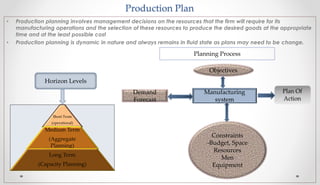
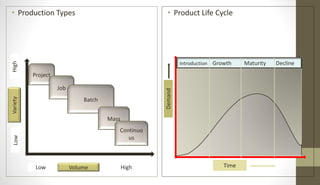
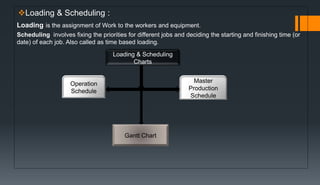
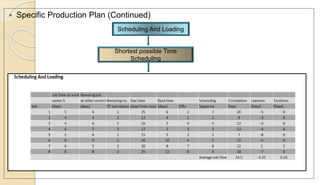
The document outlines the production planning and control process for a group project consisting of 4 members. It defines production planning, discusses horizon levels and objectives. It also covers forecasting, product design, routing, materials requirements planning, scheduling, loading, production control forms and functions, control systems, and provides a specific production plan for Kakar Steel Mills.