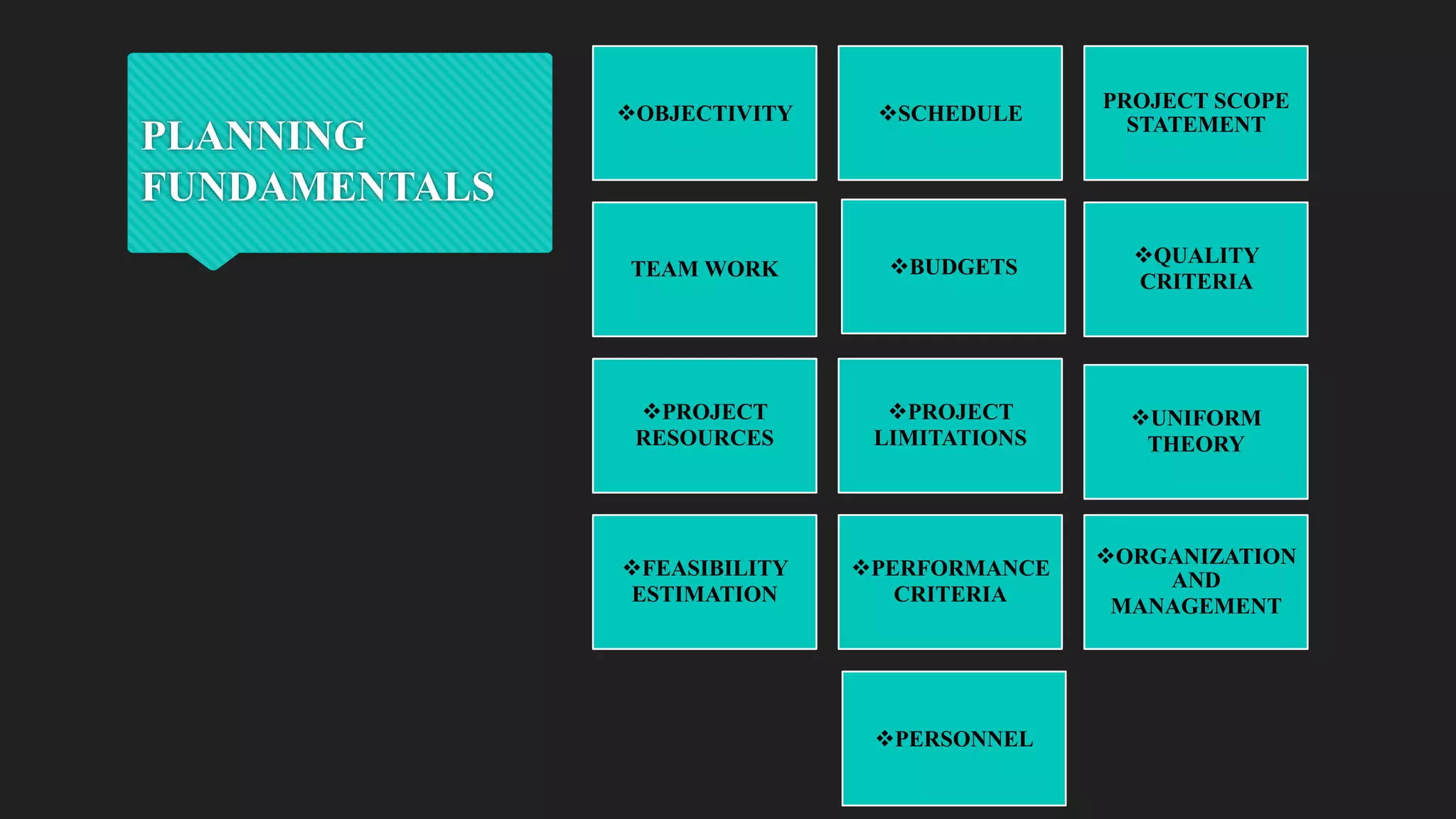
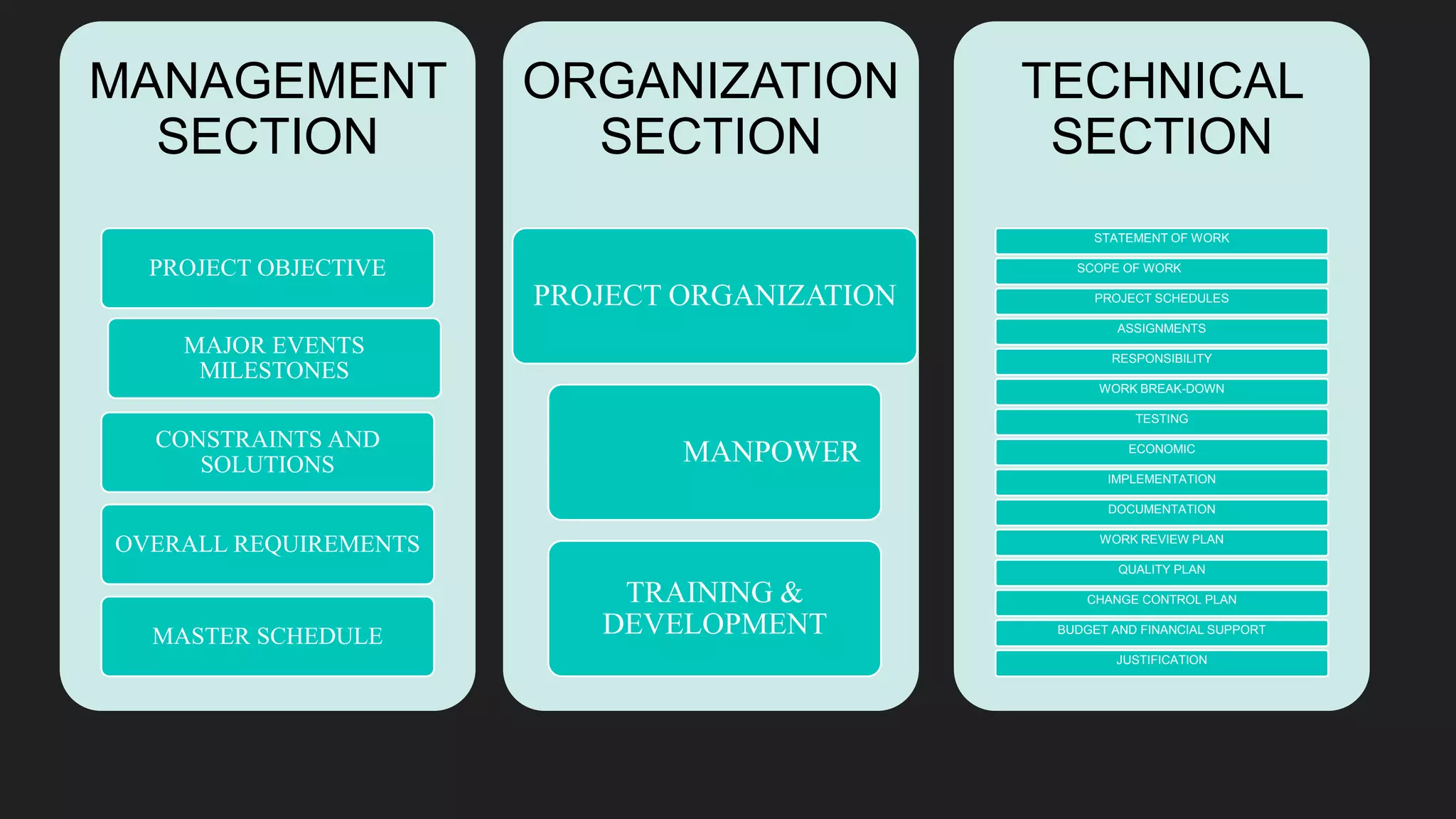
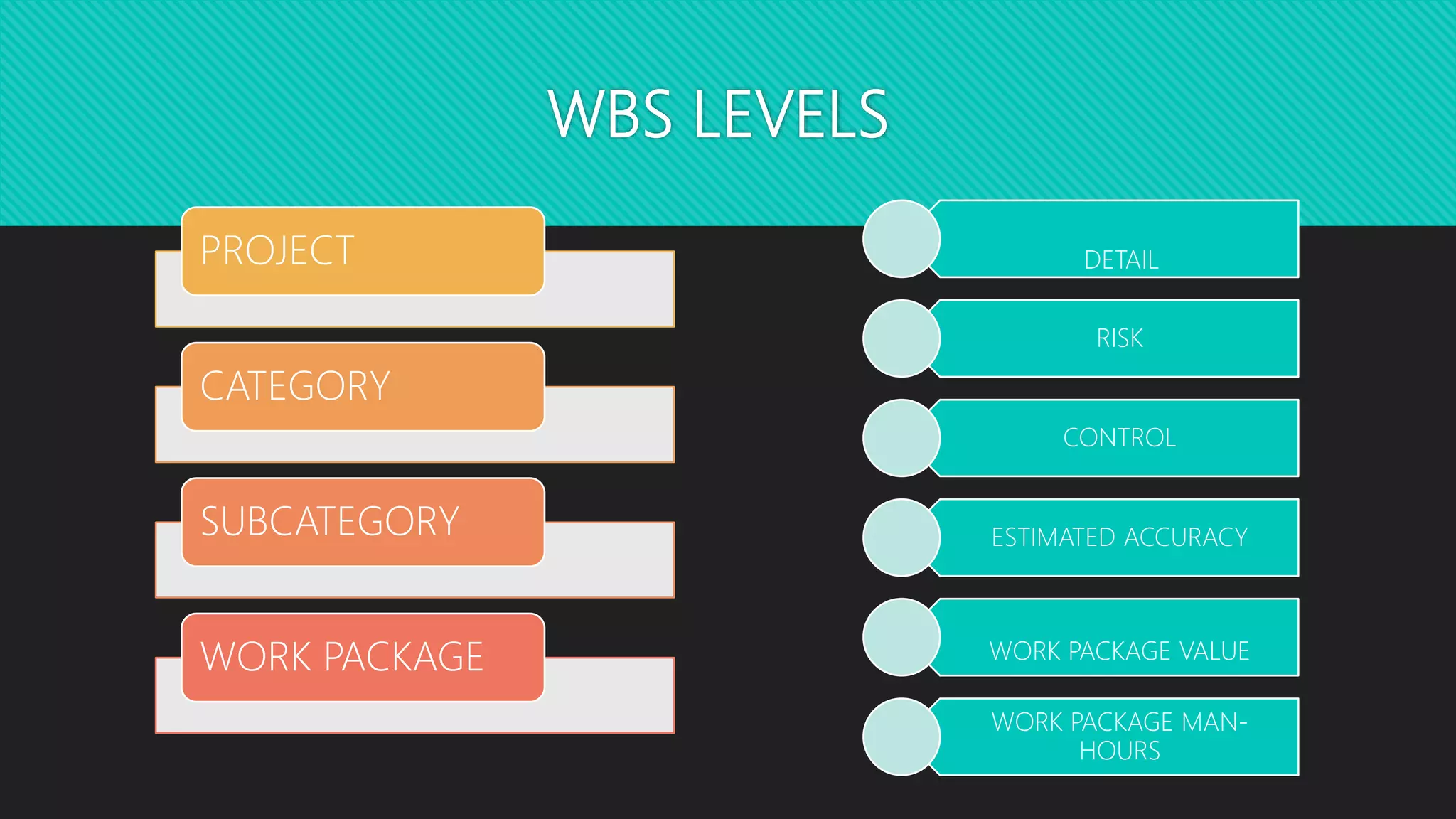
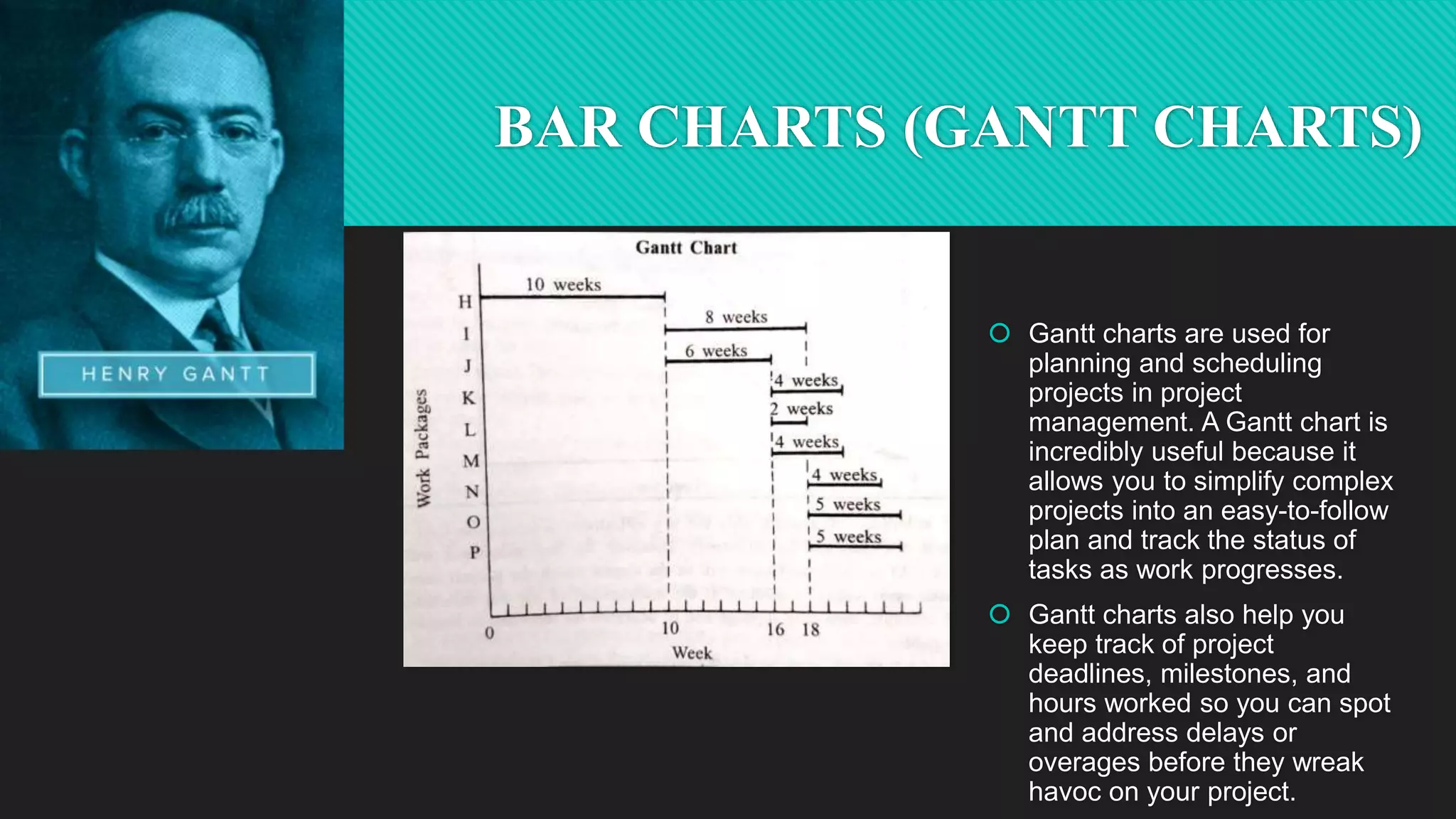
