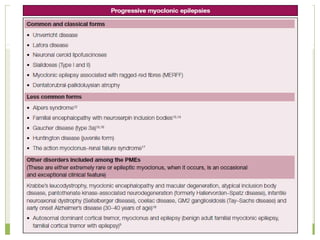
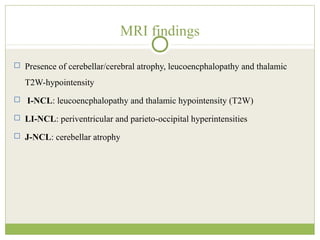
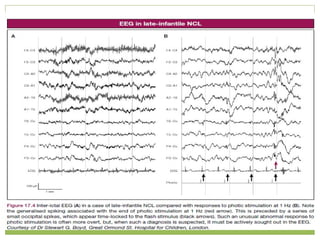
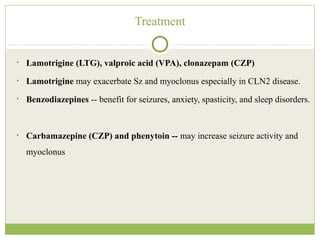
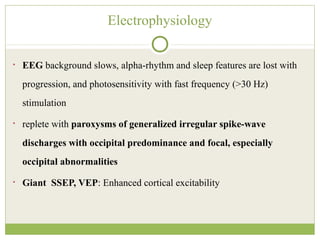
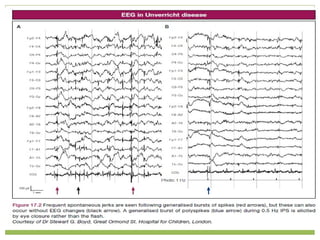
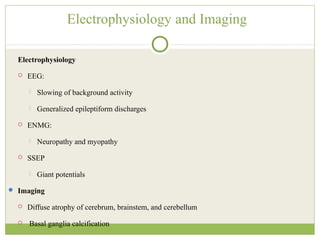
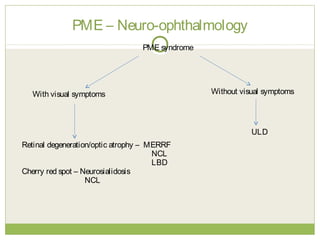
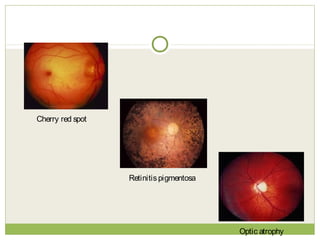
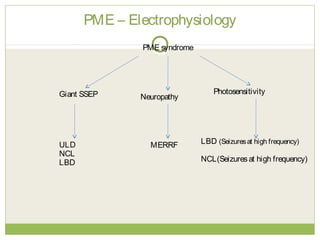
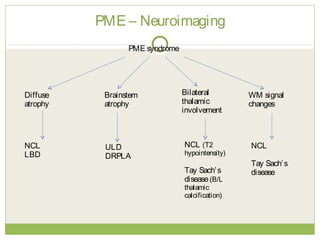
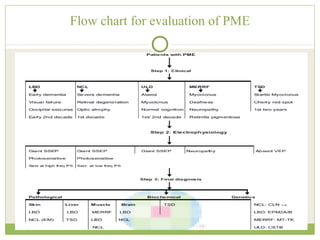
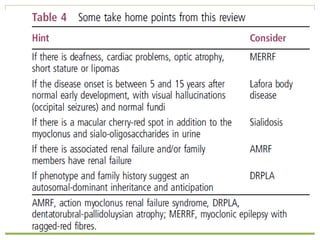
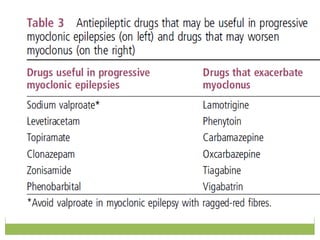
This document discusses progressive myoclonic epilepsy (PME), a group of rare genetic neurological disorders characterized by myoclonus and epileptic seizures with progressive neurological decline. It describes several specific forms of PME, including neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs), Lafora body disease, Unverricht-Lundborg disease, and myoclonic epilepsy with ragged-red fibers. For each, it covers clinical features, genetics, investigations such as EEG and MRI findings, pathology, treatment approaches, and prognosis. The document provides a detailed review and comparison of these progressive myoclonic epilepsy syndromes.