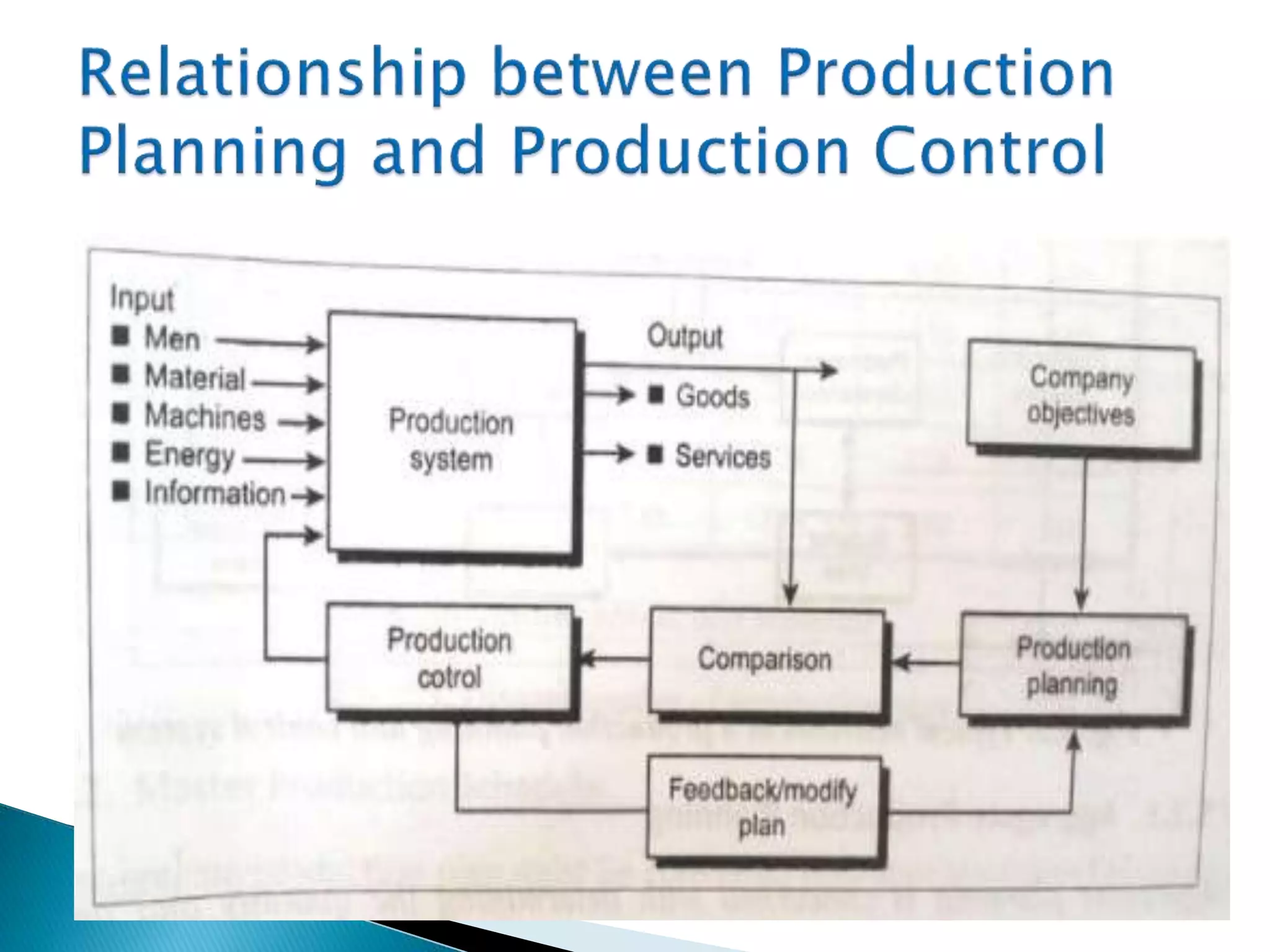
