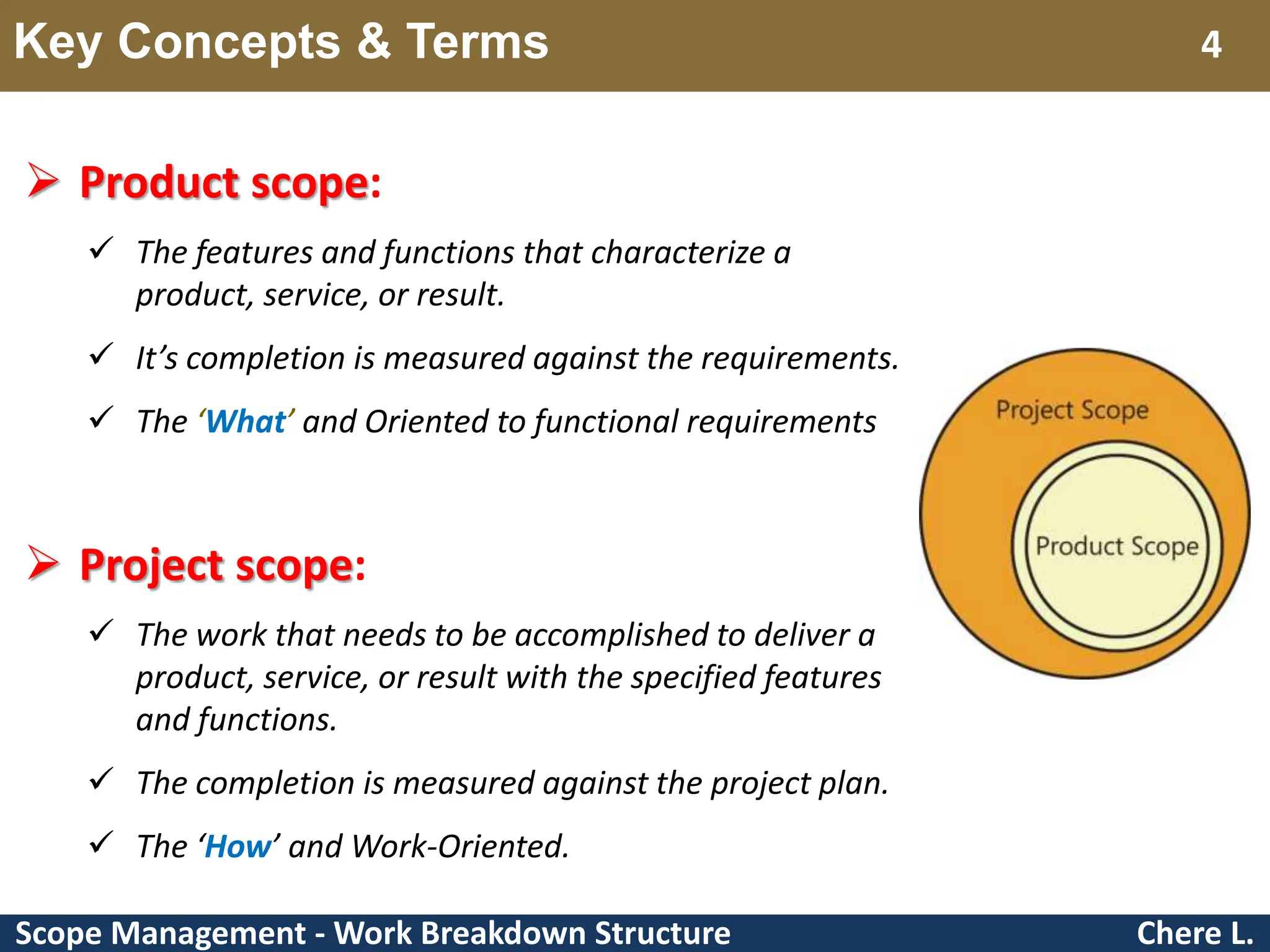
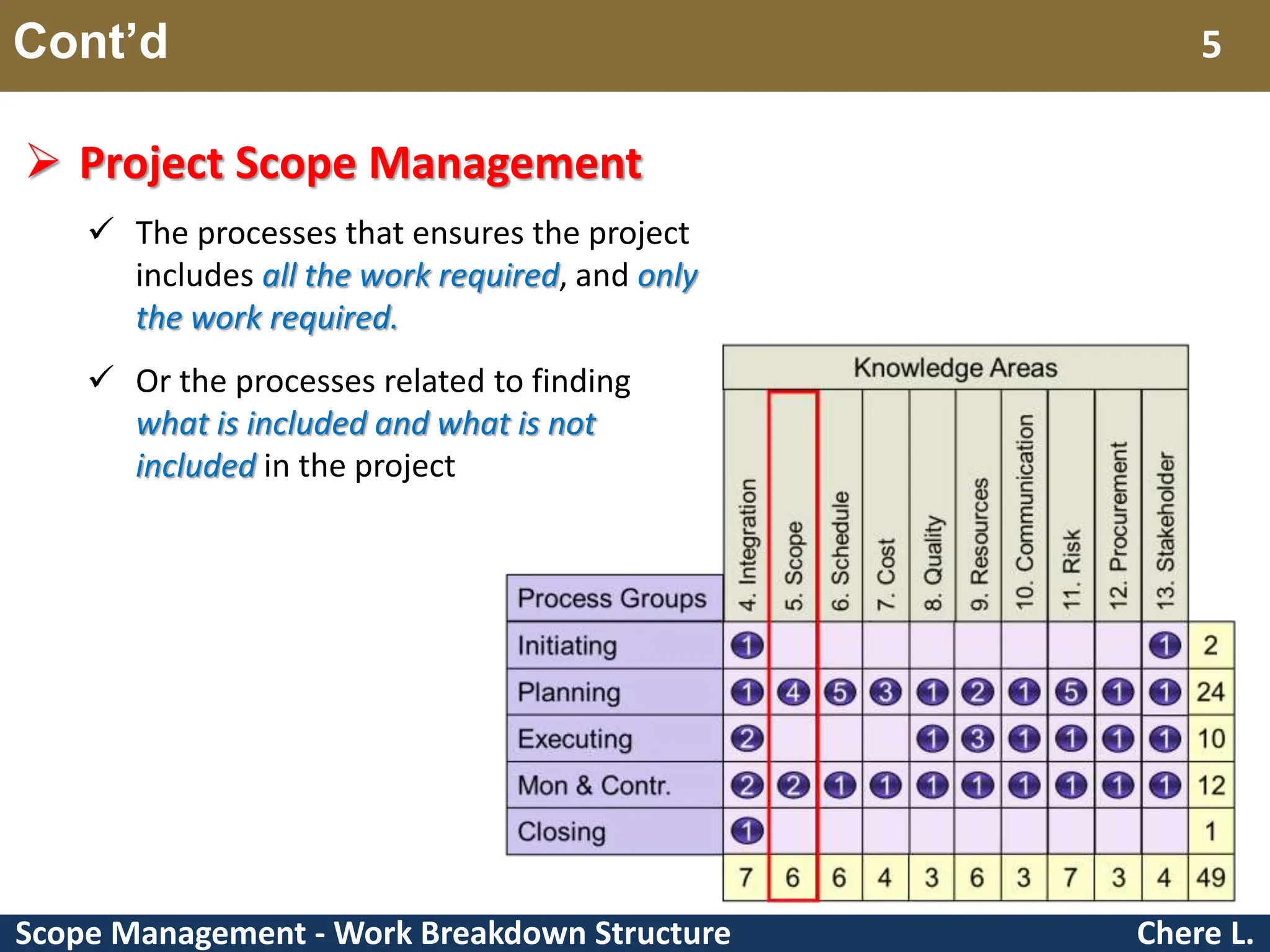
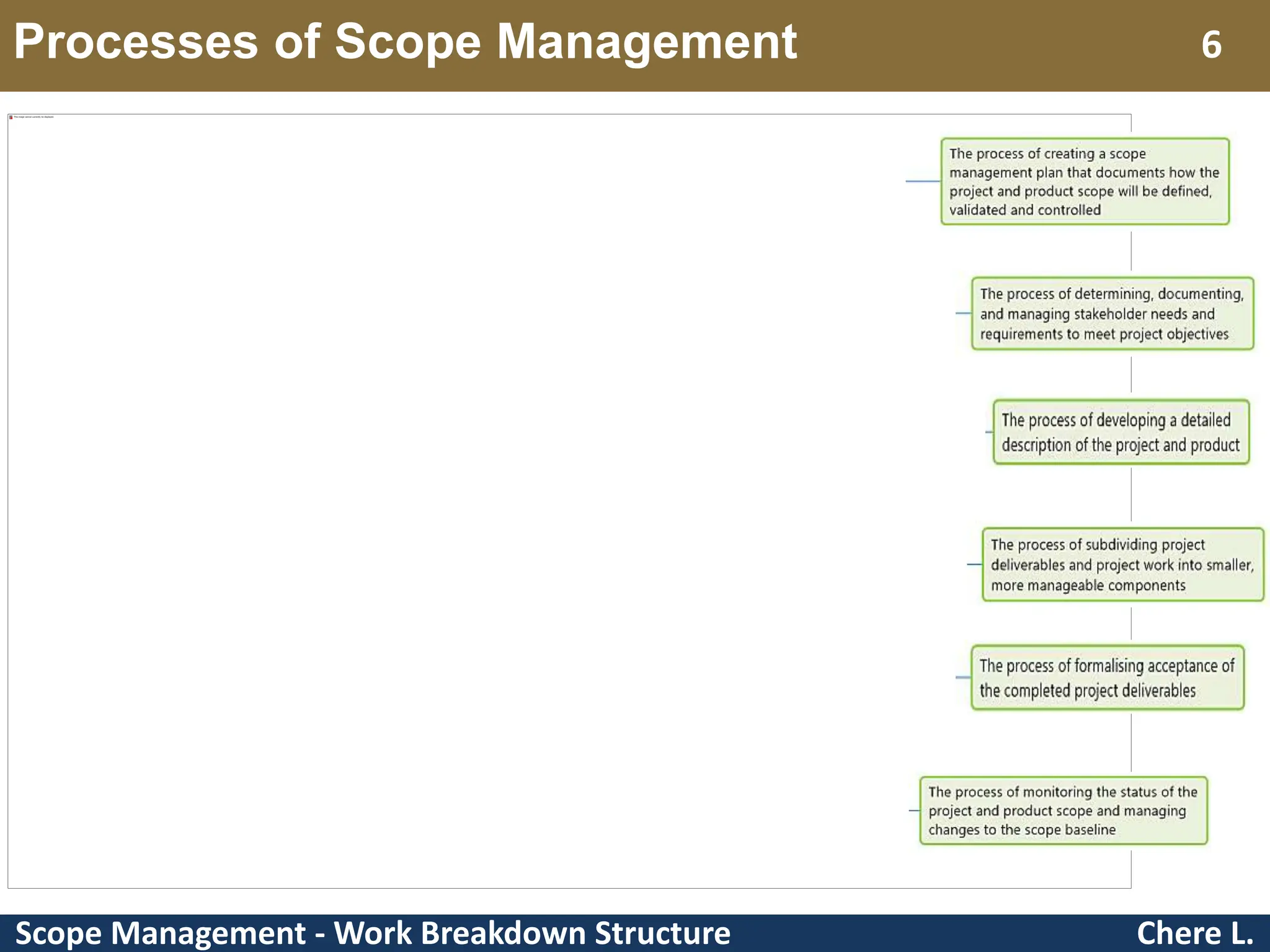
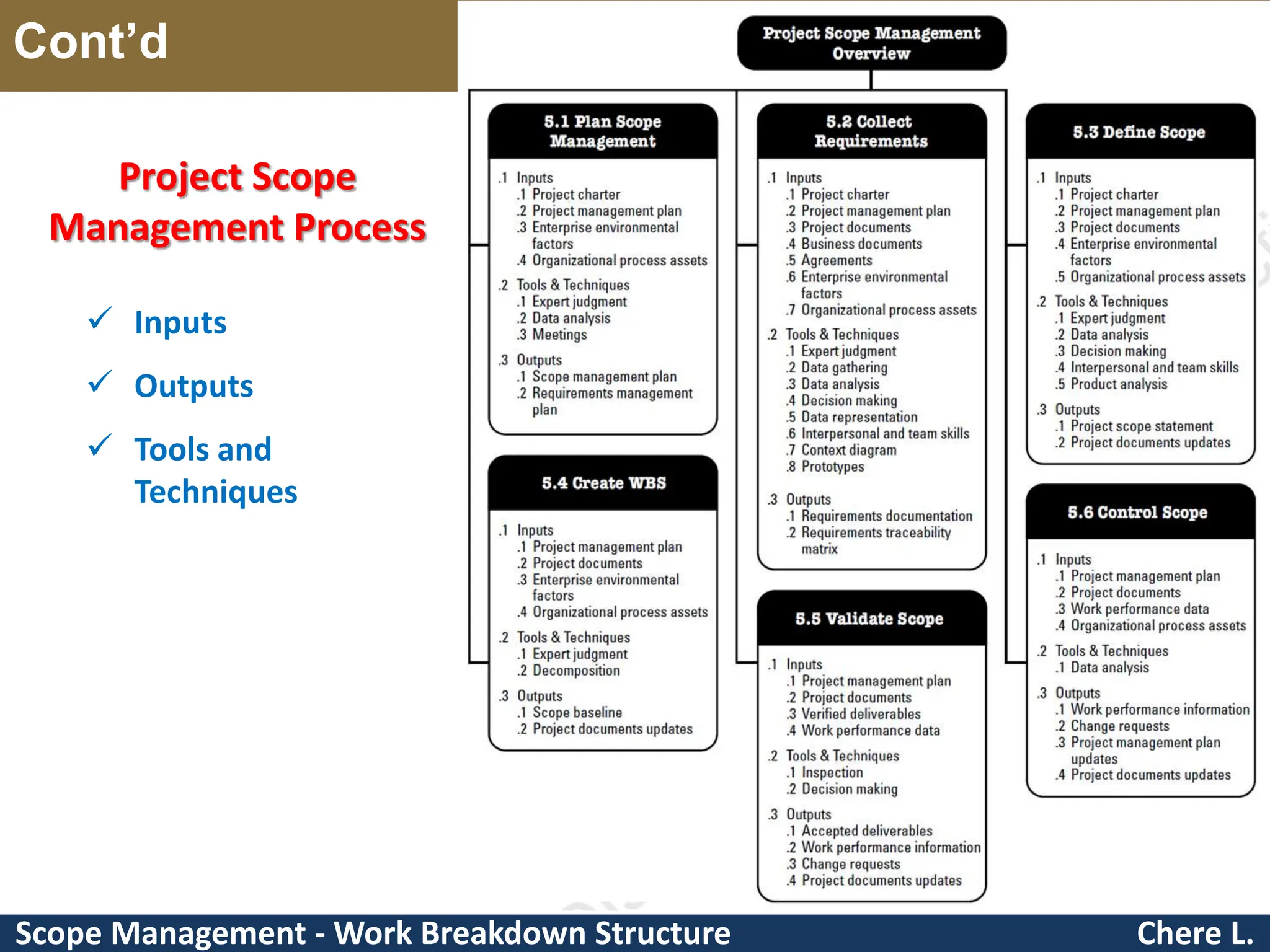
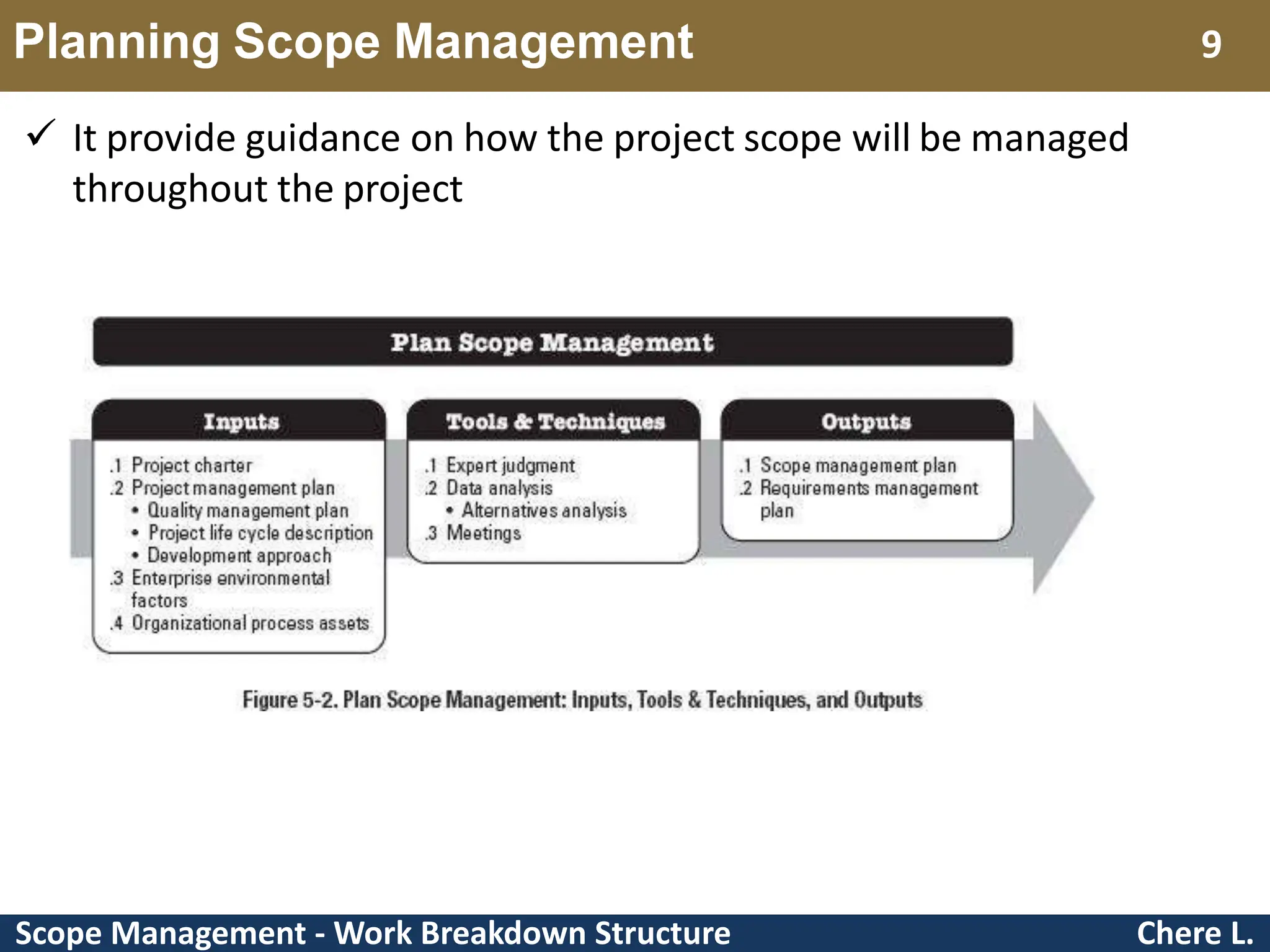
