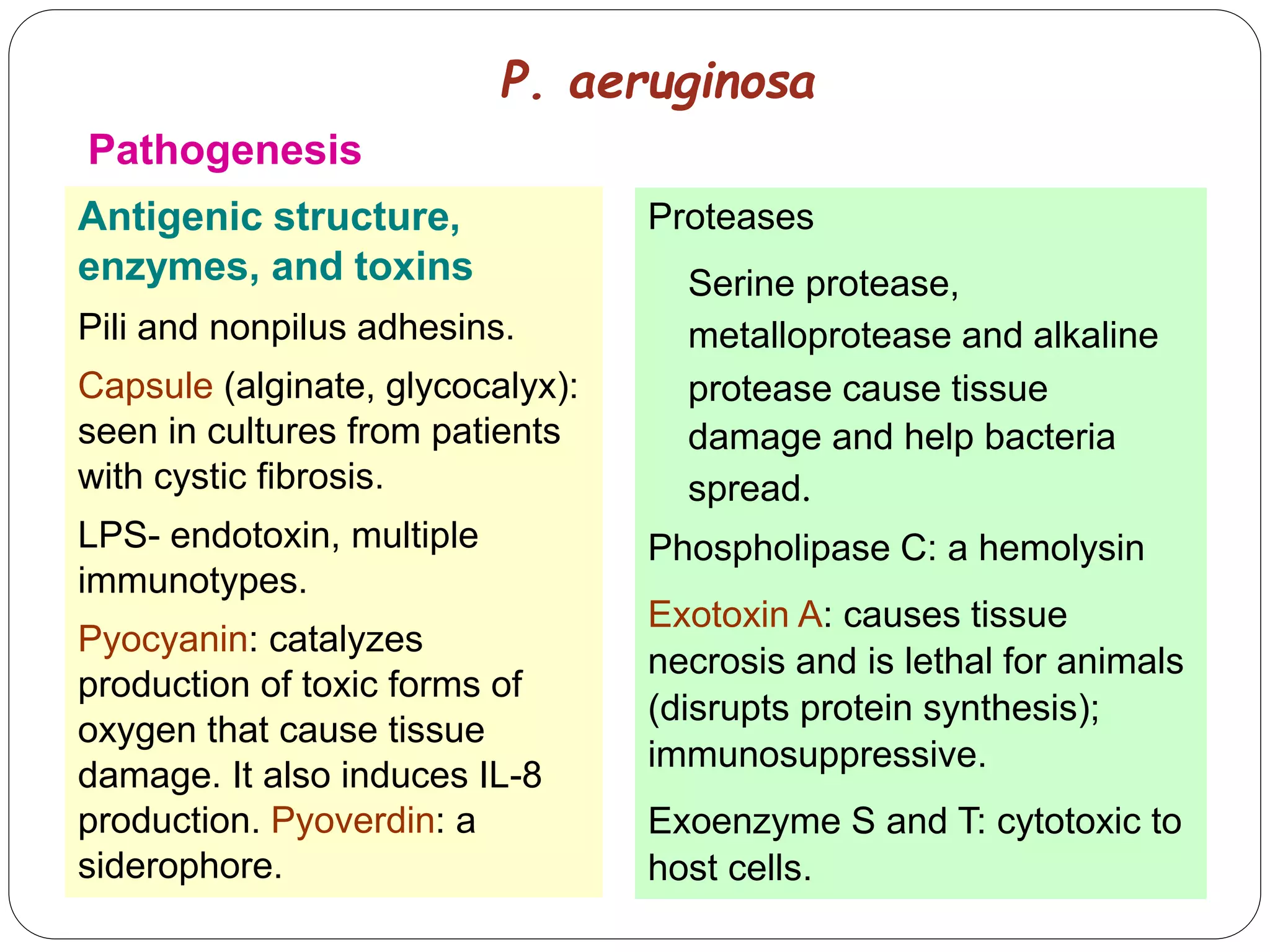
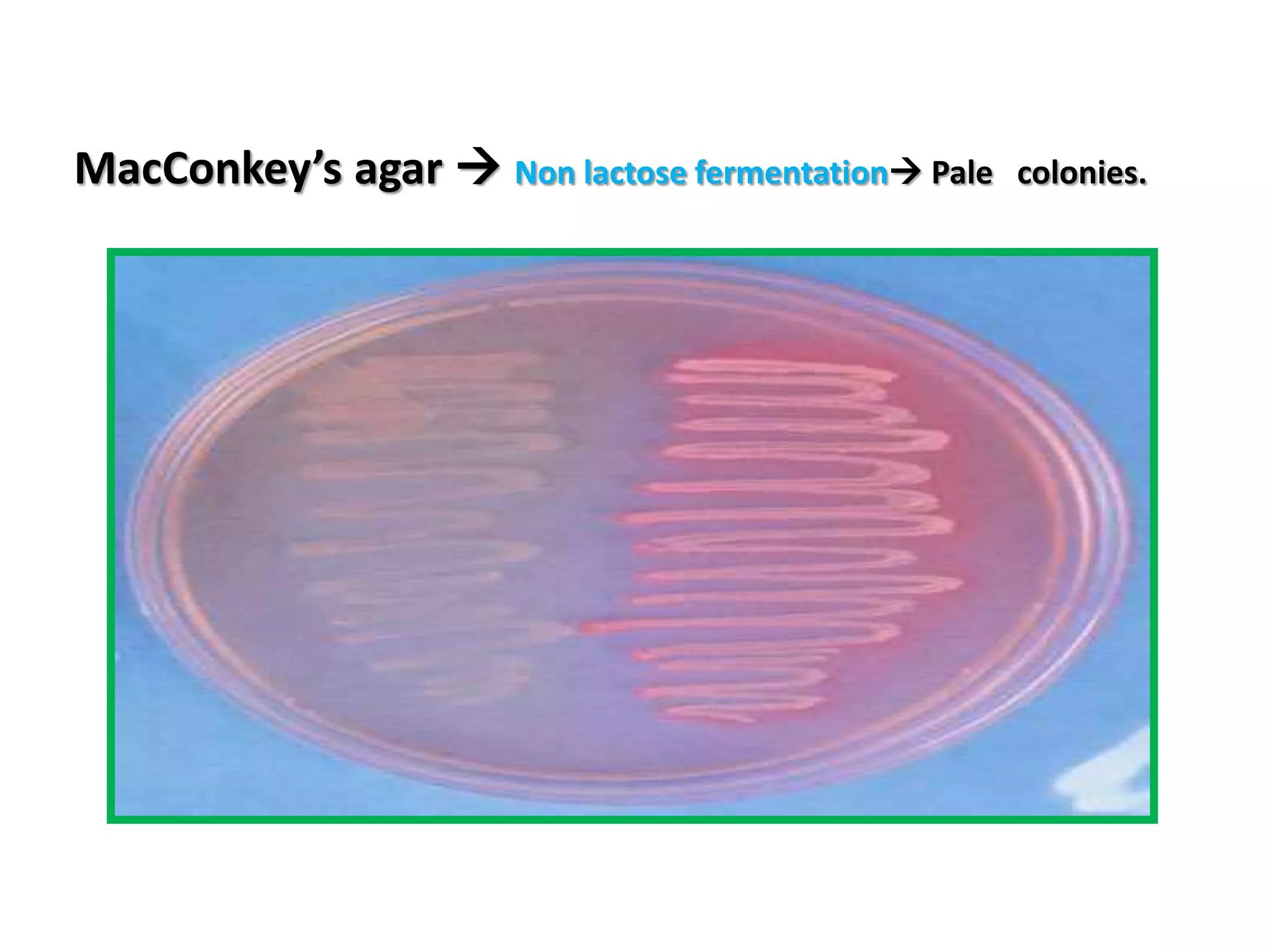
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a motile, aerobic, gram-negative bacterium known for causing opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients and in disrupted environments. It is characterized by its resistance to multiple antibiotics, production of distinctive pigments, and capability to infect various sites including wounds, lungs, and urinary tract. Prevention and control involve strict hygiene practices and isolation measures, especially for high-risk populations.