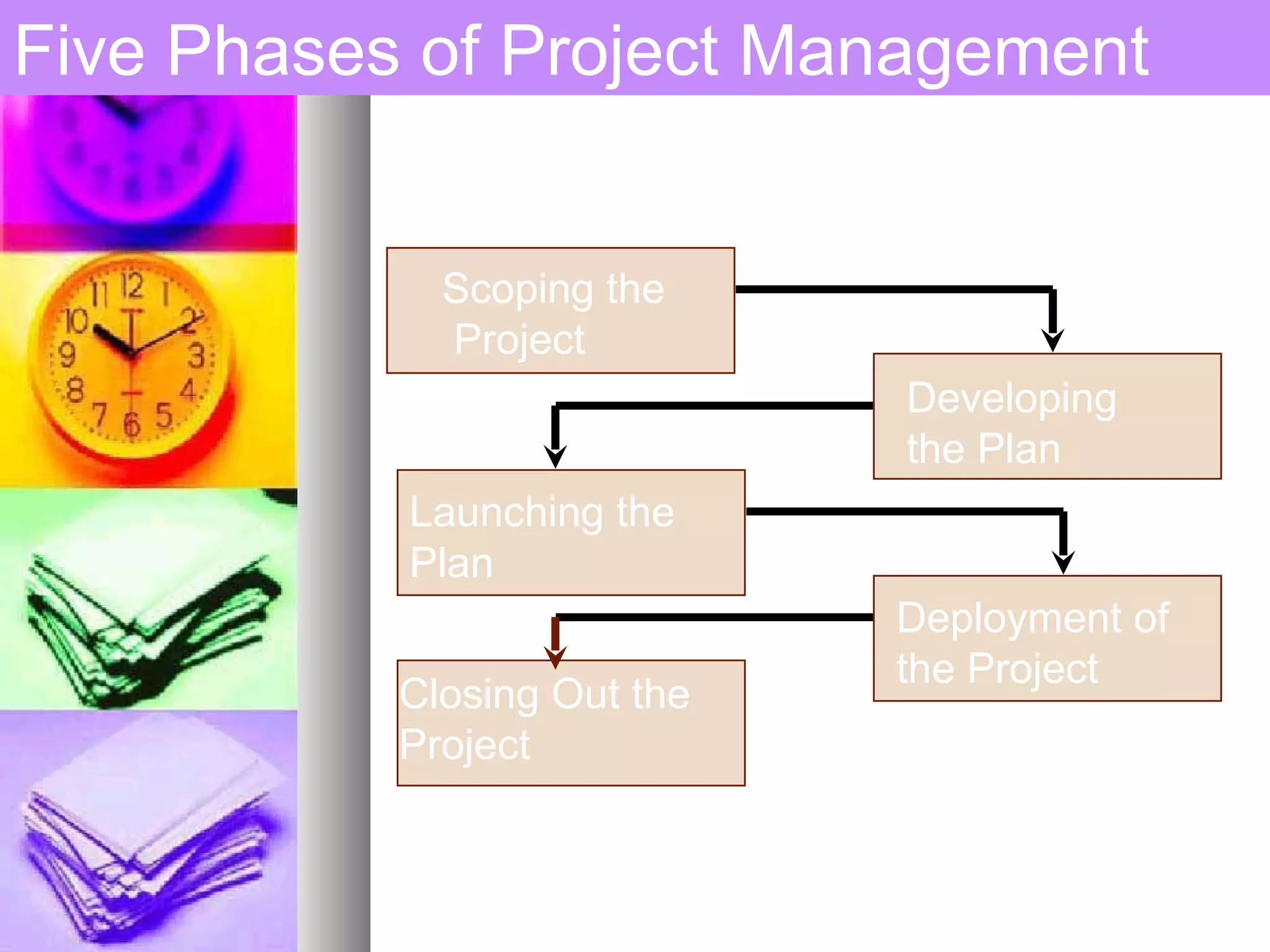
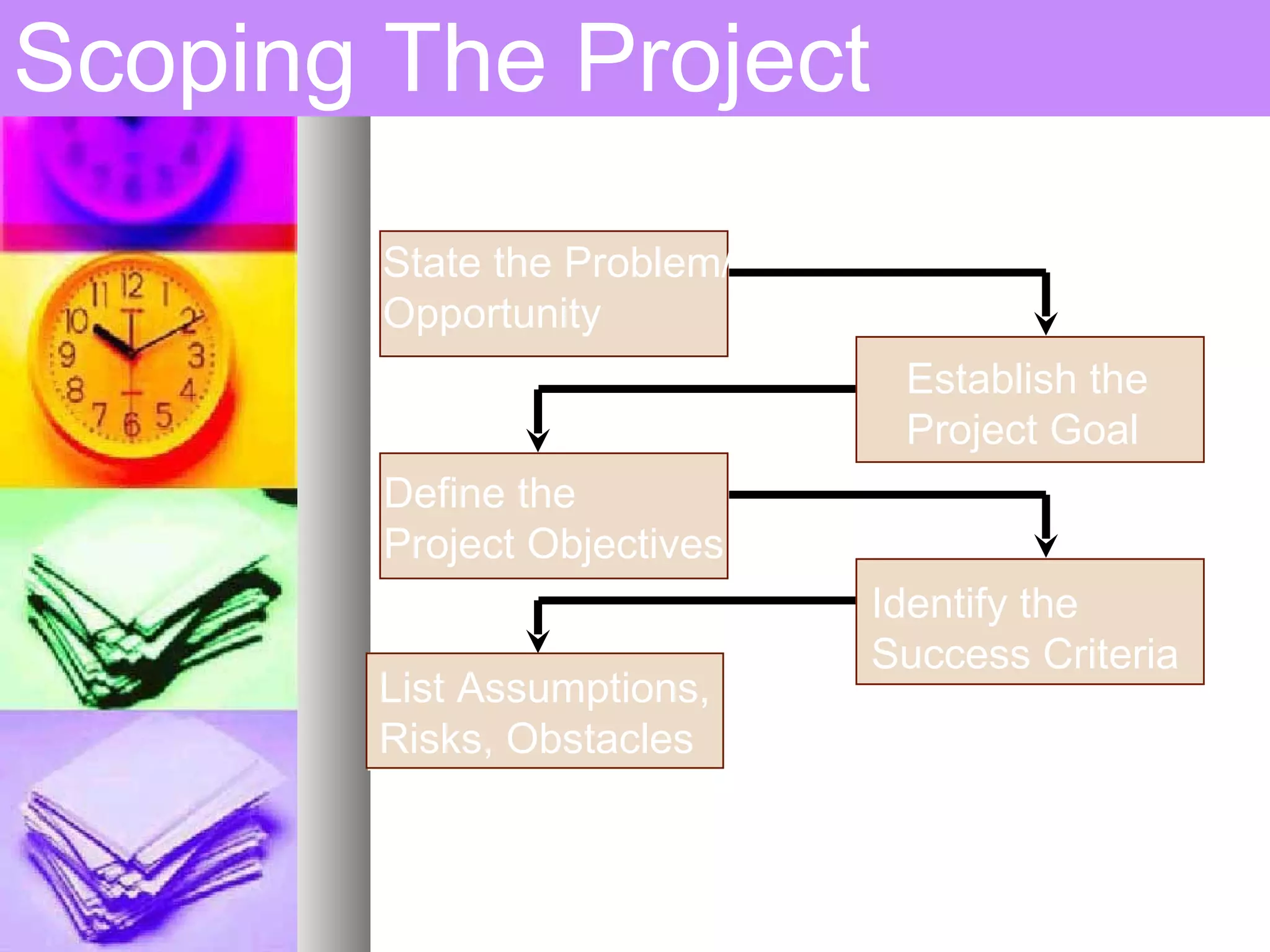
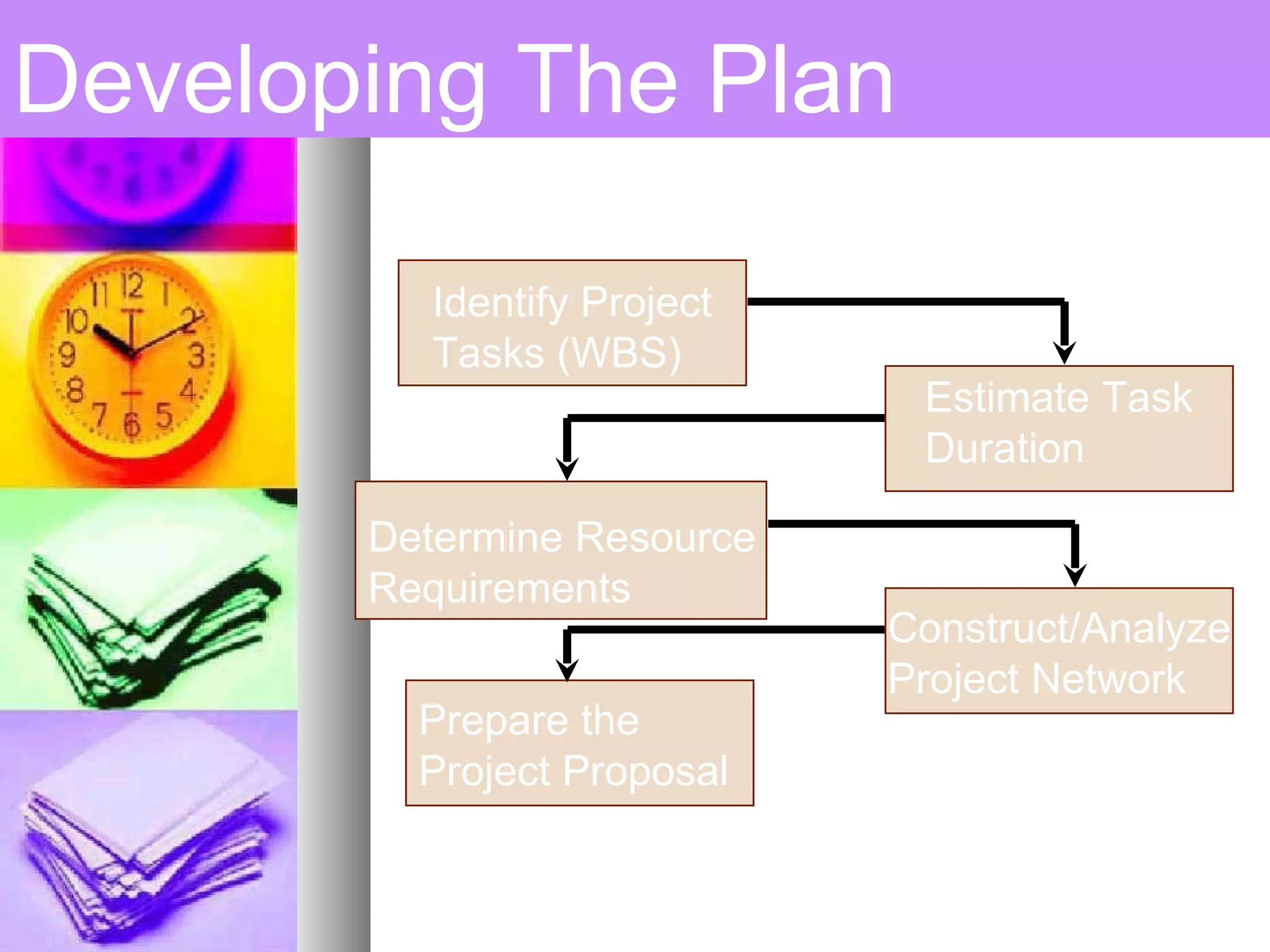