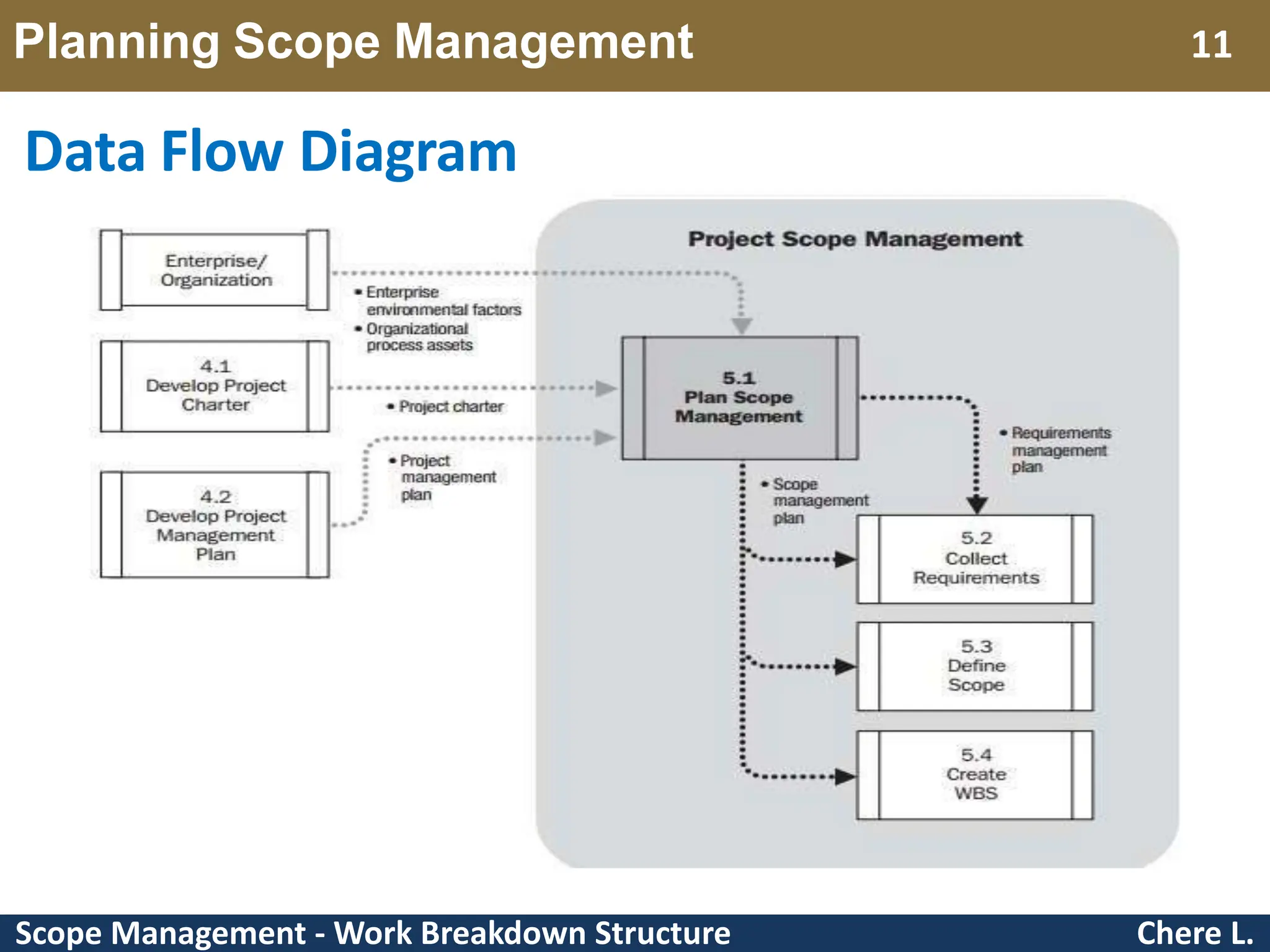
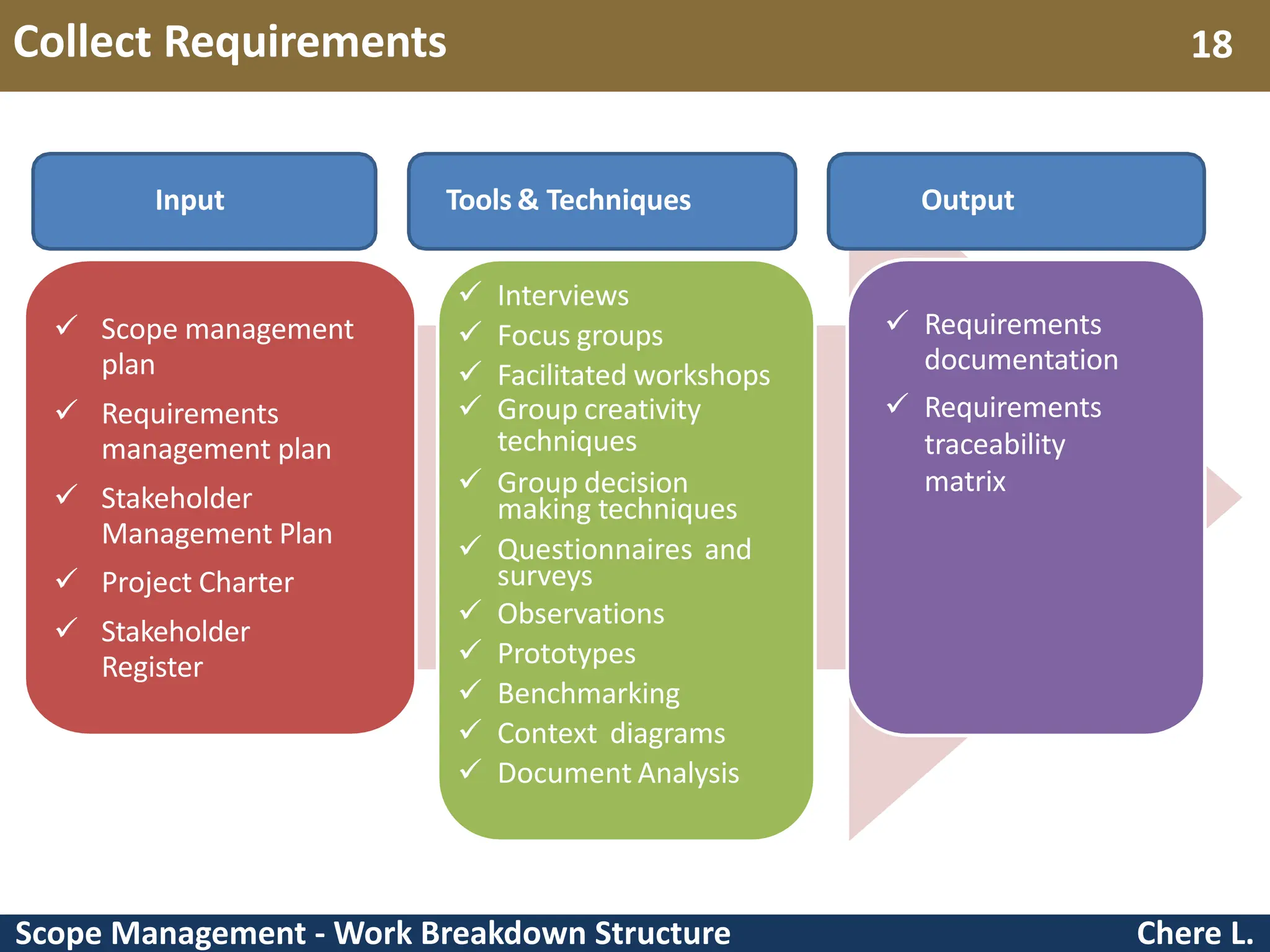
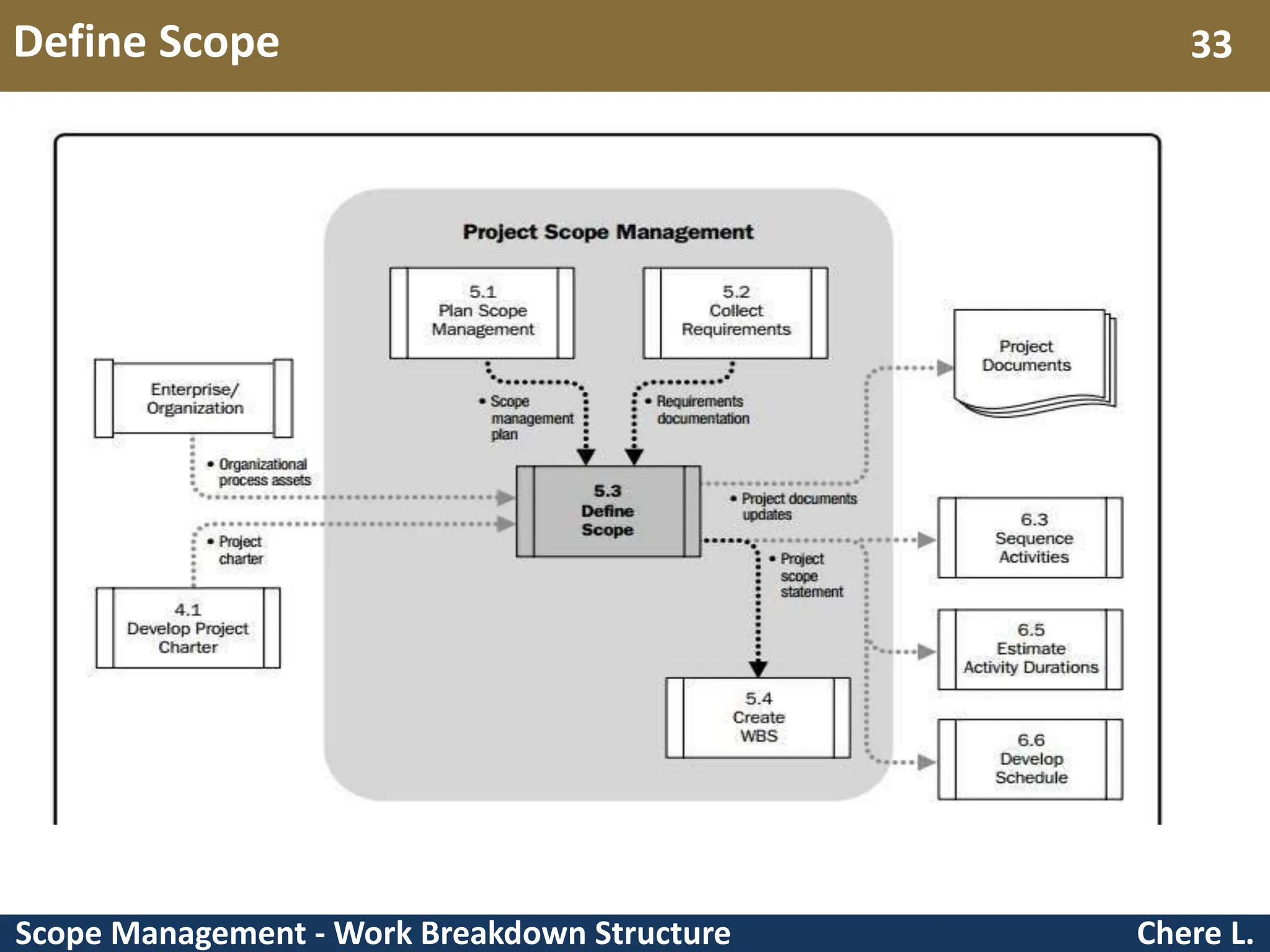
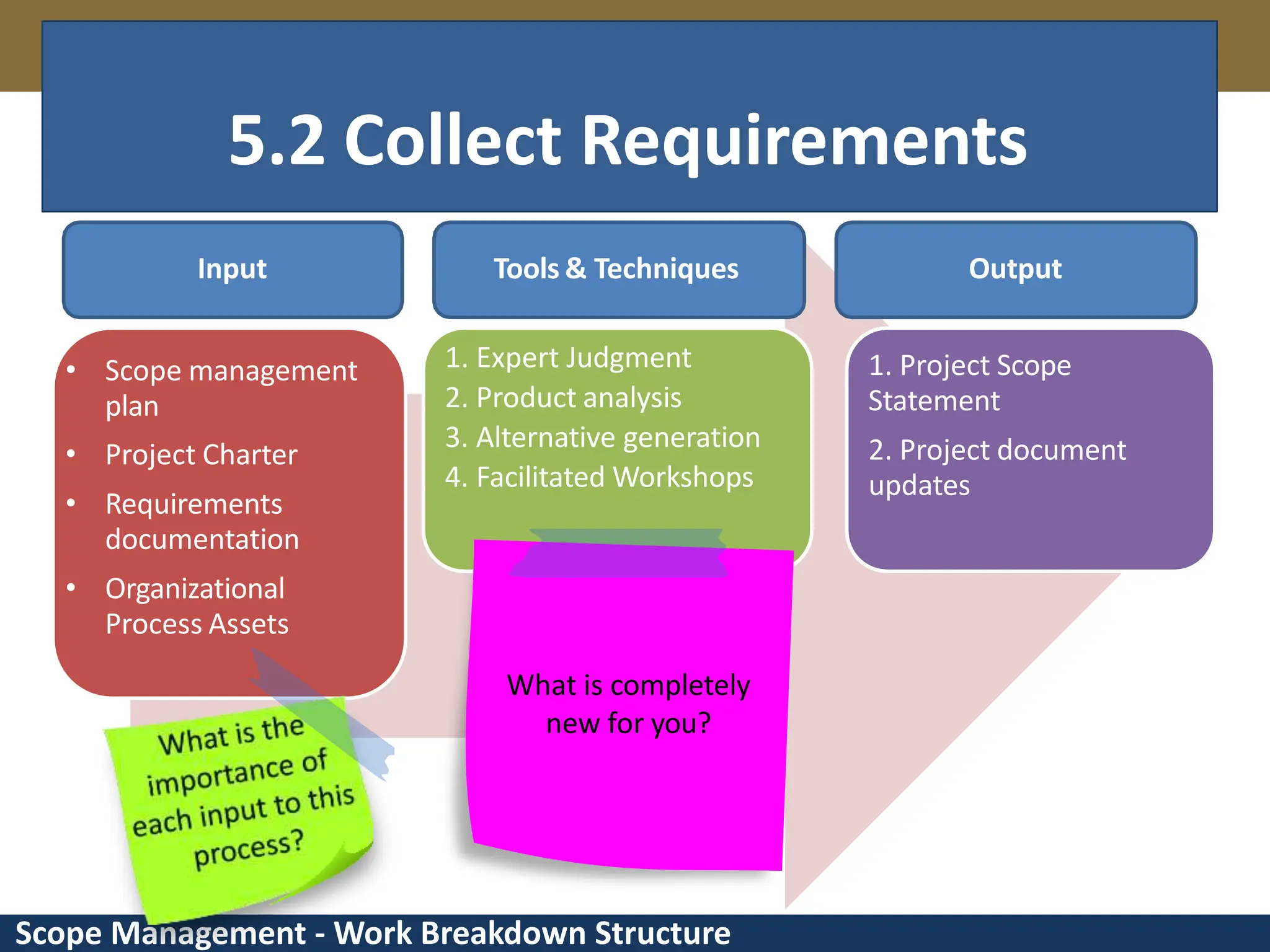
