This document defines and describes different types of pronouns:
- Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things and include subject and object cases.
- Possessive pronouns indicate possession.
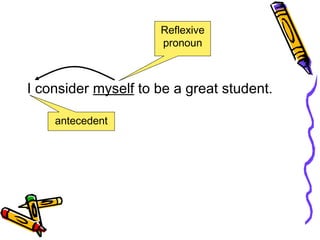
- Reflexive pronouns reflect back to a noun, add new information, and cannot be removed from sentences.
- Intensive pronouns add emphasis and can be removed from sentences.
- Demonstrative pronouns point out specific nouns and include this/that for singular and these/those for plural.
- Interrogative pronouns form questions.
- Relative pronouns begin subordinate clauses.
- Indefinite pronouns refer to unspecified persons or things