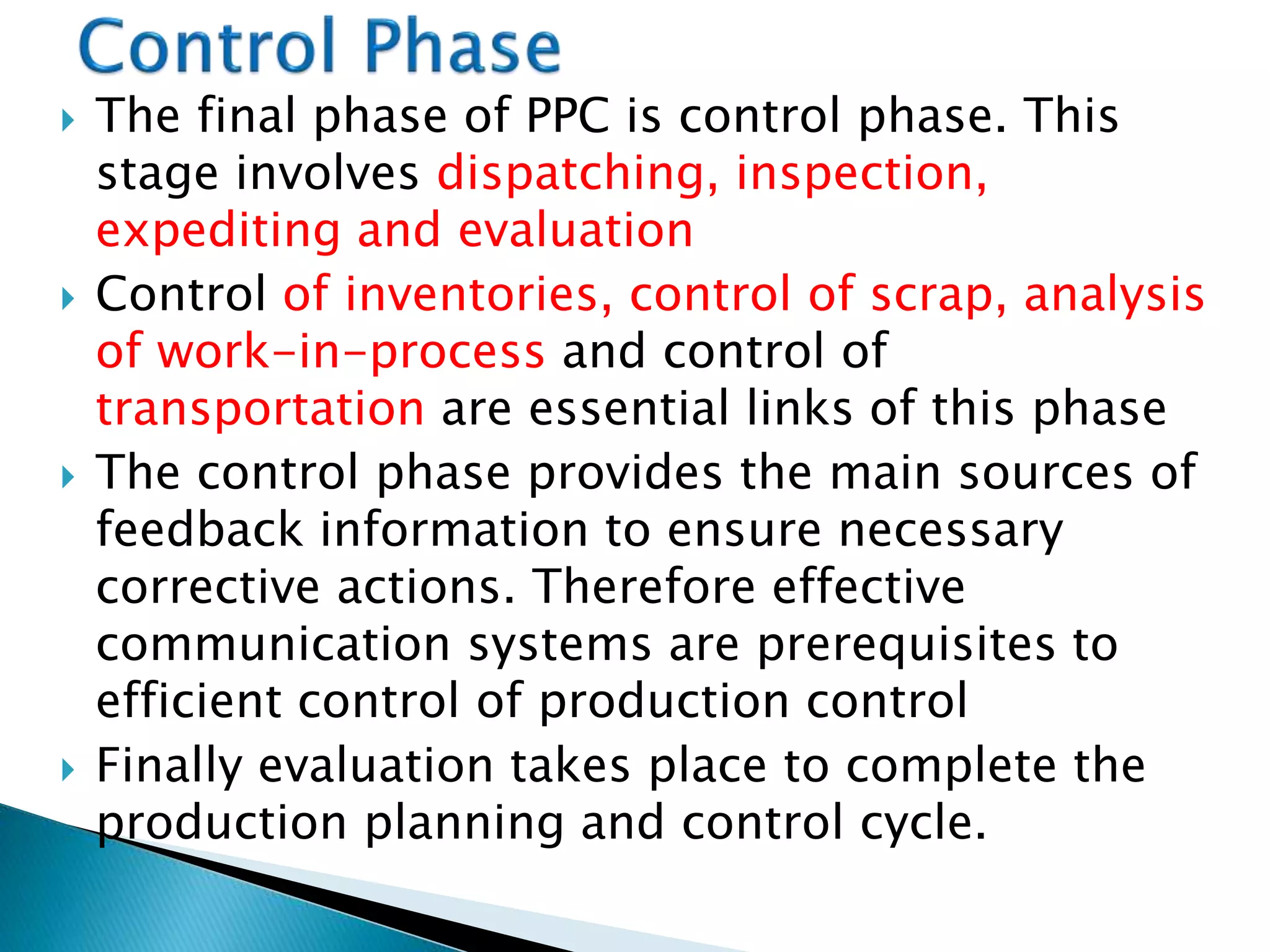