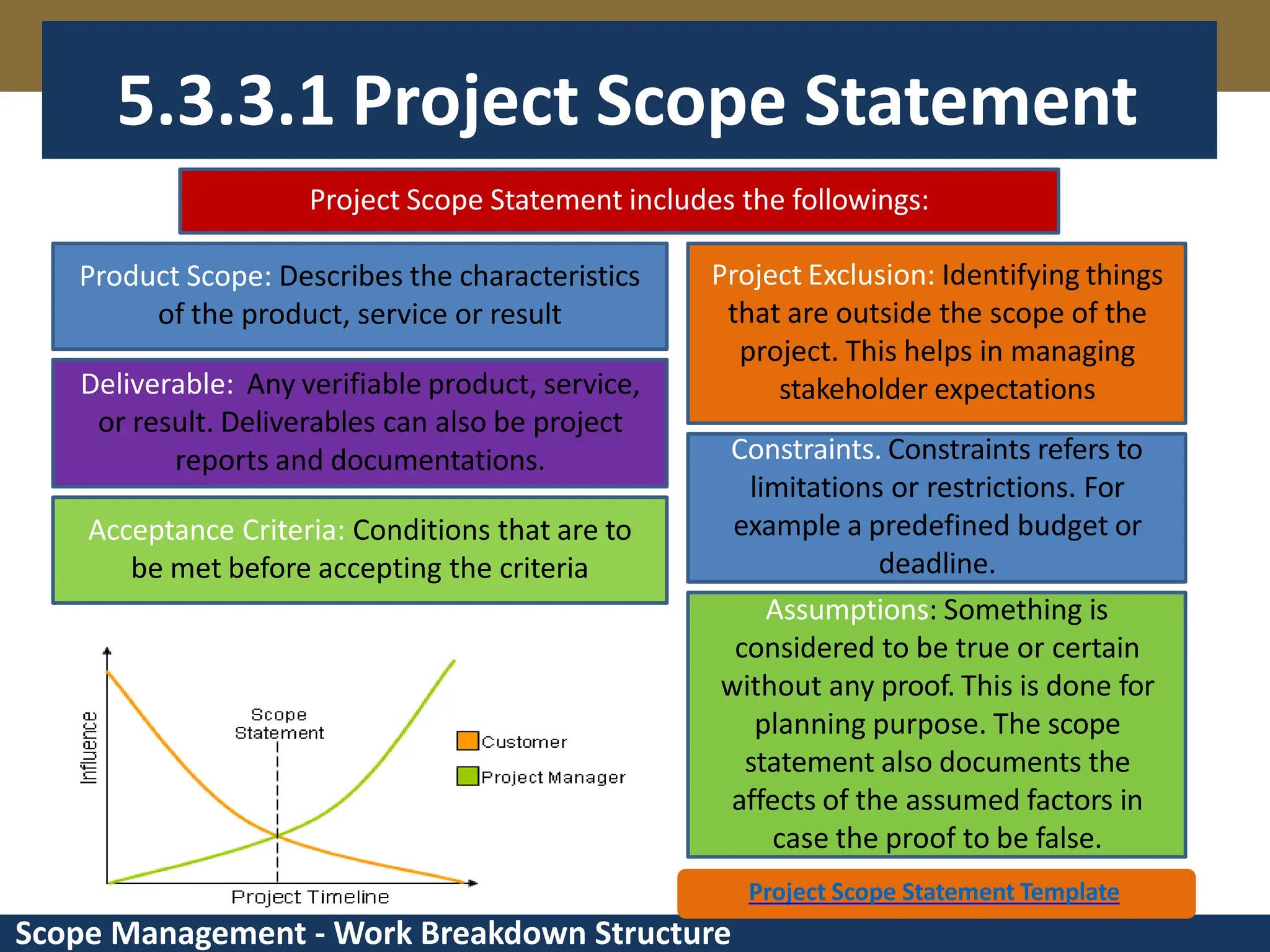
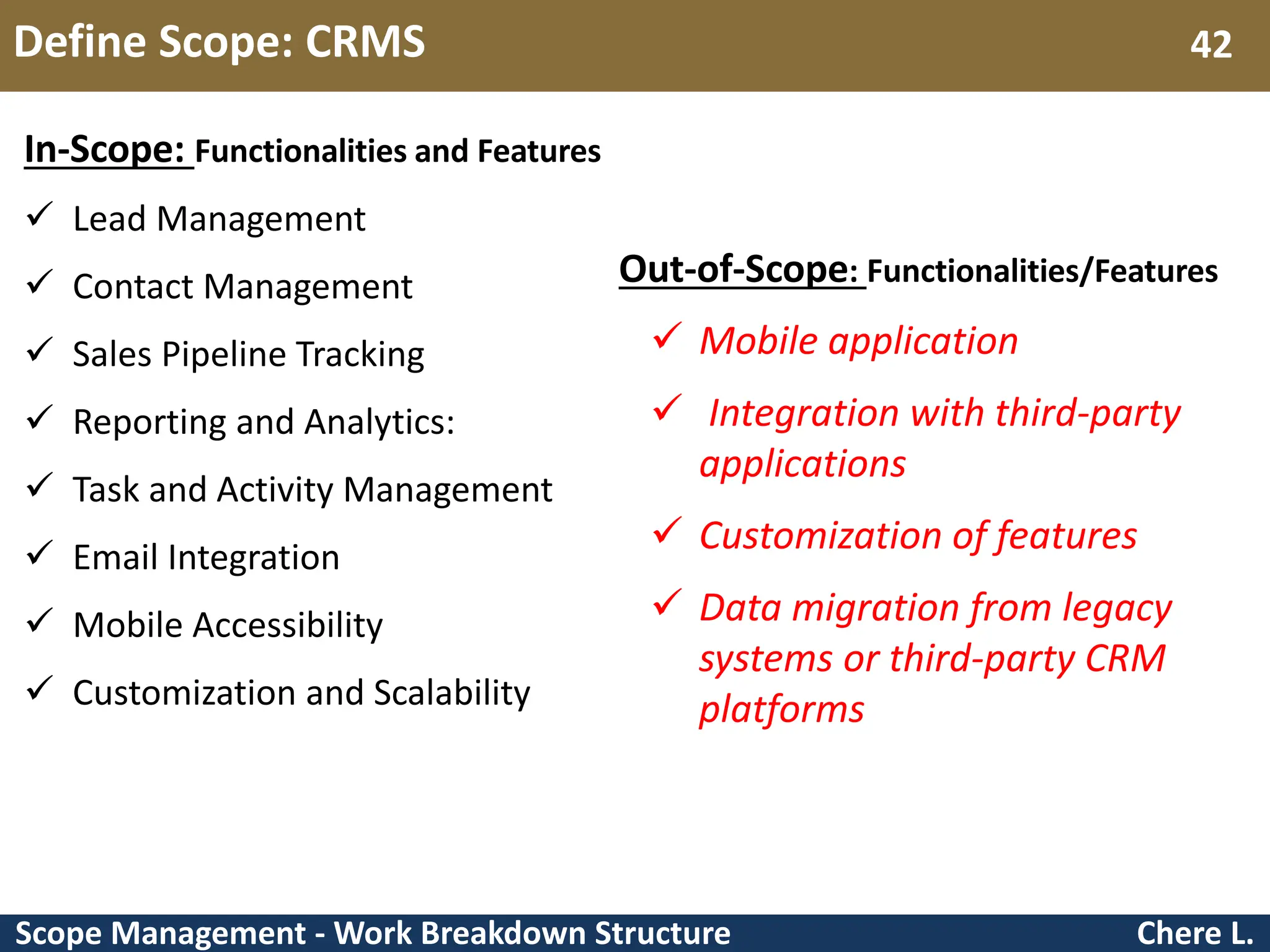
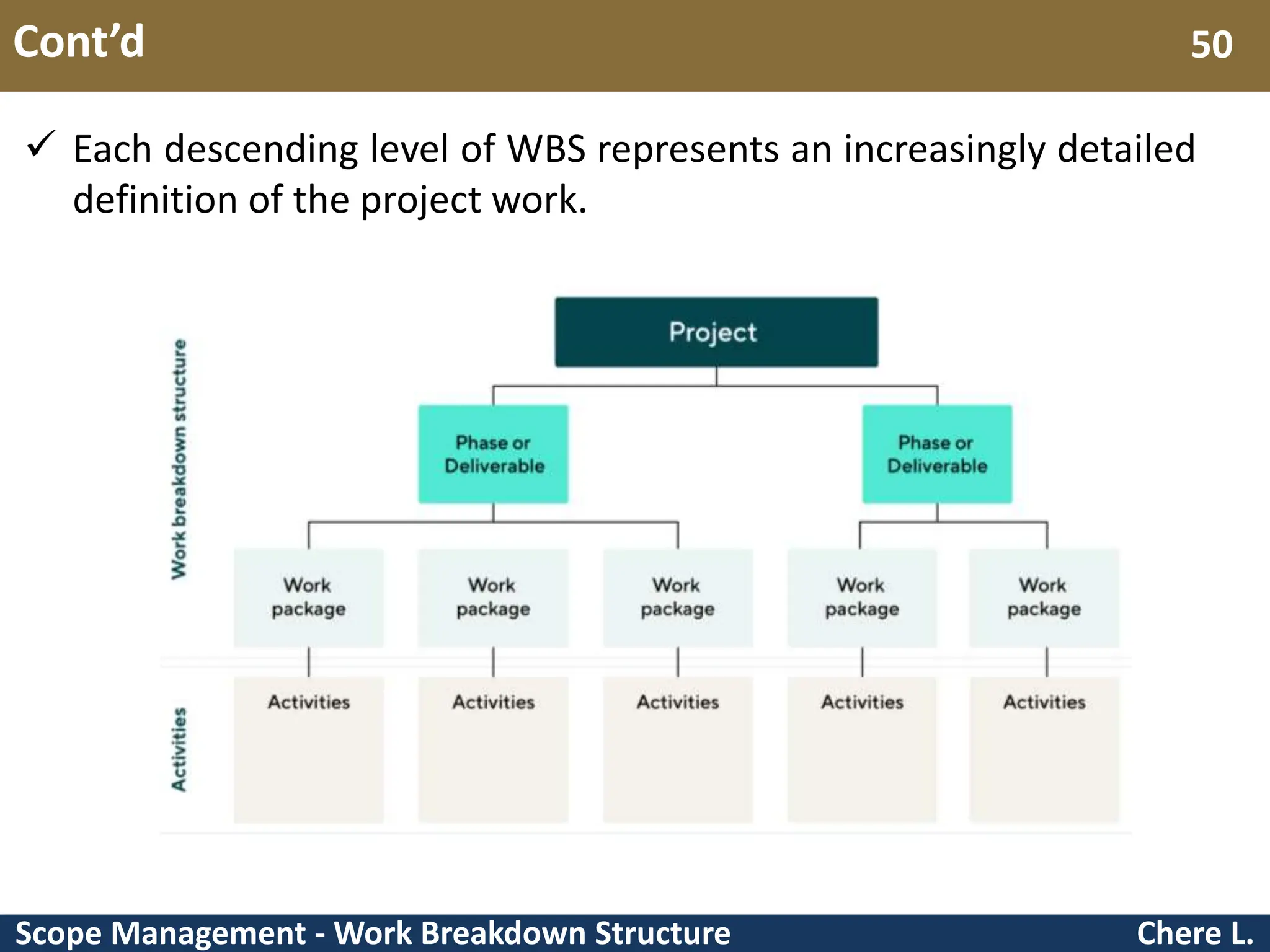
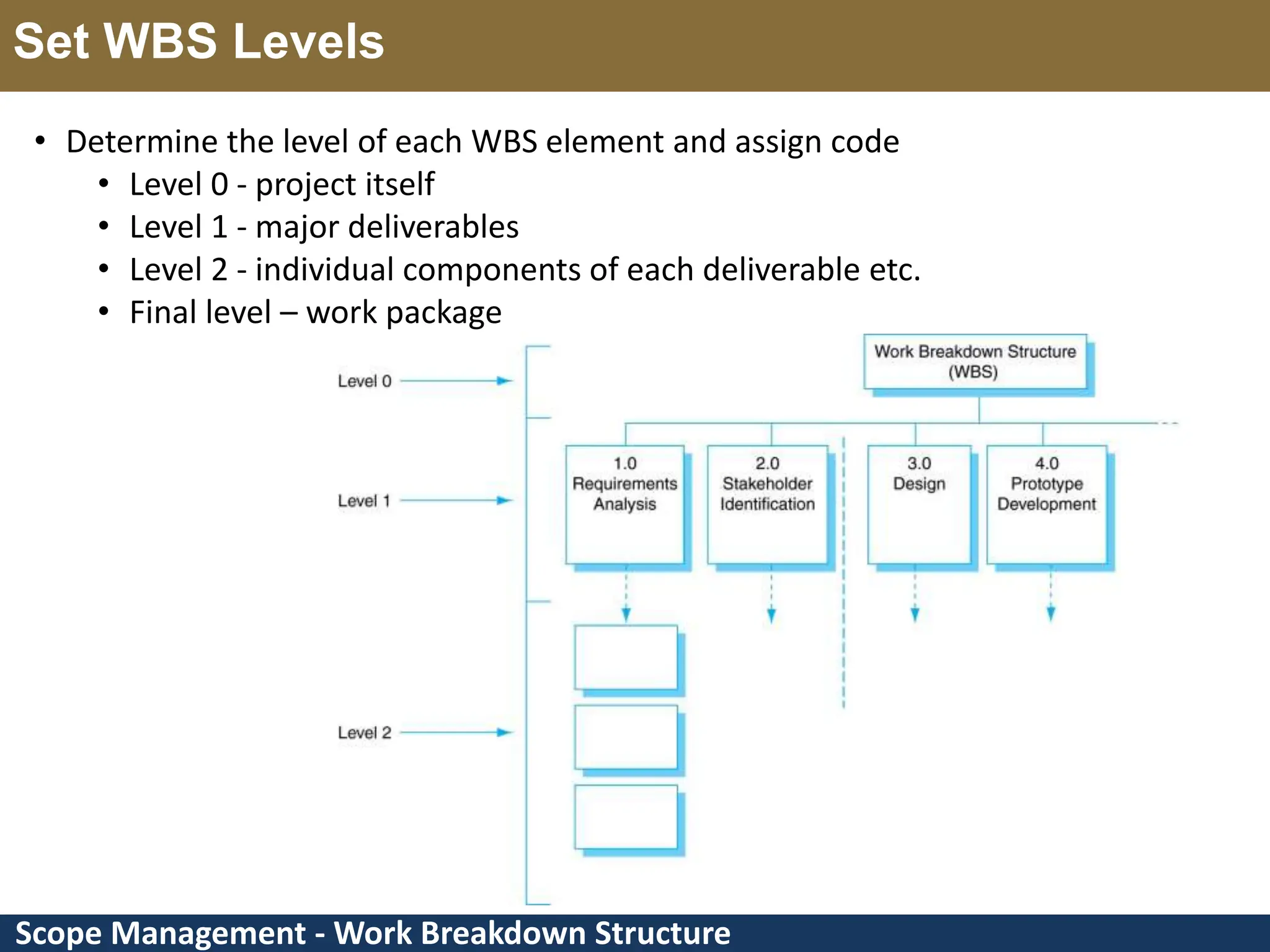
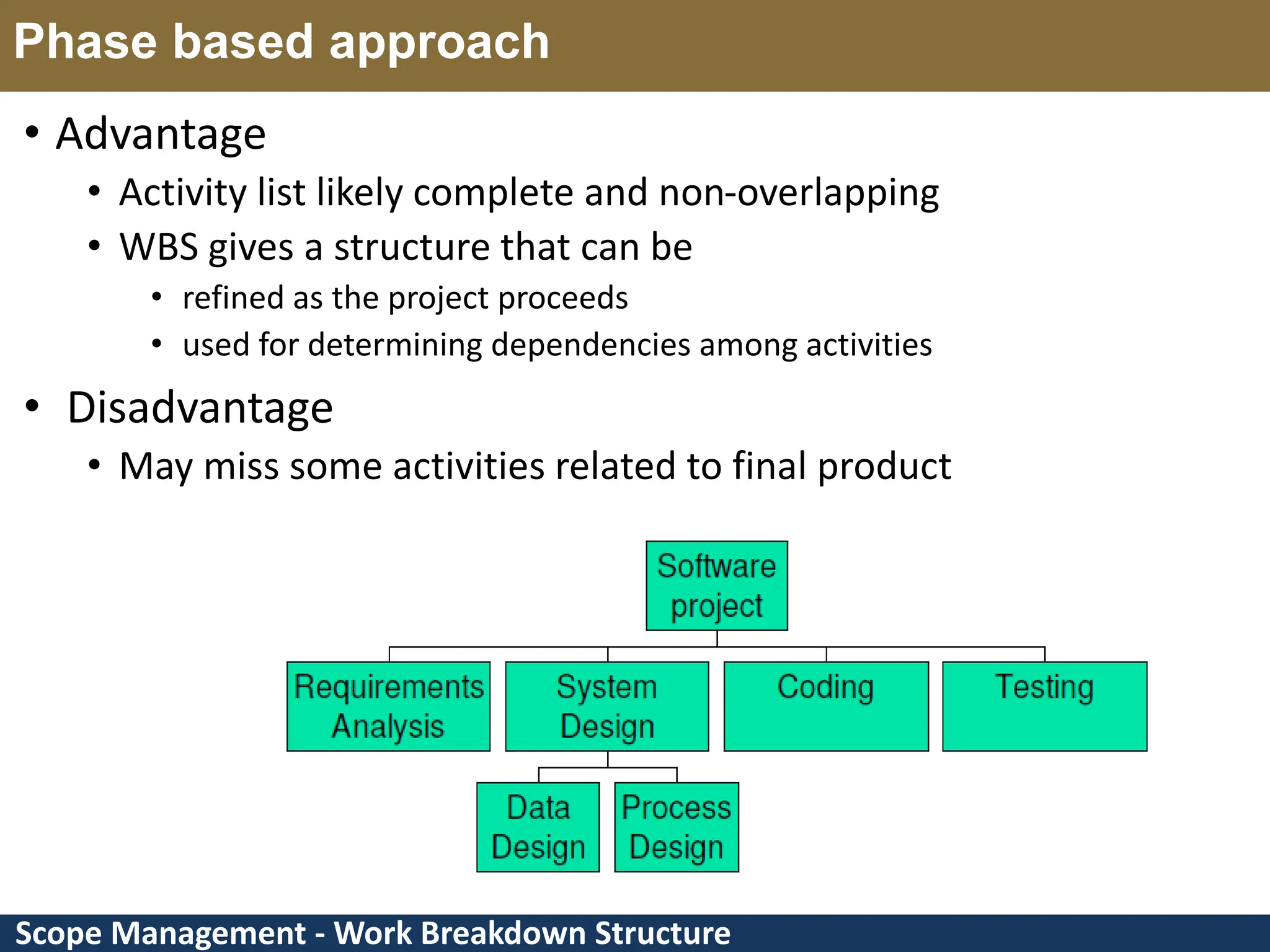
