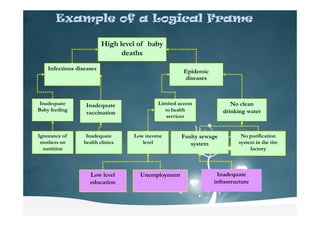
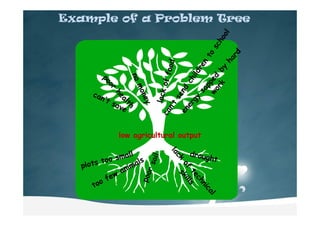
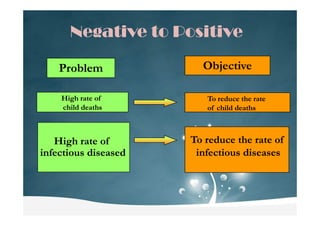
Logical Framework Analysis is a tool used to improve project design and implementation. It helps project planners understand the needs of those affected by a problem and identify potential positive and negative impacts. It also encourages participation from stakeholders with relevant knowledge. The analysis identifies rights, interests, resources, and abilities to determine who should be involved in project planning and implementation. It examines problems, their causes and effects to construct a problem tree diagram and helps set objectives to address the core problems.