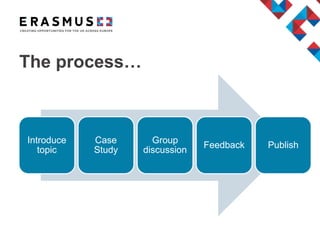
This document outlines the agenda for a workshop on project management and implementation. The workshop will focus on two topics: participant mobility and managing international partnerships. For participant mobility, the goal is to identify and address barriers to incorporating non-staff mobility into projects funded by Erasmus+. For managing partnerships, the aim is to determine best practices and processes for facilitating successful collaboration between project partners. Both sessions will involve introducing the topic, a case study, group discussion, and sharing lessons learned.