Embed presentation
Downloaded 63 times


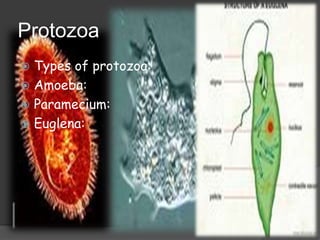




Protozoa are unicellular eukaryotes that can range in size from 10 to 52 micrometers but sometimes grow up to 1 millimeter. They exist throughout water and soil and occupy different trophic levels. While previously grouped with algae and fungi in the Protista kingdom, modern classification systems do not consider Protozoa a formal taxon, instead categorizing them along with ciliates, mastigophorans, and apicomplexans as animal-like protists below the kingdom Metazoa. Common examples of protozoa include amoebas, paramecia, and trypanosomes.





