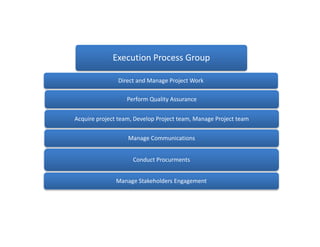
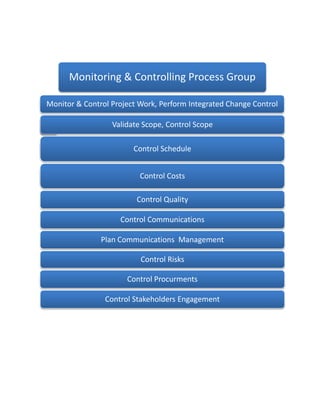
This document summarizes the PMBOK 5th edition, detailing project management processes and their interactions across five process groups: initiating, planning, executing, monitoring & controlling, and closing. It emphasizes the importance of specific processes, communication with stakeholders, and the continuous collection and analysis of project data. The document also highlights the need for adapting and updating project plans throughout execution and encourages reading the full PMBOK guide for comprehensive understanding.