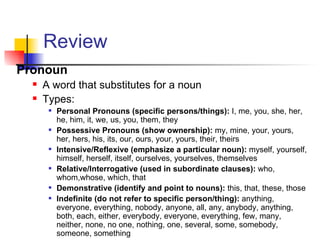
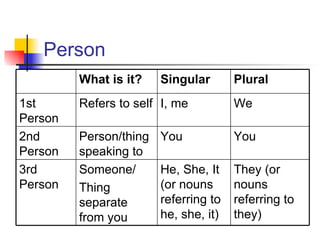
The document discusses pronouns and antecedents. It defines different types of pronouns such as personal, possessive, intensive/reflexive, relative/interrogative, and demonstrative pronouns. It also defines antecedents as the nouns that pronouns replace. The general rule is that pronouns and antecedents must agree in number, person, and gender. Some special cases of tricky pronoun-antecedent situations are also discussed, such as indefinite pronouns, collective nouns, antecedents with "every", "each", and "one", antecedents joined by "and", and antecedents ending in "s".