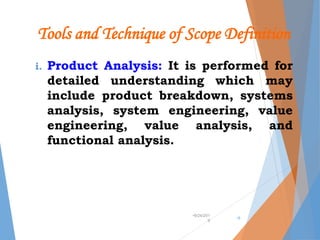
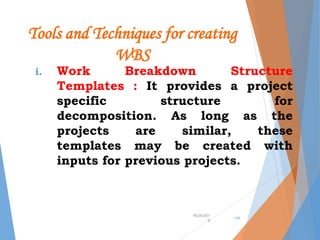
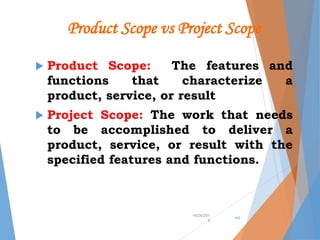
The document outlines the concept of project scope management, emphasizing the processes necessary to define, control, and verify project scope to ensure successful completion. It details methods for scope planning, definition, and control, including the use of expert judgment, templates, and stakeholder analysis. Additionally, the document discusses the creation of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and the significance of scope verification and control in managing project boundaries, deliverables, and change requests.