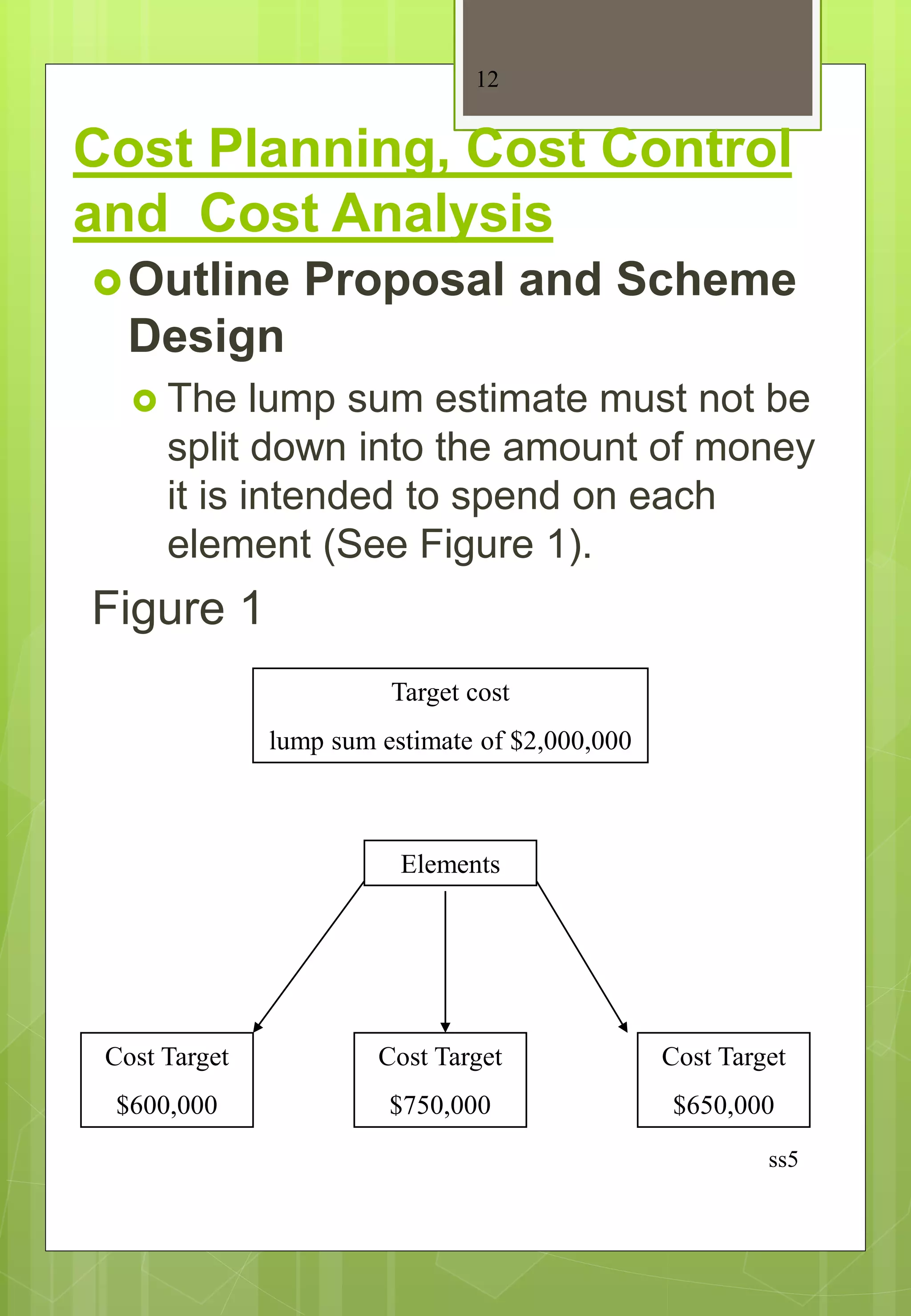
This document discusses cost planning, cost control, and cost analysis for construction projects. It explains that cost planning involves determining a project's probable cost, controlling the design to provide value for money, and monitoring variations during construction. Cost control techniques are used to keep the project within budget. Cost analysis breaks down actual costs for future cost planning. The document outlines the various project stages and emphasizes that cost targets should be set early and regularly checked during design development to avoid going over budget.