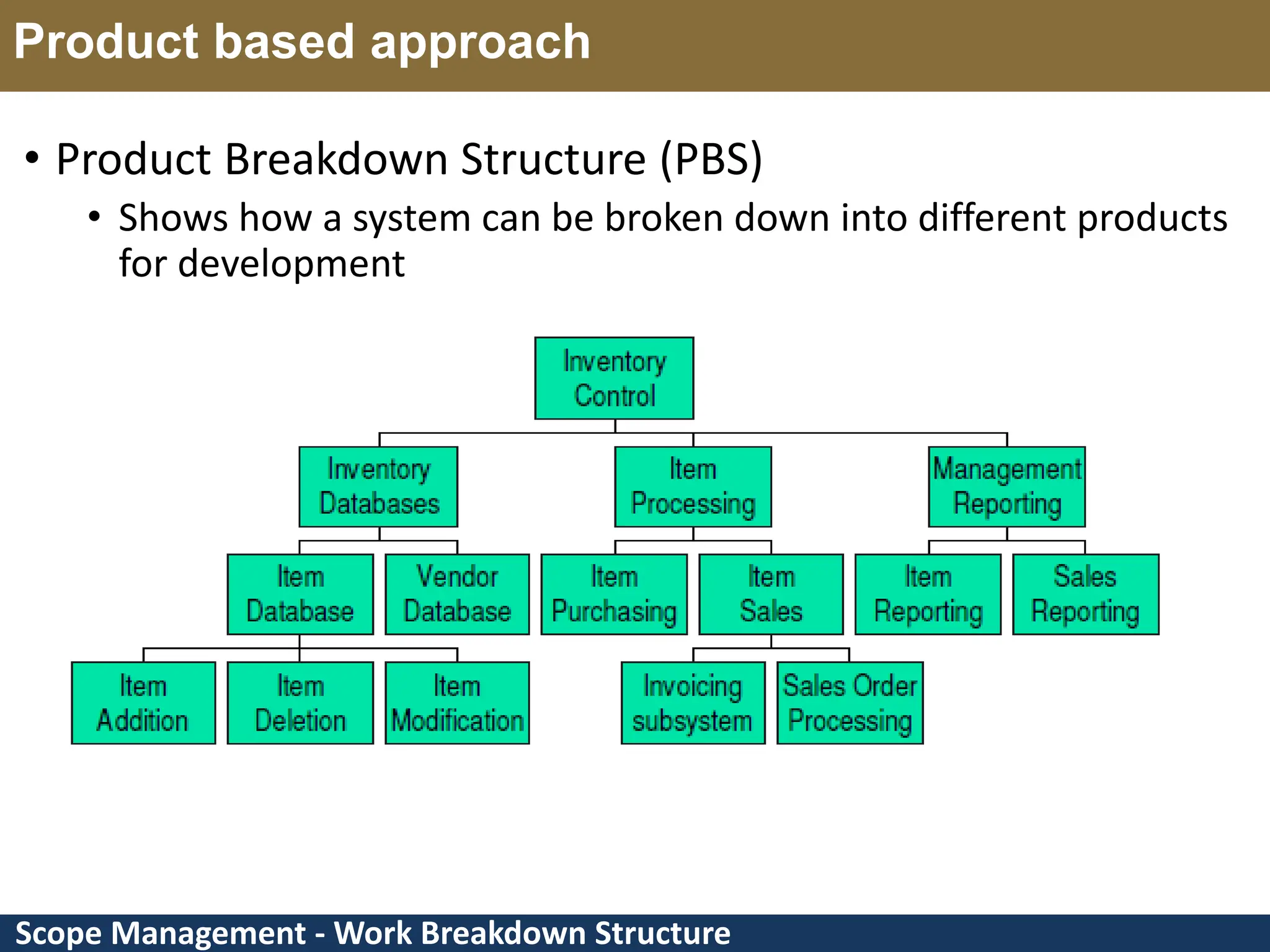
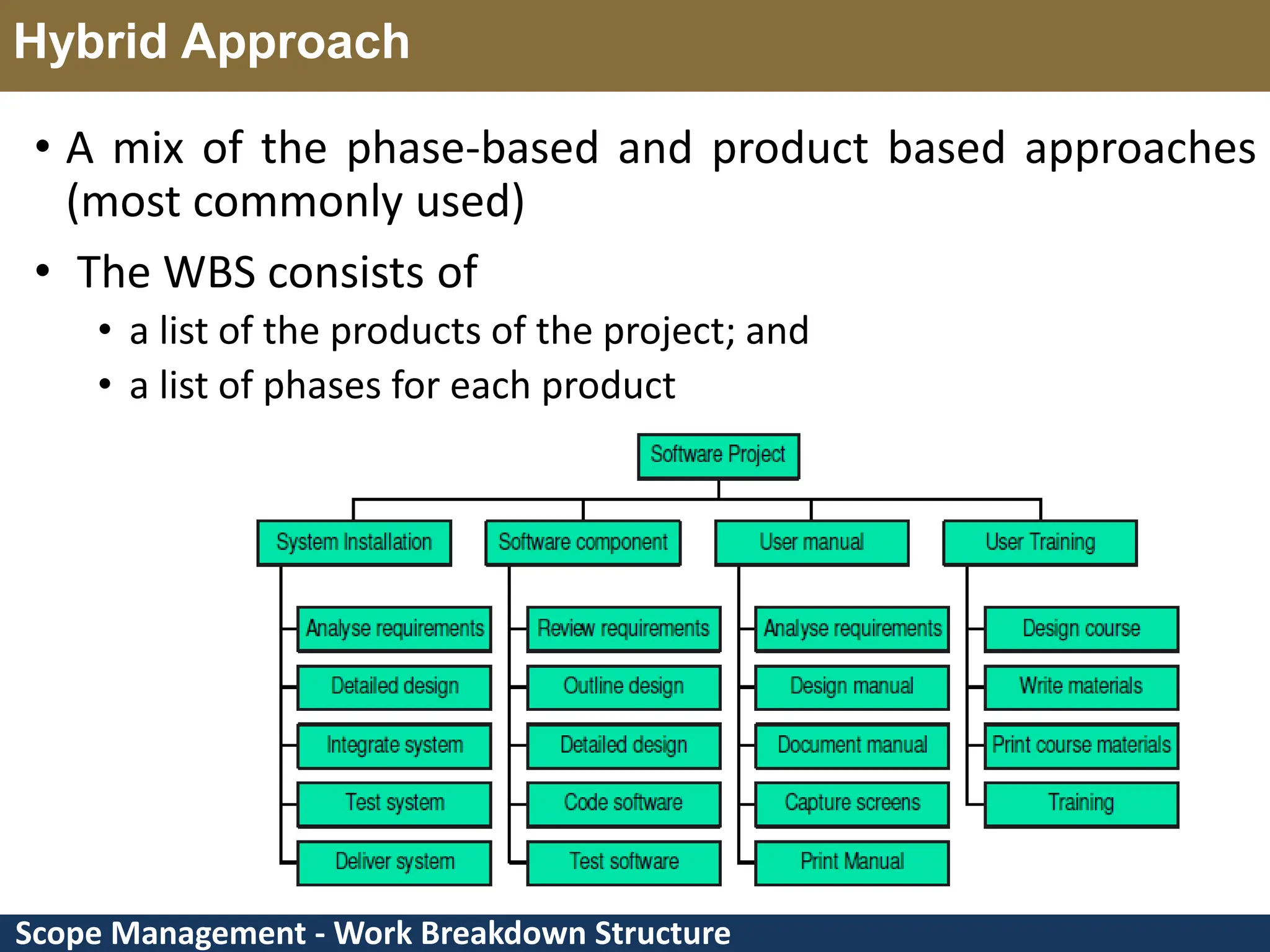
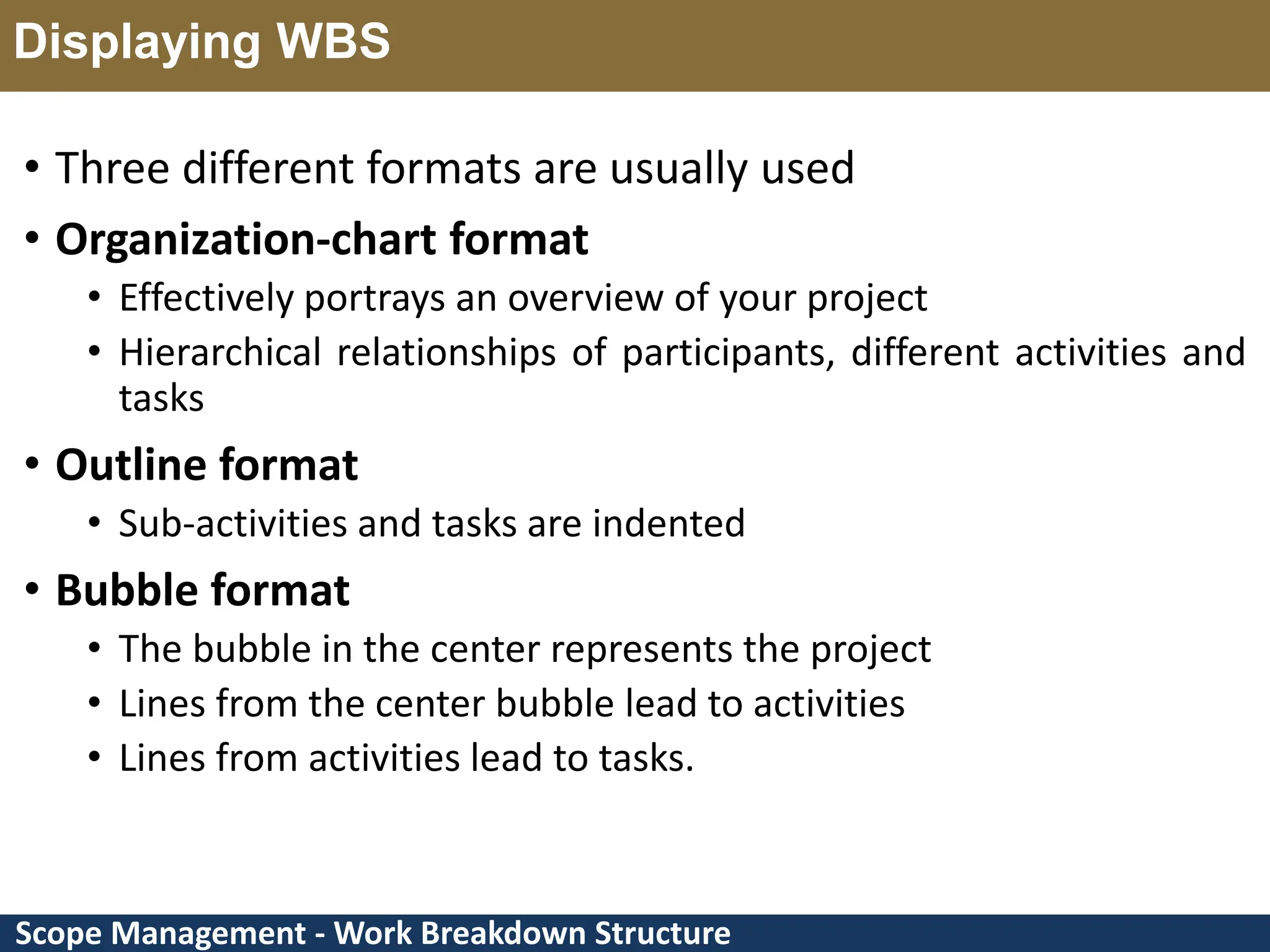
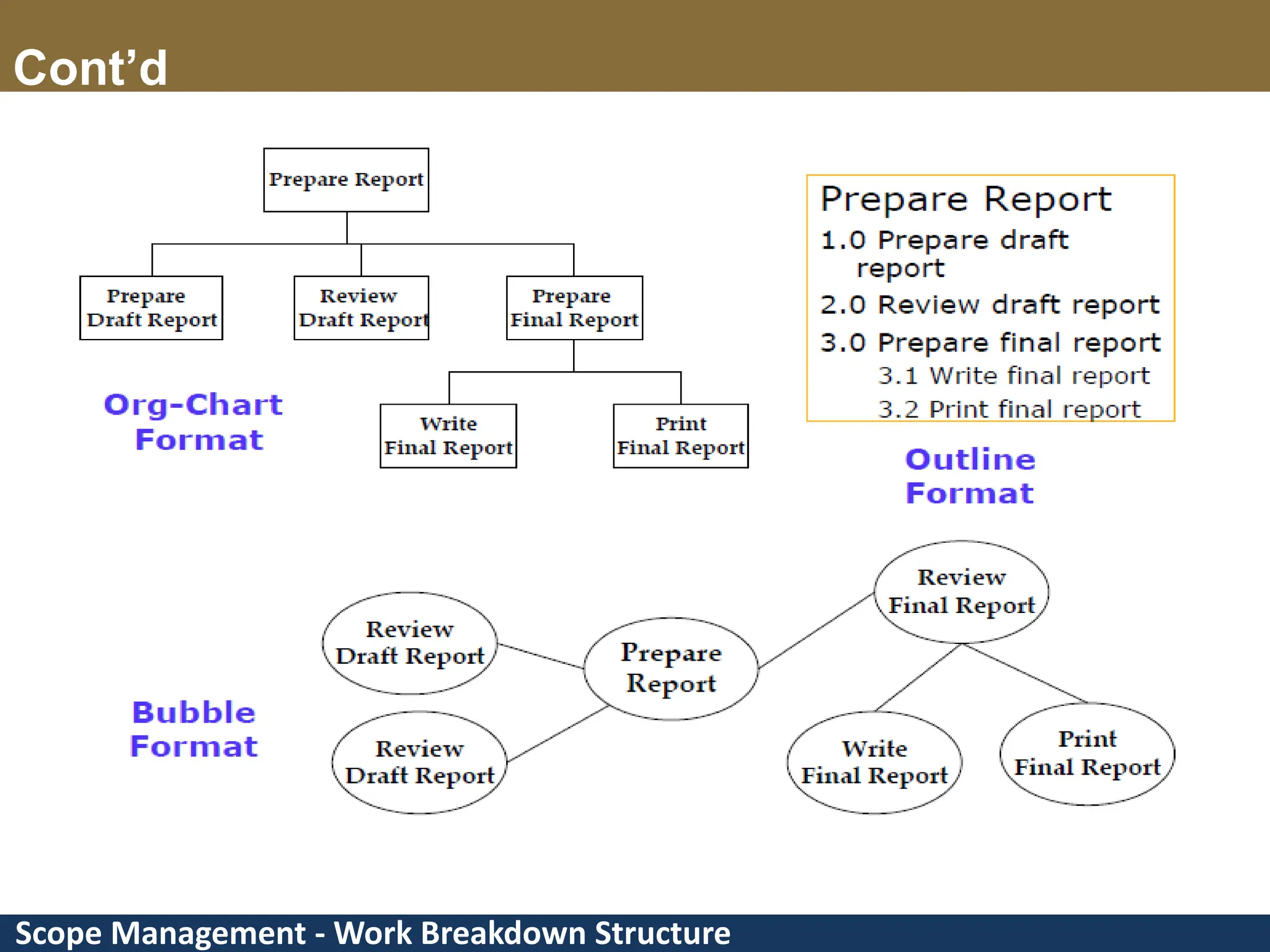
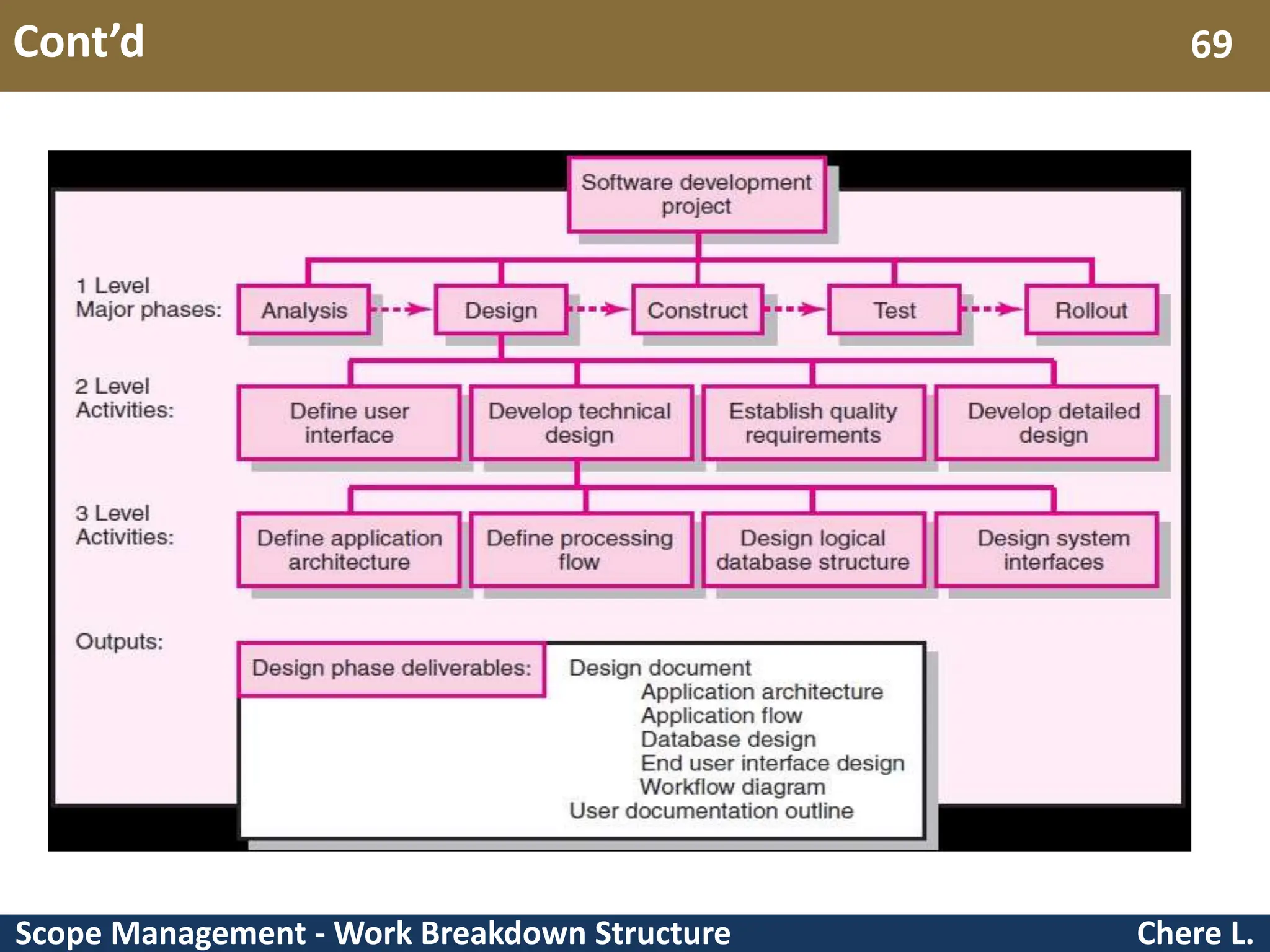
