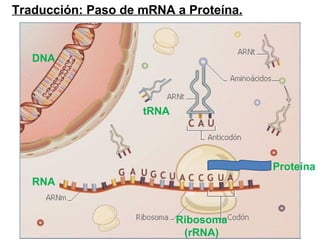
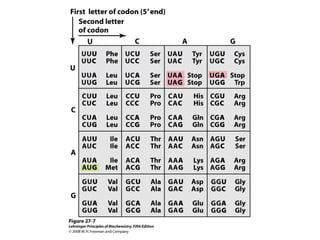
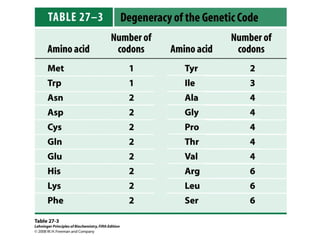
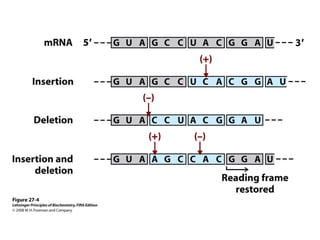
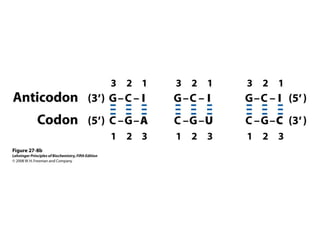
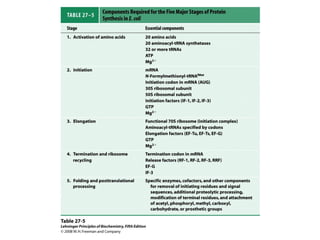
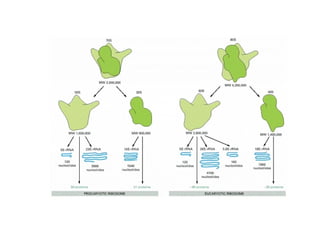
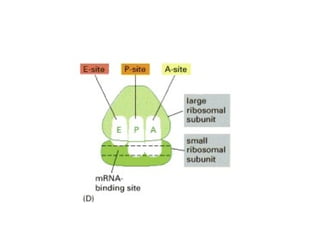
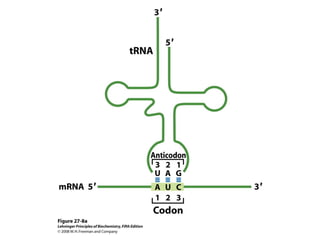
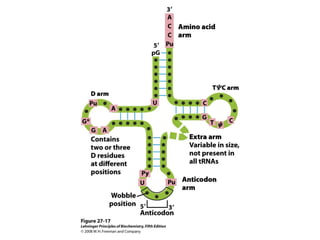
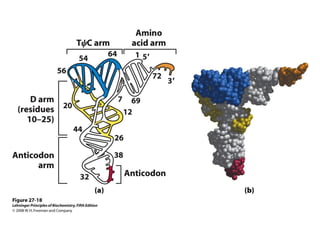
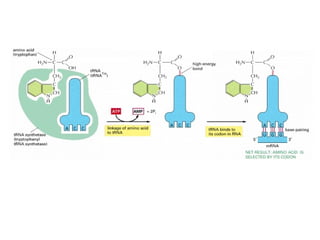
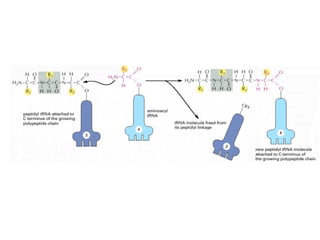
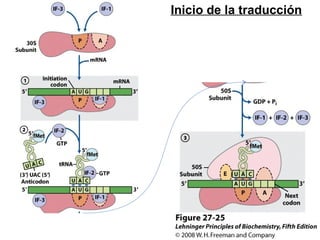
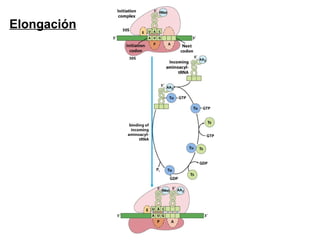
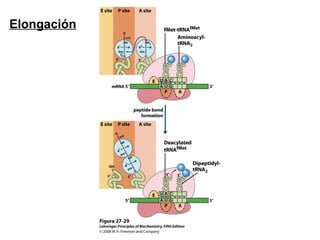
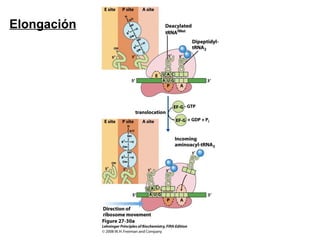
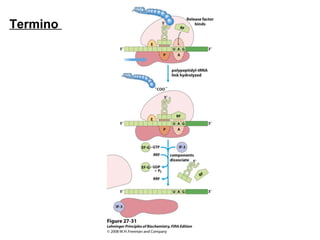
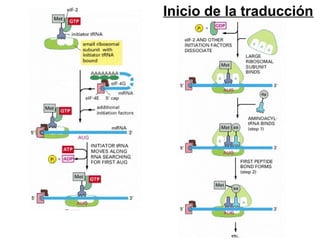