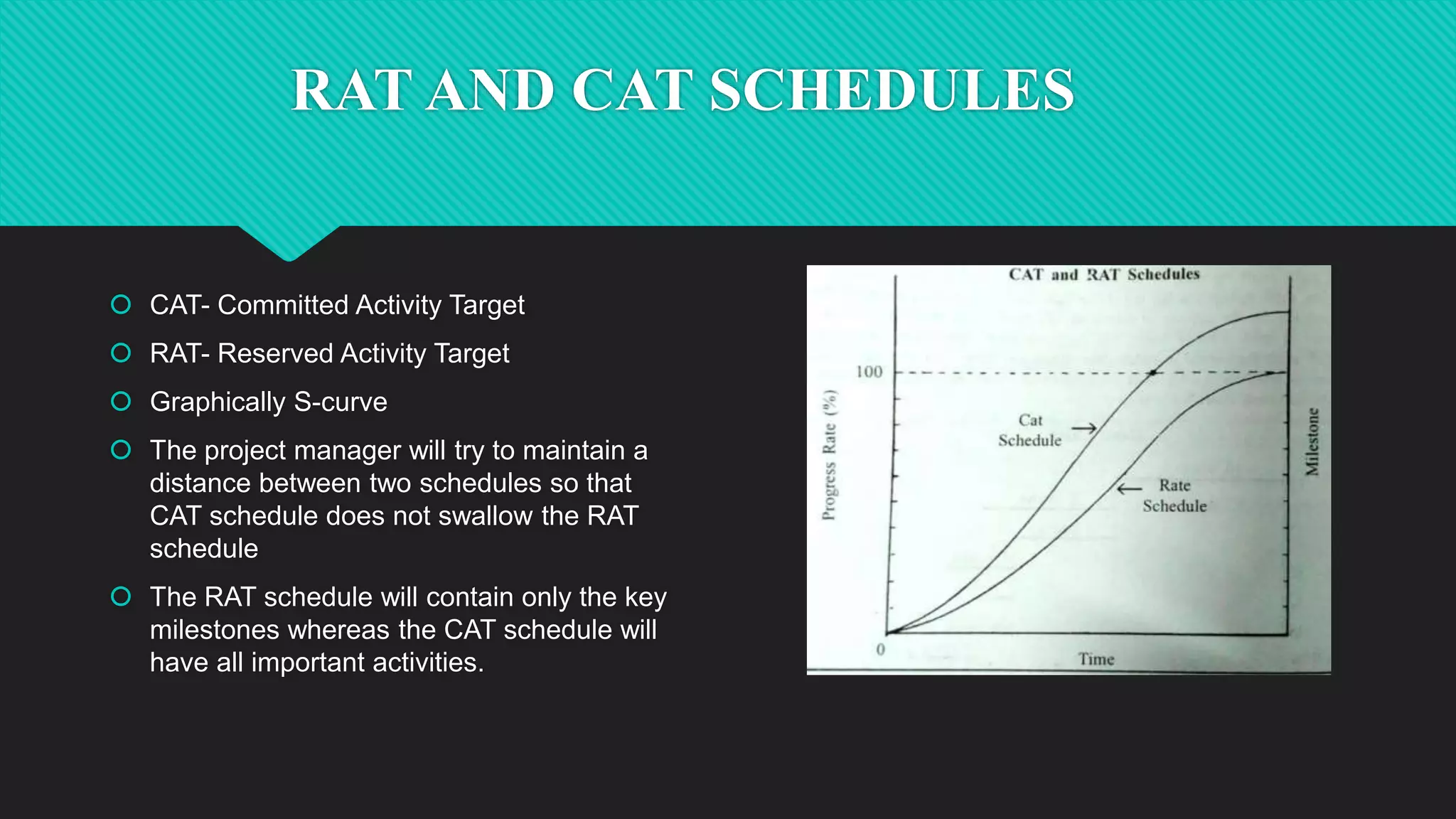
Dr. Richa Singhal presented information on project planning techniques. The document outlined various components of an effective project plan including work breakdown structure, work packages, scheduling methods like bar charts, RAT/CAT schedules and network schedules. It emphasized the importance of the project master plan which defines the overall scope and contains sections on management, organization, technical details and economics. Project planning allows for direction, control, motivation and efficient resource use which helps ensure project success.