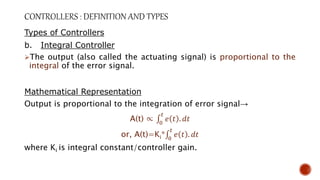
A controller seeks to minimize the difference between the actual value of a system and the desired set point value. It receives an input signal, compares it to the set point, and determines the appropriate output signal to provide corrective action. Controllers can be continuous or discontinuous. Common controller types include proportional, integral, derivative, and PID controllers. The transfer function represents the relationship between the input and output signals of a control system, and gain determines the strength of a controller's action above or below the set point.