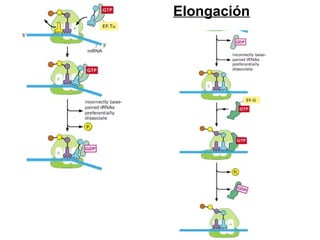
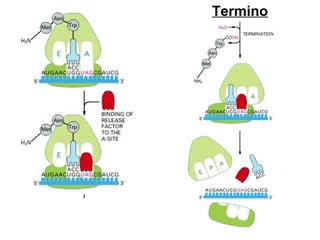
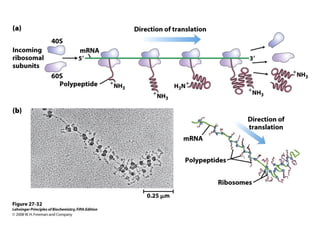
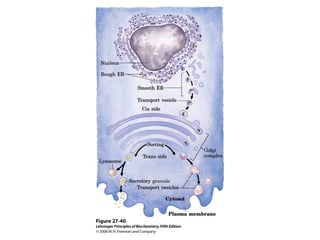
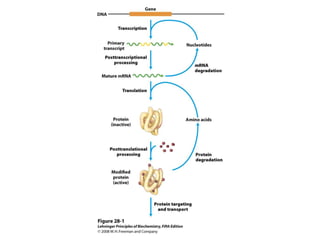
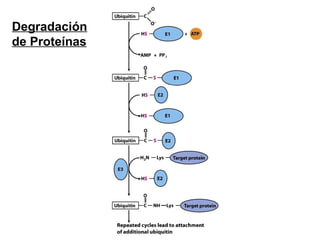
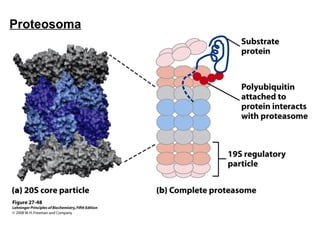
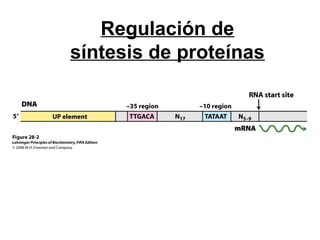
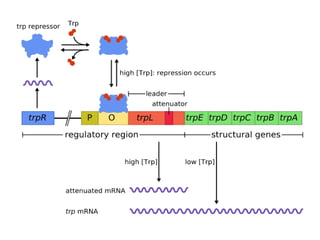
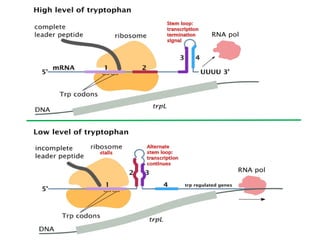
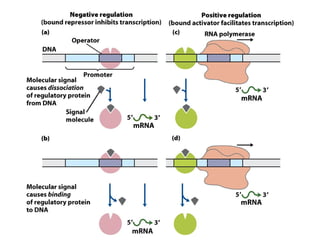
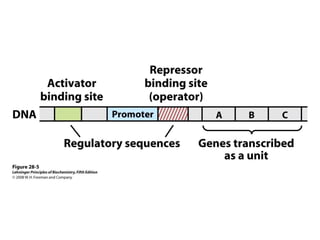
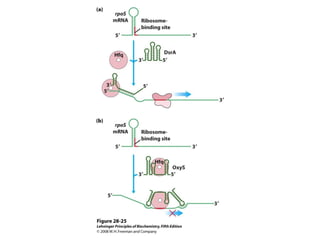
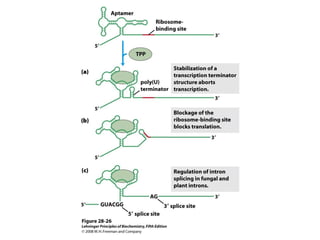
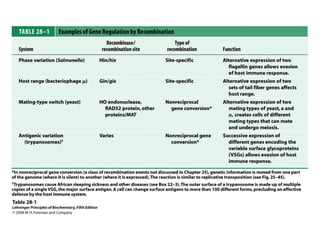
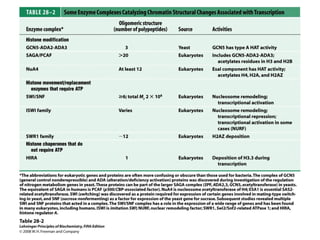
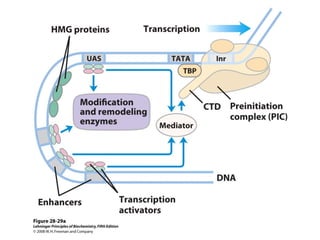
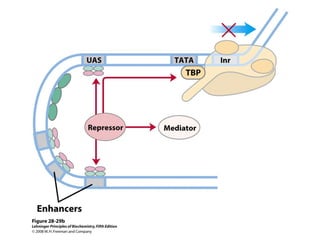
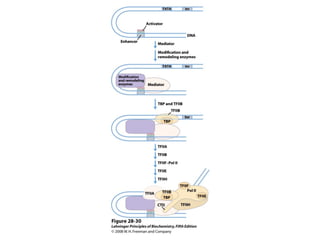
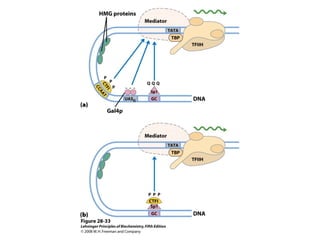
