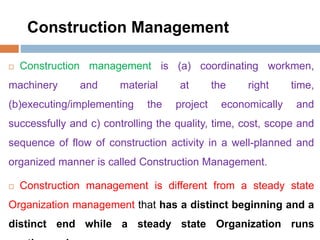
1. Construction project management involves planning, implementing, and controlling construction projects to deliver them on time, within budget, and according to specifications.
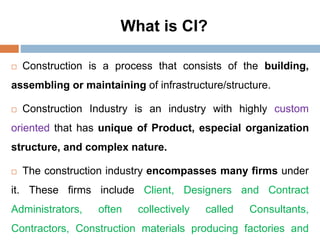
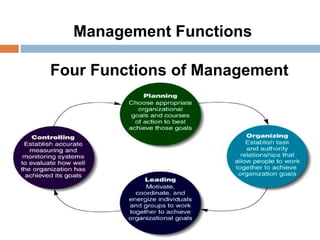
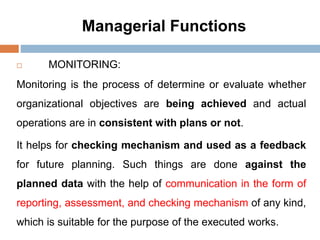
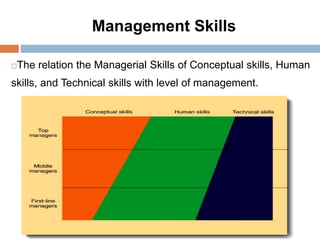
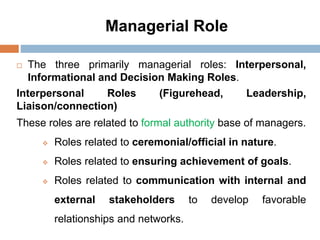
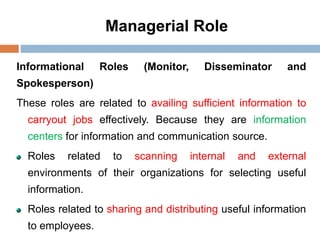
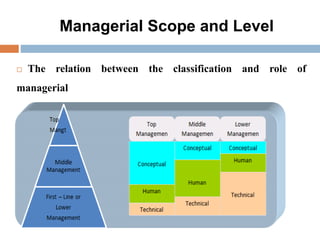
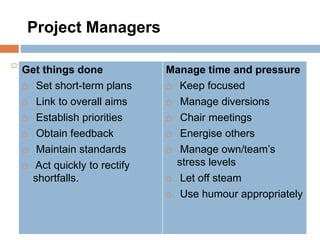
2. The key functions of management in projects are planning, organizing, implementing, and monitoring. Planning involves setting goals and strategies, organizing is arranging resources, implementing is executing the work, and monitoring checks progress against plans.
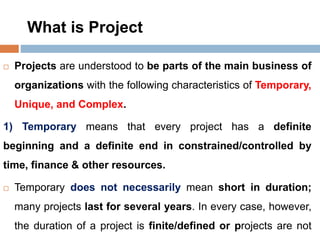
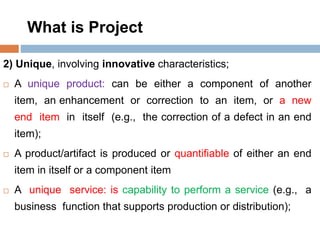
3. Projects are temporary endeavors with a defined start and end, undertaken to create unique products, services, or results. They have objectives to fulfill and deliverables to produce.
![Welcome
By
Dr. (Eng.) Tsegaye G.
Advance Construction Project Management [CoTM –521]
Department of Construction Technology and Management
Faculty of Civil Technology
TVTI
Semester I
2021/2022](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapteroneintroductionppt-240322161912-556a7e26/75/Chapter-one-Introduction-advanced-construction-project-management-ppt-ppt-1-2048.jpg)