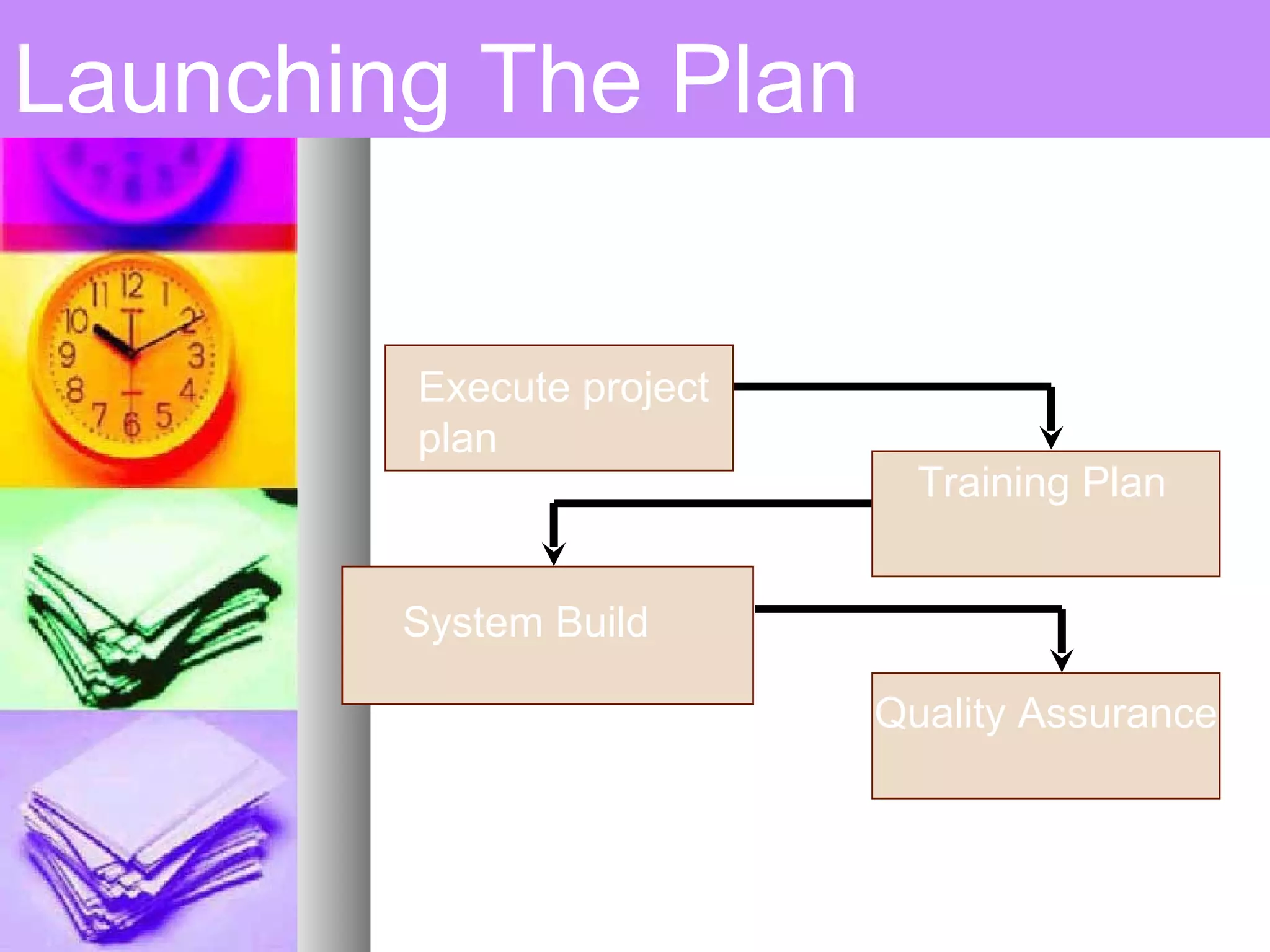
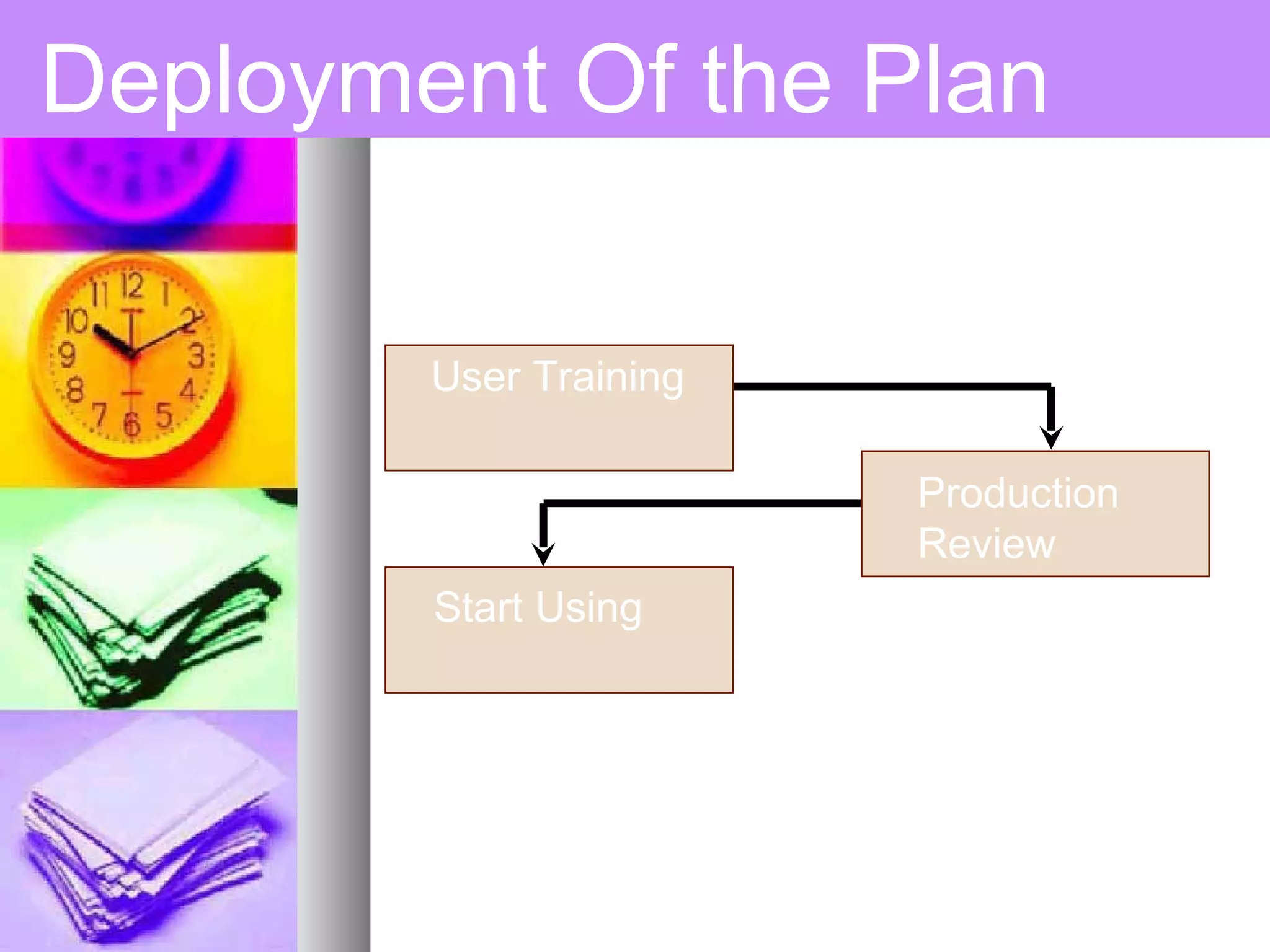
