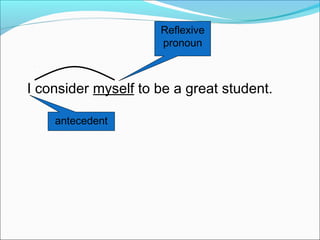
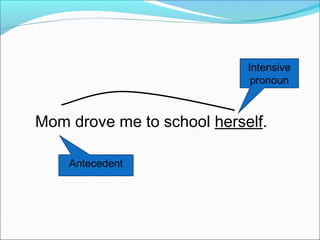
The document discusses pronouns and provides guidance on their proper use. It defines pronouns as words that take the place of nouns and defines antecedents as the words pronouns refer to. It describes the different types of pronouns and provides examples. Key rules discussed are that pronouns must have clear antecedents and agree with their antecedents in number, gender, and person. Examples are given of both correct and incorrect pronoun usage.