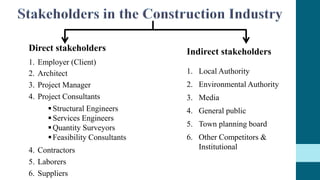
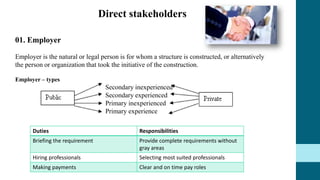
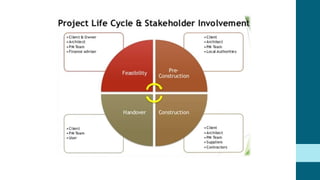
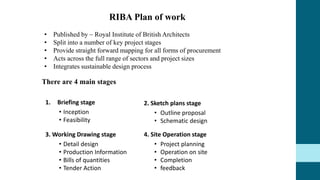
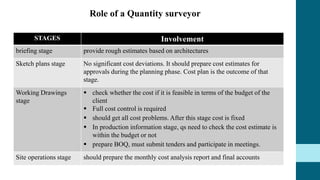
This document discusses the roles and involvement of key stakeholders throughout the different stages of a construction project lifecycle based on the RIBA Plan of Work. It introduces direct stakeholders like the client, architect, project manager, contractor, laborers and suppliers. It also covers indirect stakeholders such as local authorities and the public. For each stage of the RIBA Plan of Work, the document outlines the typical involvement and responsibilities of different direct stakeholders, including the client, architect, quantity surveyor, and structural engineer. It also includes an interview with a structural engineer stakeholder discussing their background and role.