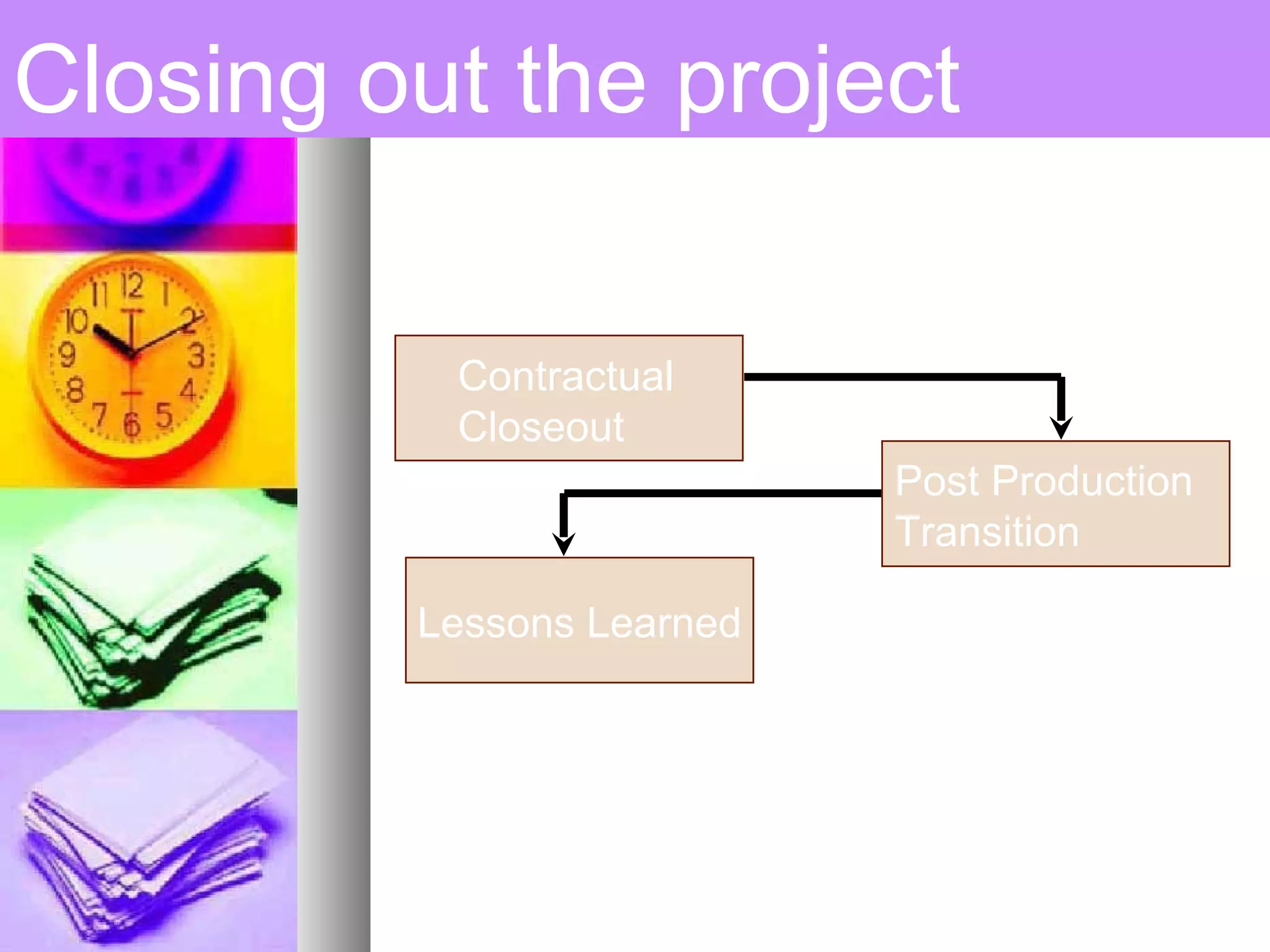
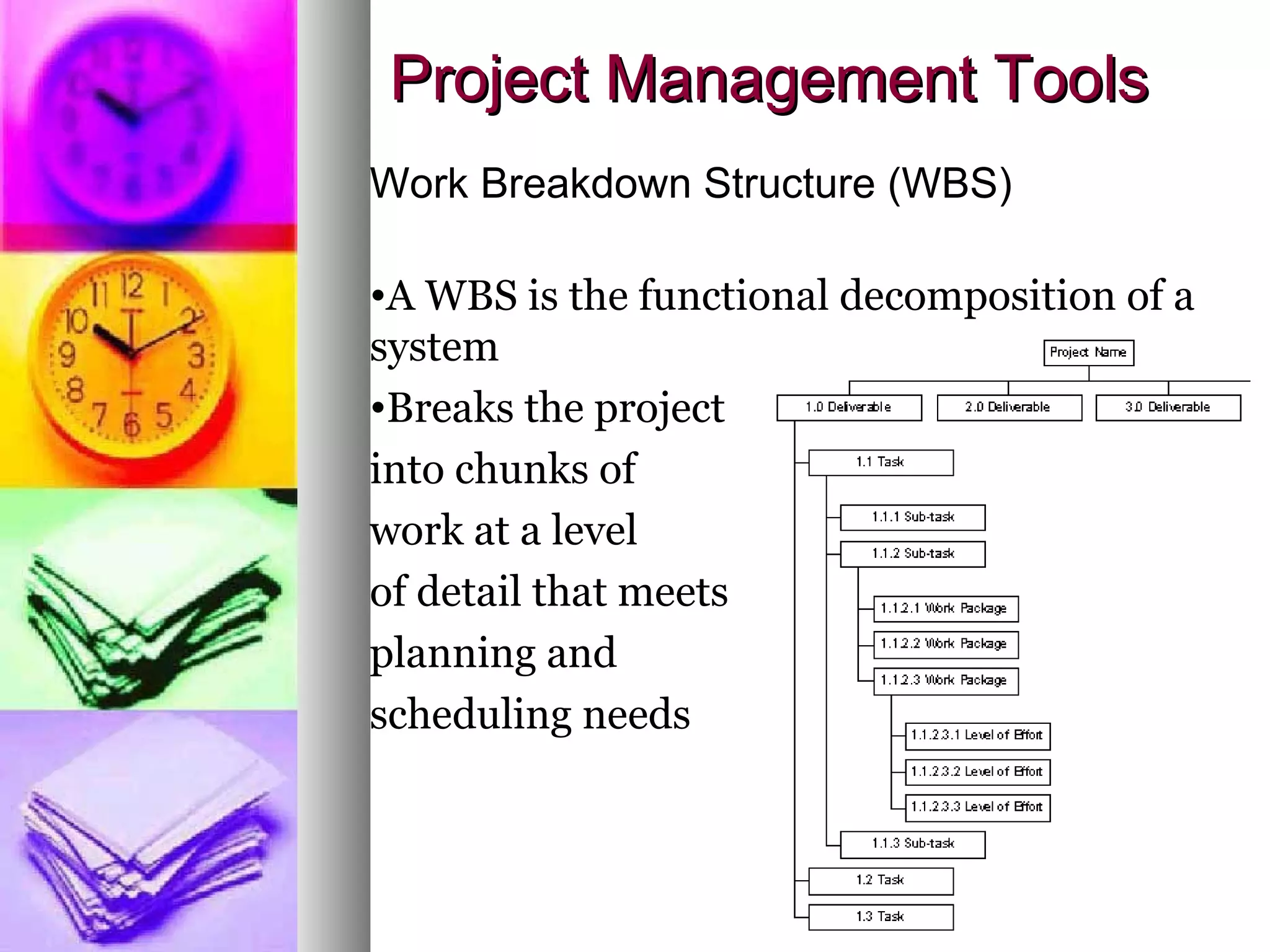
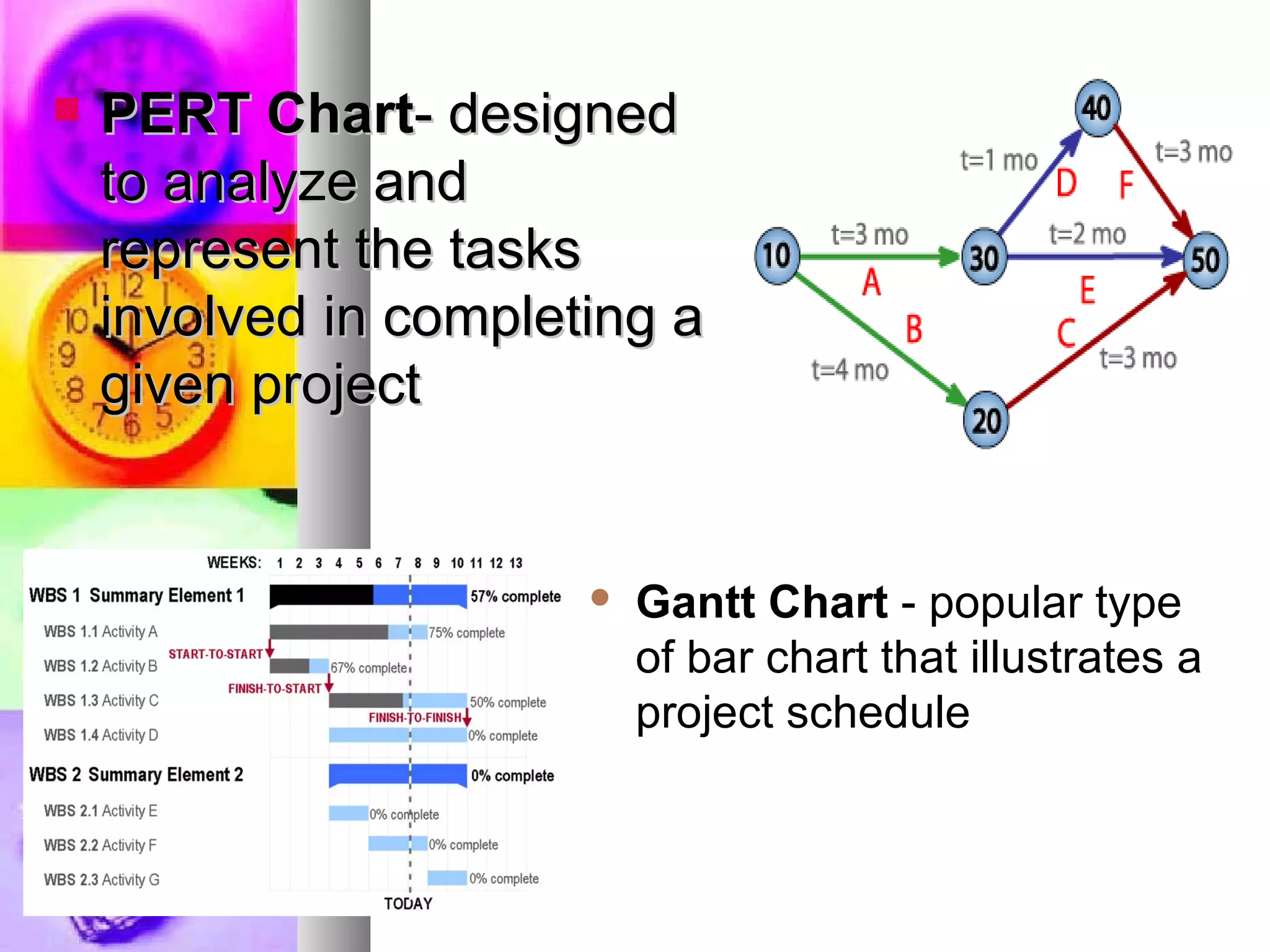