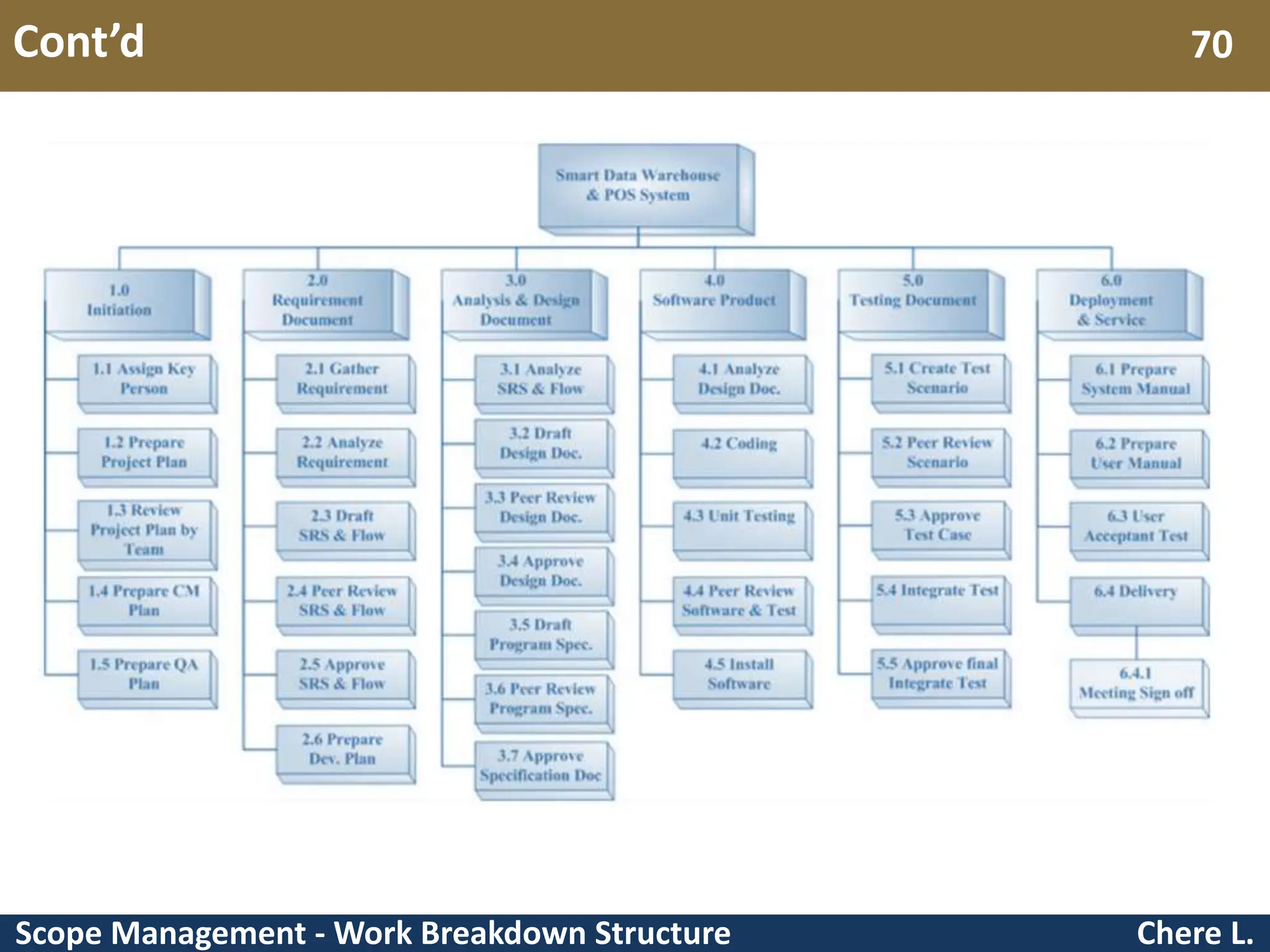
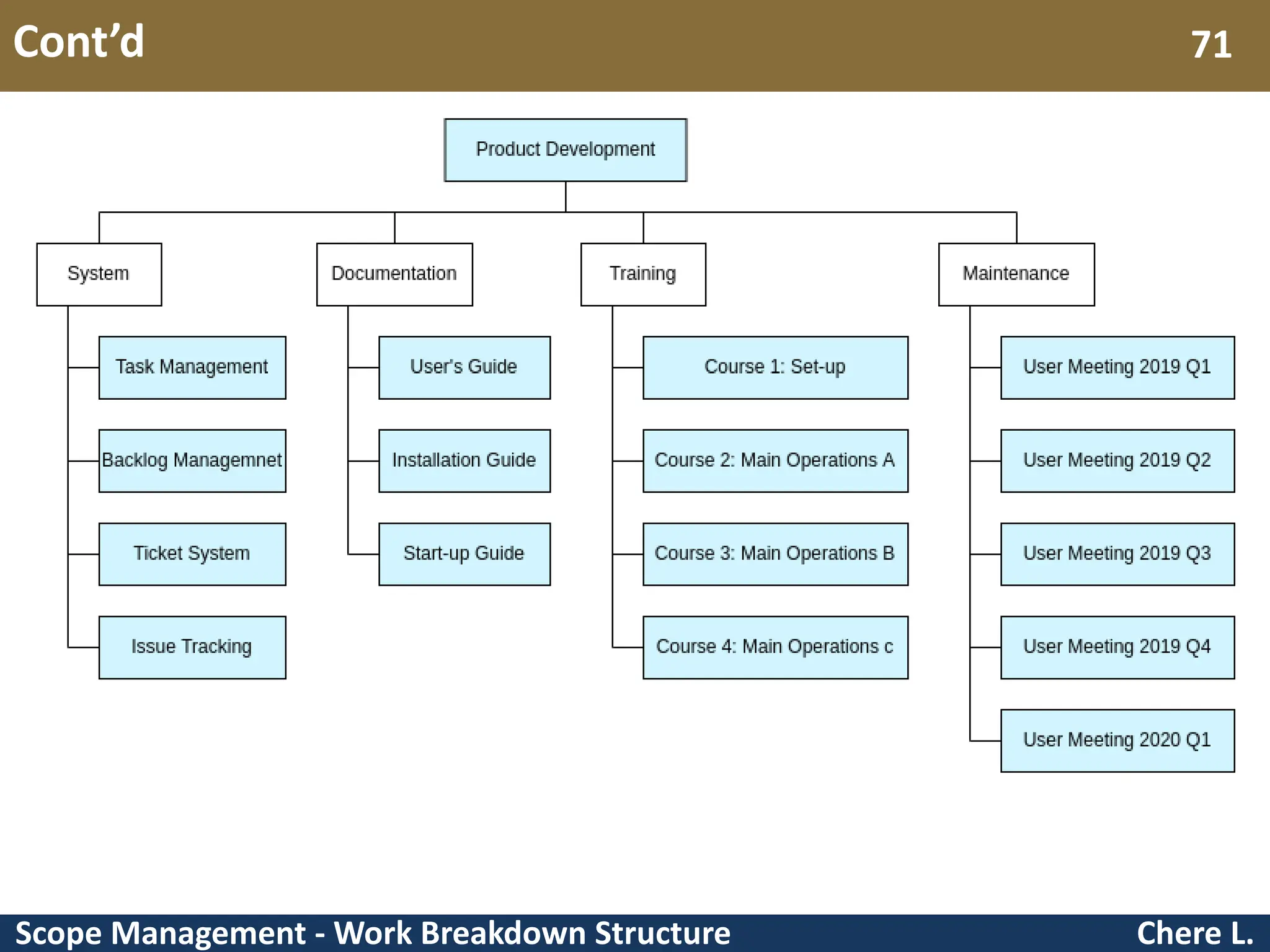
This document provides an overview of scope management and work breakdown structures (WBS). It begins with key concepts such as product scope, project scope, and the processes of scope management. It then discusses planning scope management and collecting requirements. Considerable detail is provided on defining the project scope, including developing a project scope statement, identifying what is in/out of scope, and documenting assumptions and constraints. The document focuses on WBS, explaining what it is, its benefits, elements and how to create one using different approaches and formats. An example of a WBS for developing a personal portfolio website is also included.