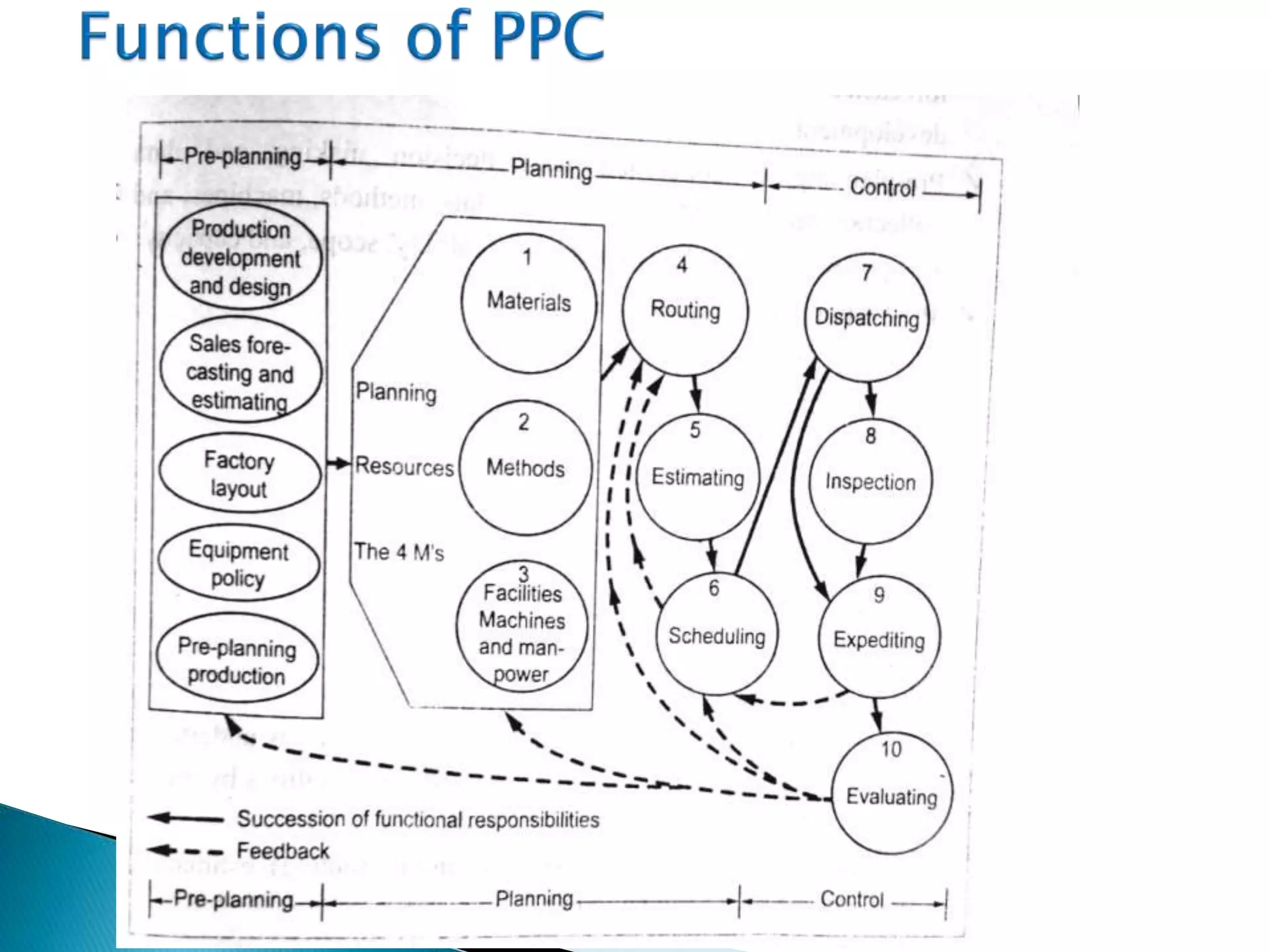
