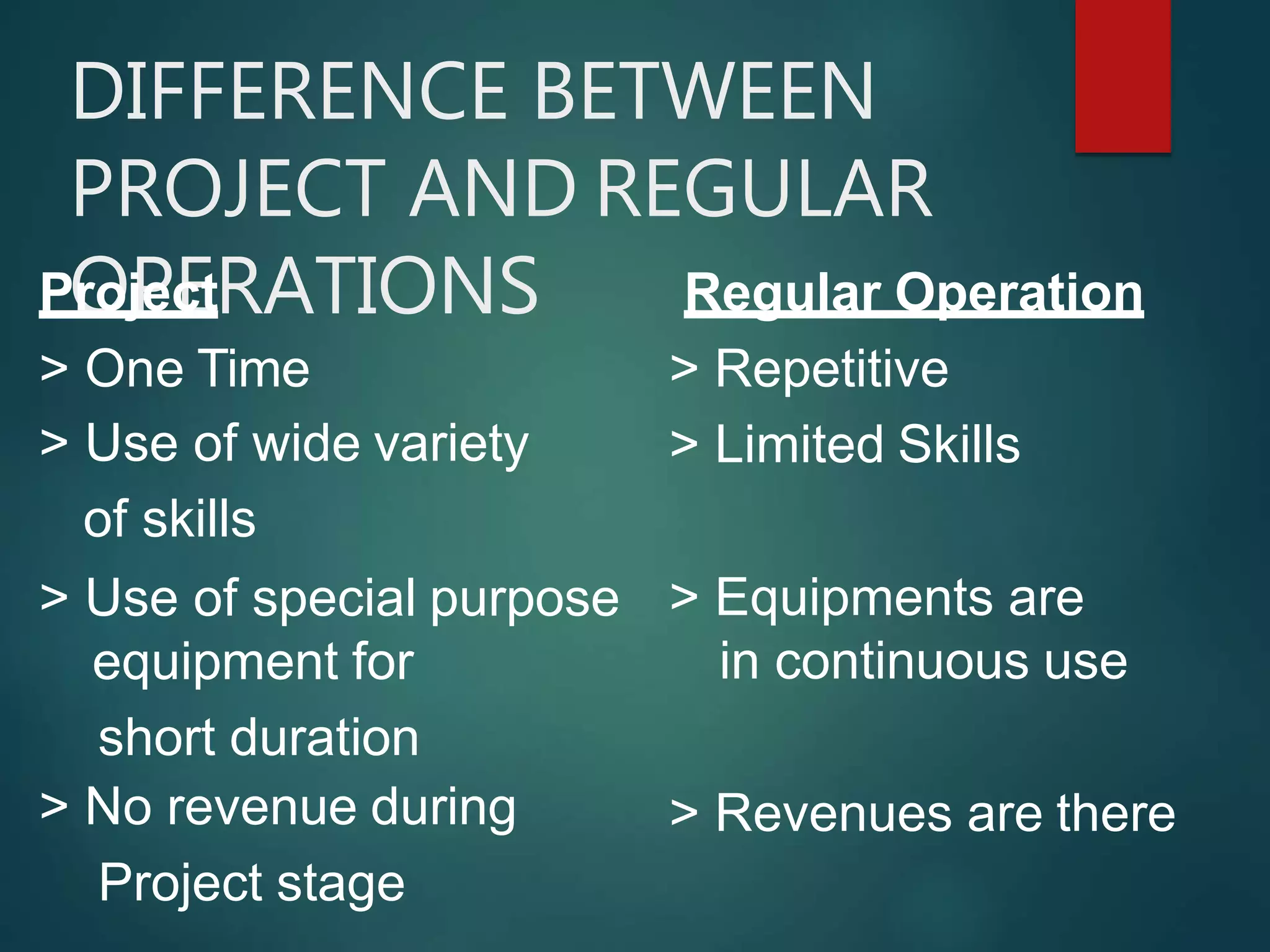
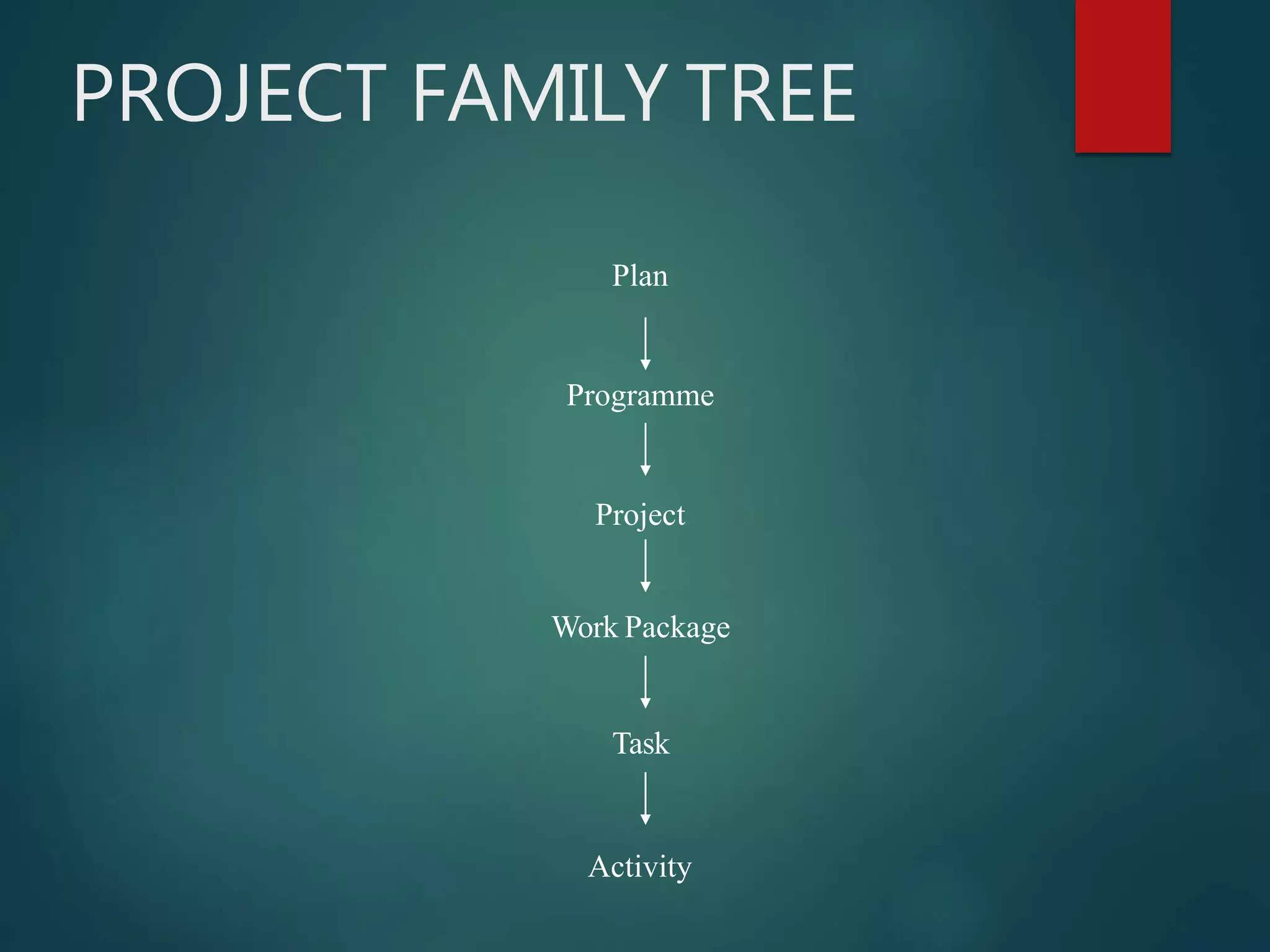
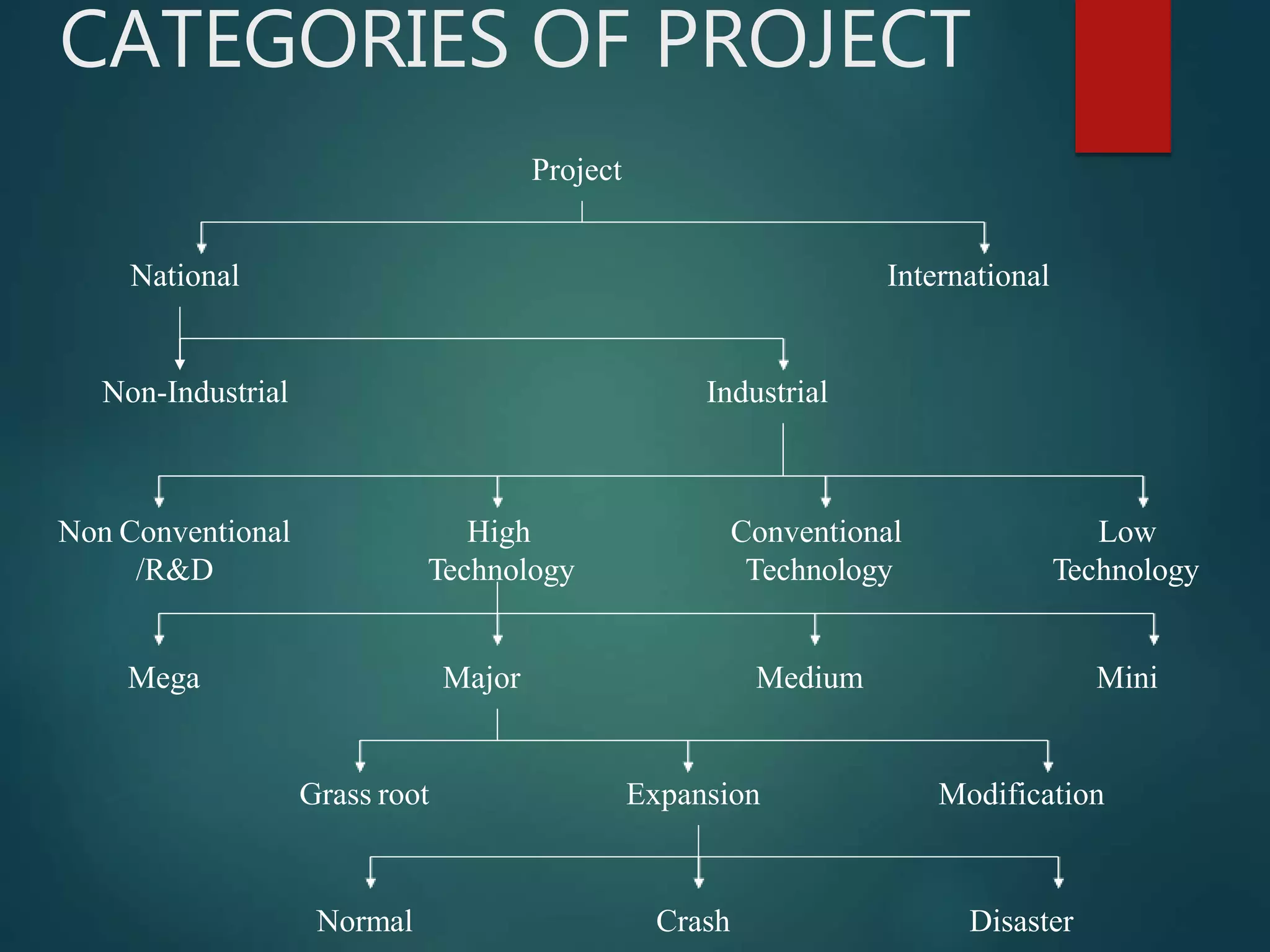
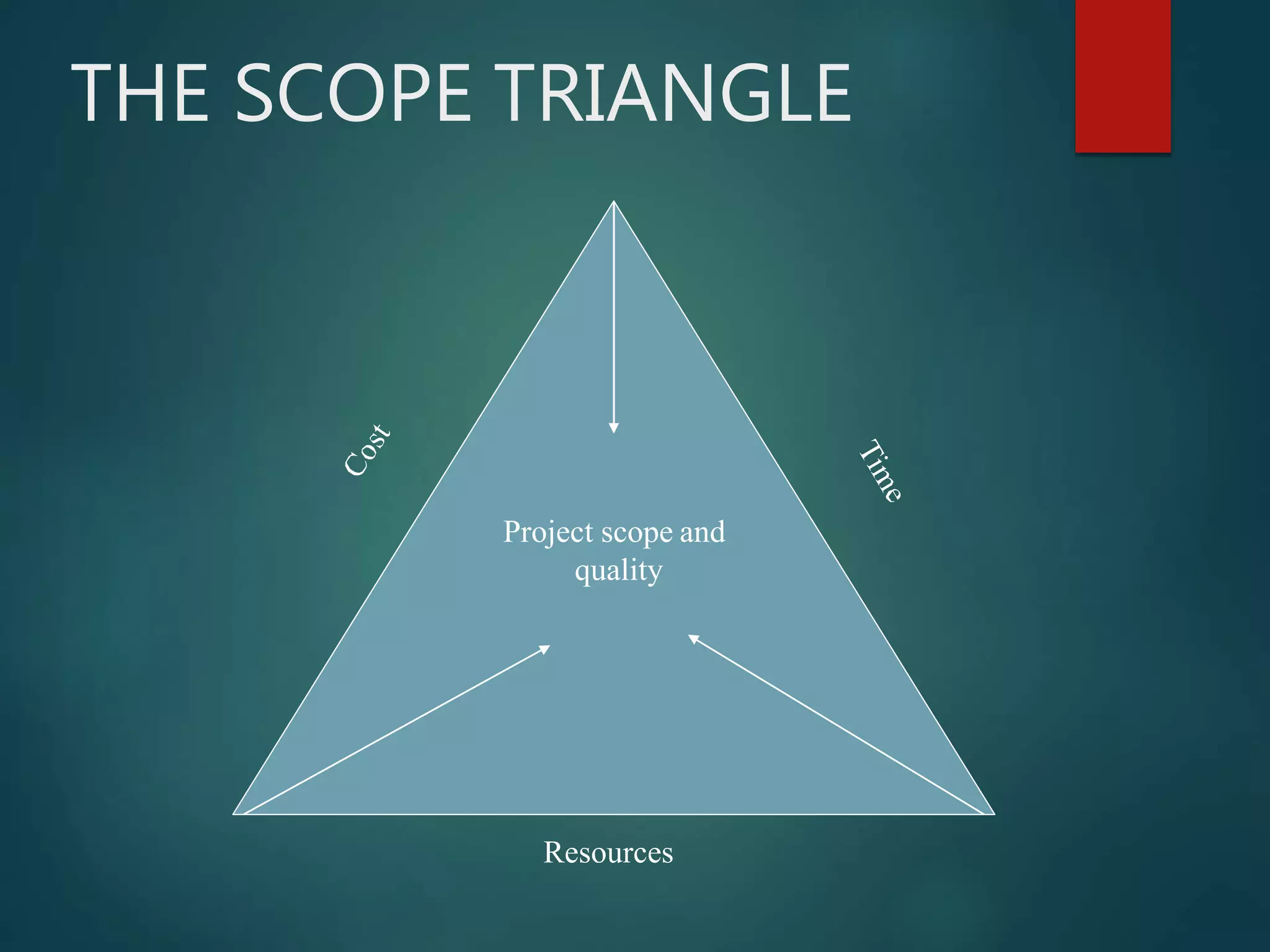
This document discusses project management. It defines a project as a combination of interrelated activities with well-defined objectives to be completed within a specific time period. Project management is then defined as the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities to meet requirements. The document outlines the importance of project management, including increasing project sizes, financial controls, and technology. It also discusses the benefits of project management such as clear work descriptions and timely completion.