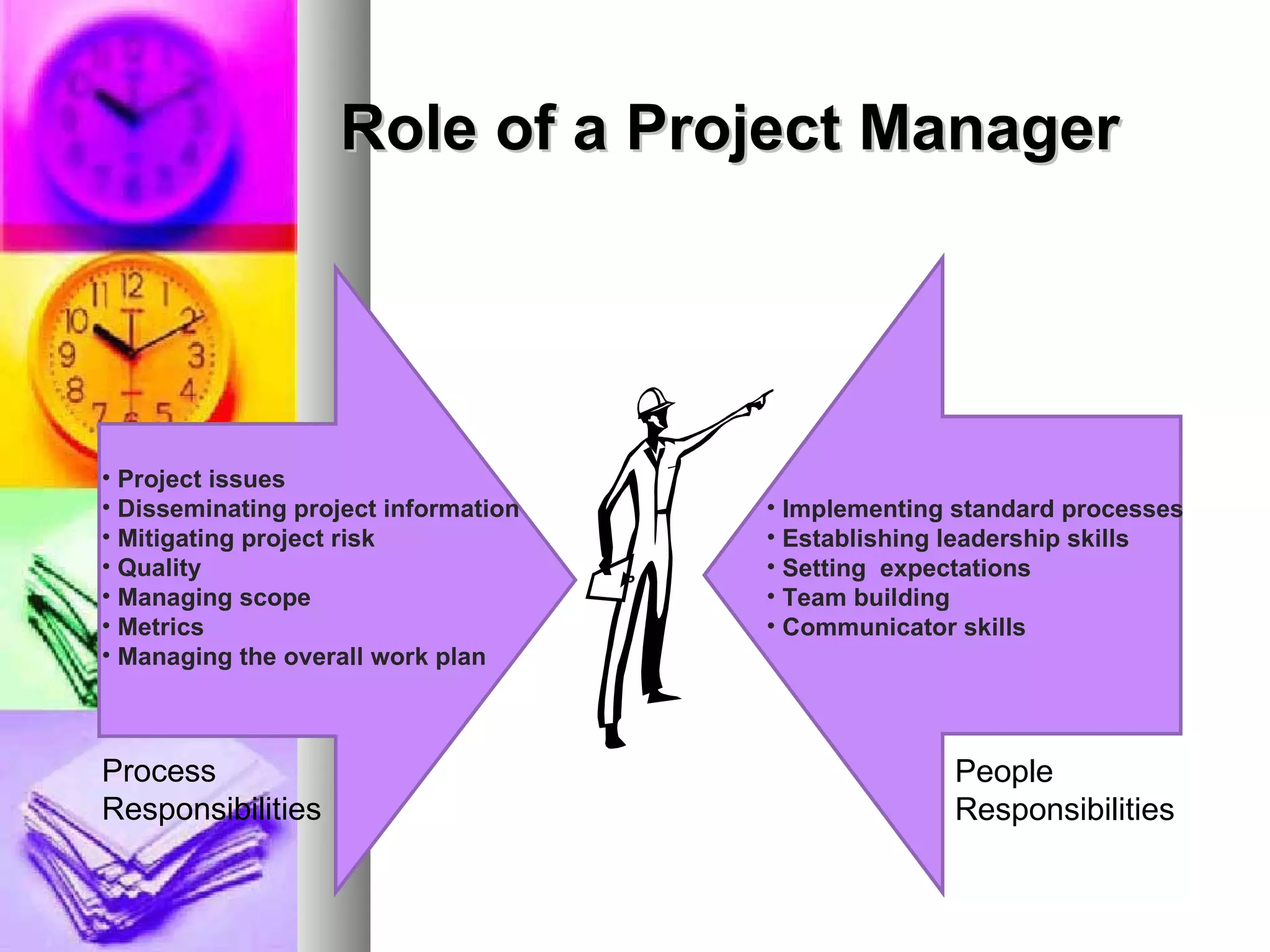
This document provides an introduction to project management. It defines a project, compares projects and operations, and outlines what makes a project successful or fail. It then defines project management and its key areas including scope, issue, cost, quality, communications, risk, and change management. The five phases of project management are also outlined. Finally, it discusses common project management tools and the role of the project manager.