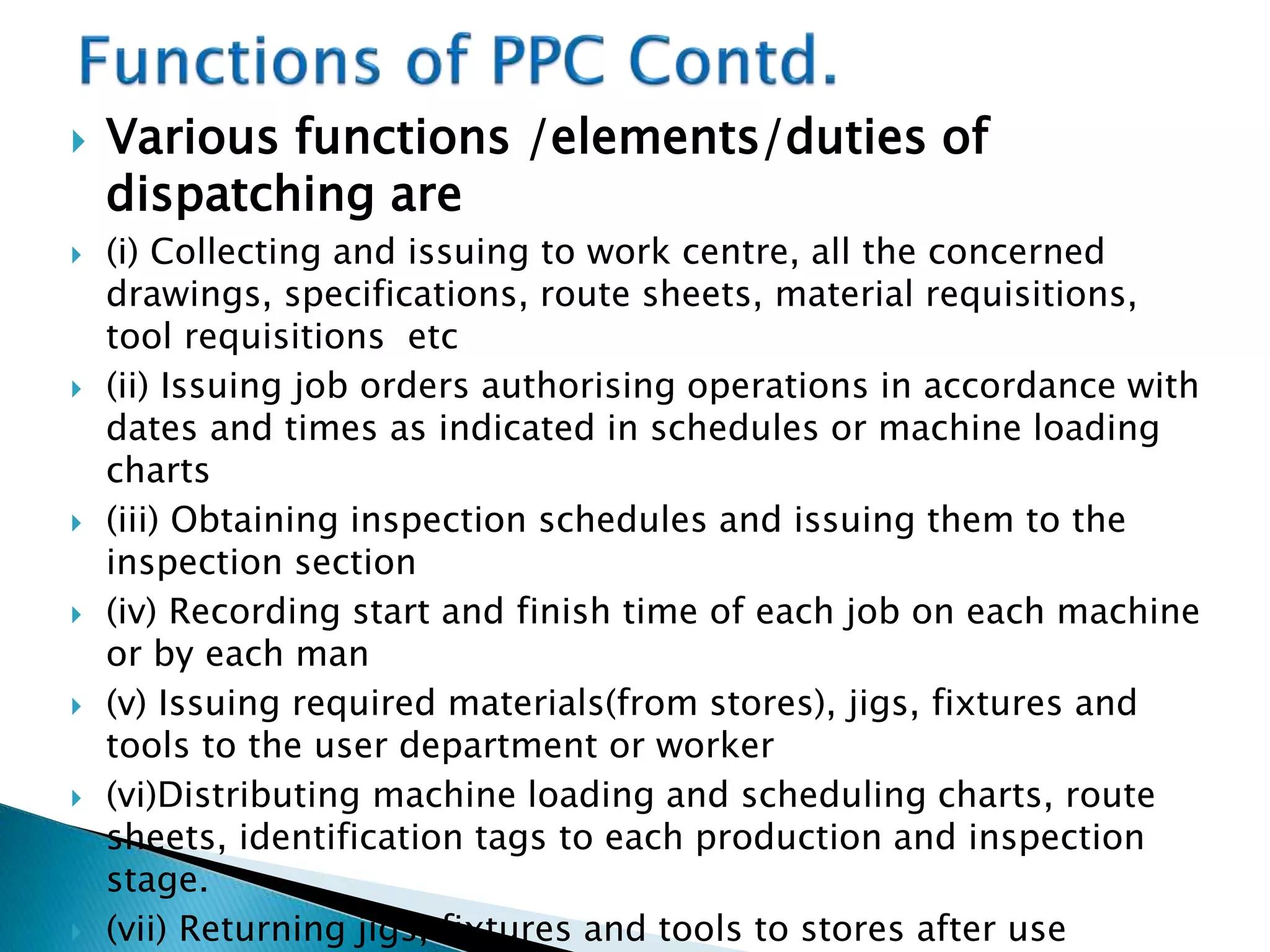
