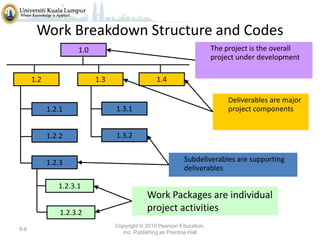
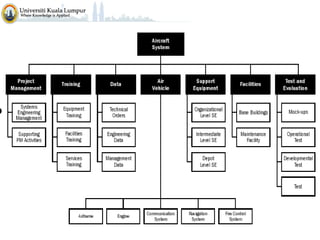
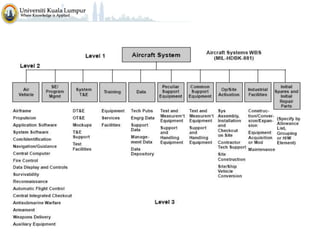
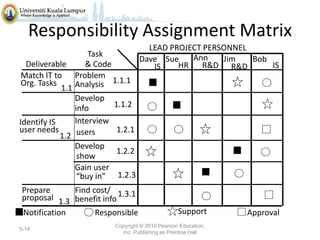
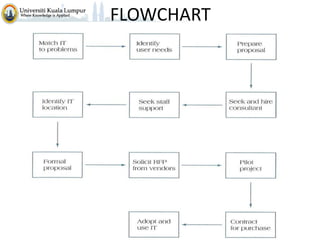
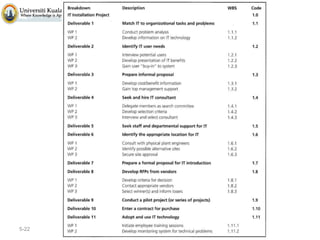
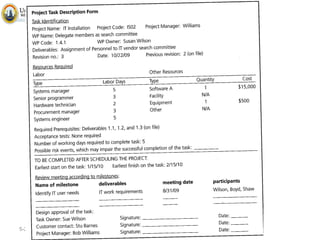
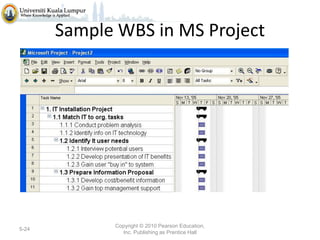
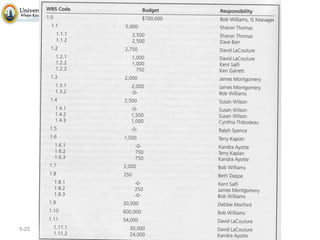
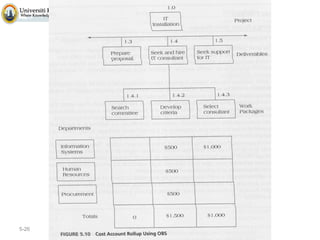
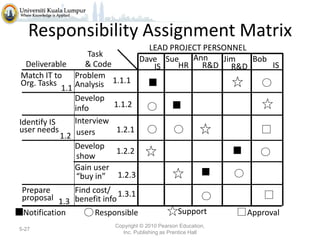
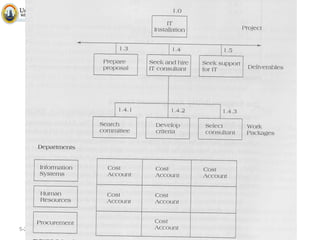
The document discusses project scope and scope management. It defines project scope as including all the work content and expected outcomes of a project. Scope management involves controlling the project goals, objectives, and consists of conceptual development, scope statement, work authorization, scope reporting, control systems, and project closeout. It provides details on each of these components, including defining problem statements, work breakdown structures, organizational breakdown structures, responsibility assignment matrices, and different types of contracts and control systems used in scope management.