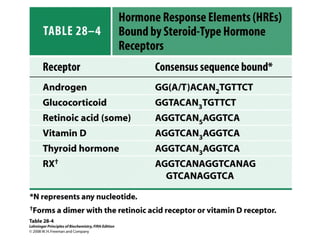
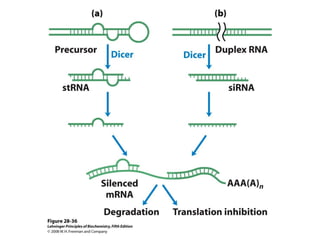
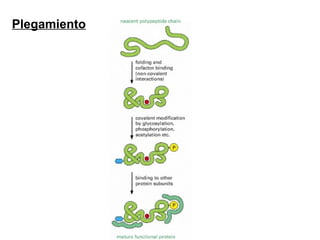
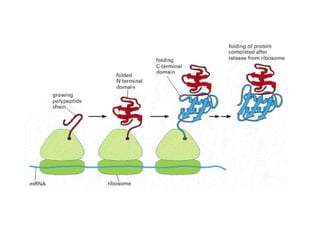
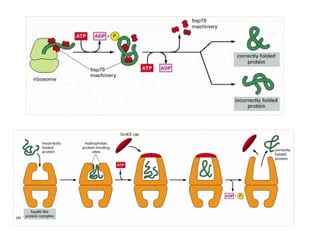
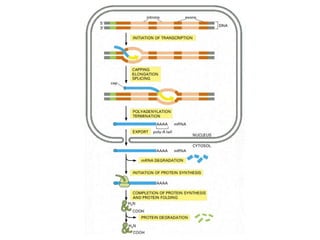
The document discusses protein synthesis and degradation. Protein synthesis occurs in the rough endoplasmic reticulum through translation - the process of mRNA being converted to protein with the help of tRNA and ribosomes. The translation process involves initiation, elongation, and termination steps. Protein degradation is carried out by the proteasome. Several inhibitors are listed that target different steps in protein synthesis, some affecting bacteria and eukaryotes, while others only affect one domain. Protein folding is also mentioned.