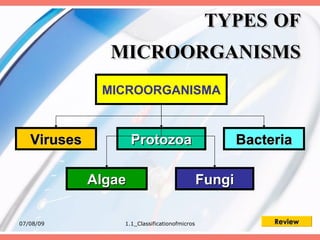
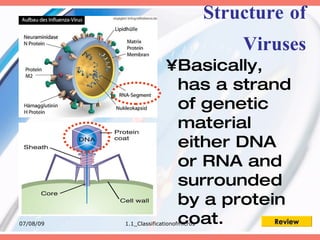
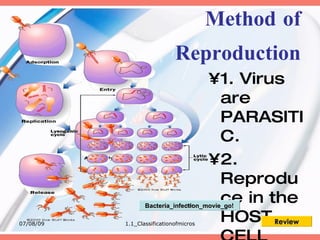
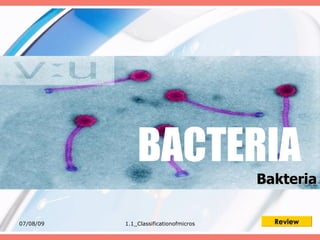
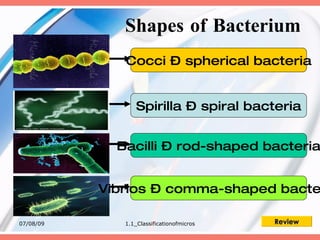
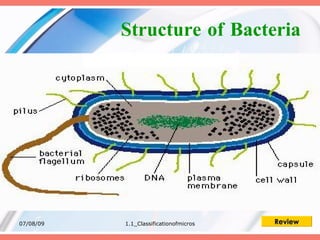
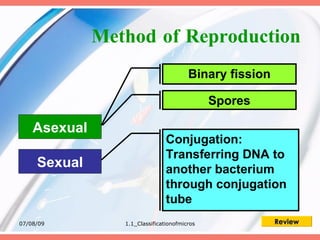
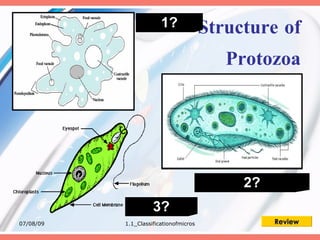
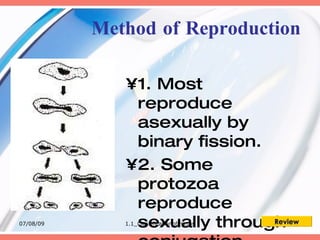
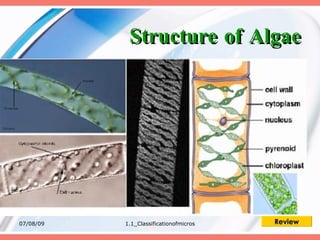
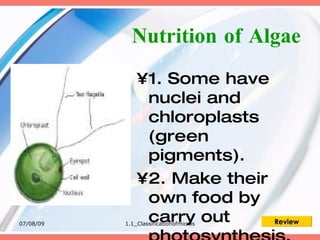
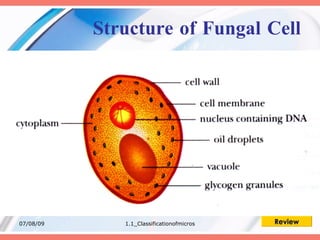
The document discusses the classification of microorganisms into five major categories: viruses, bacteria, protozoa, algae, and fungi. It provides details on the size, structure, habits, nutrition, and reproduction methods of each type of microorganism. The learning outcomes are listed as classifying microorganisms and describing the characteristics of viruses, bacteria, protozoa, algae, and fungi.