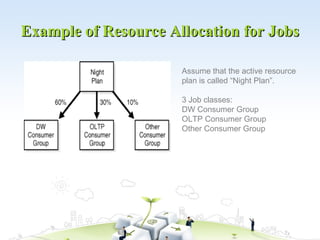
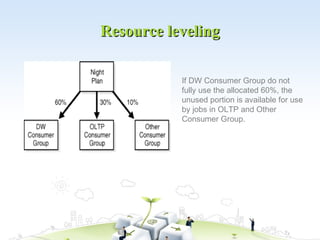
The document discusses resource allocation in project management. It defines resources as anything required to accomplish an activity or undertake an enterprise. The basic resources are land, labor, and capital. Resource allocation involves assigning available resources in an economic way and scheduling activities and their resource needs based on both resource availability and project time. Techniques to avoid over-allocating resources include resource leveling, prioritizing projects, linking tasks, leaving breathing room in schedules, and avoiding an approach where teams constantly put out fires.