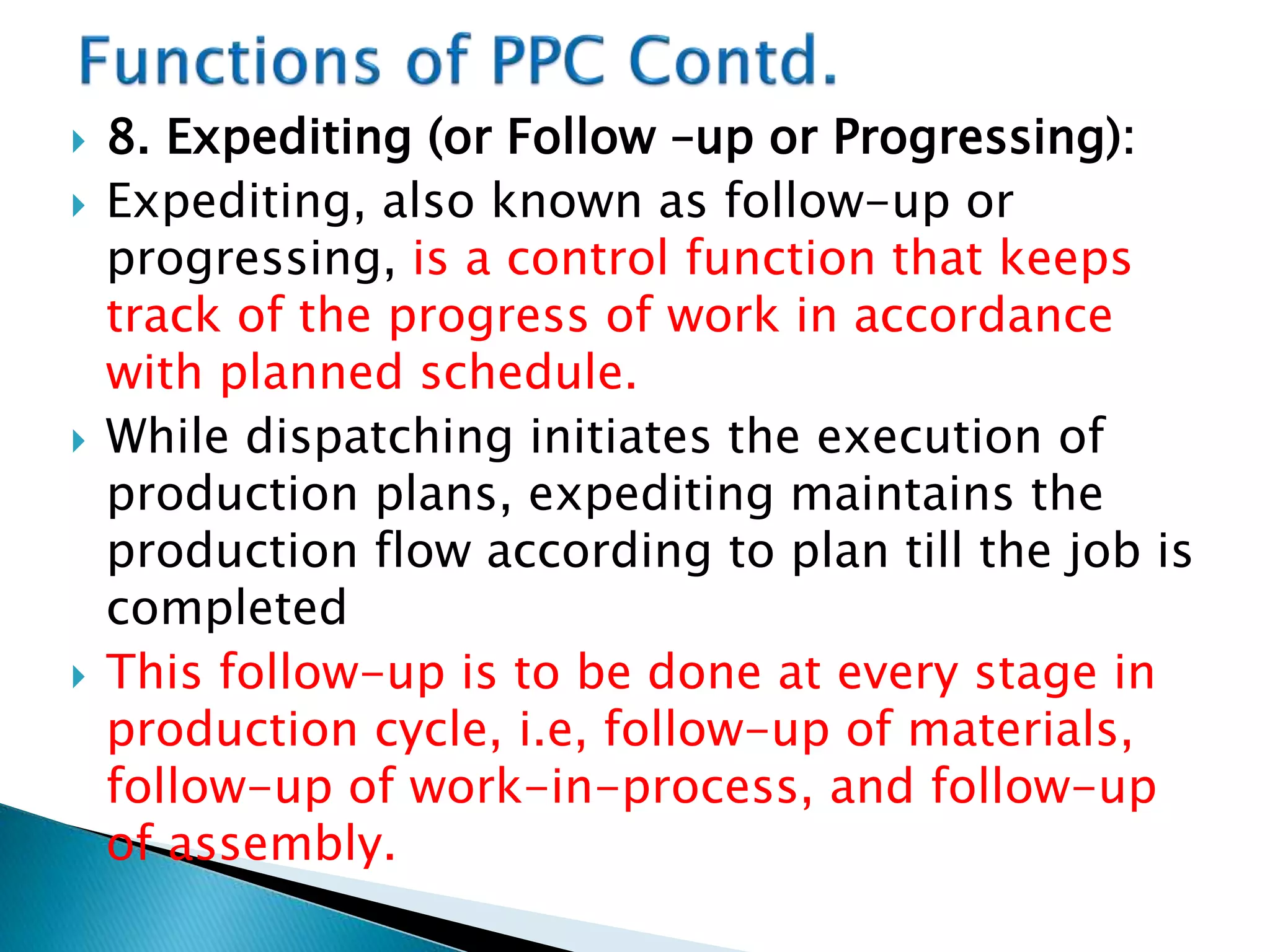
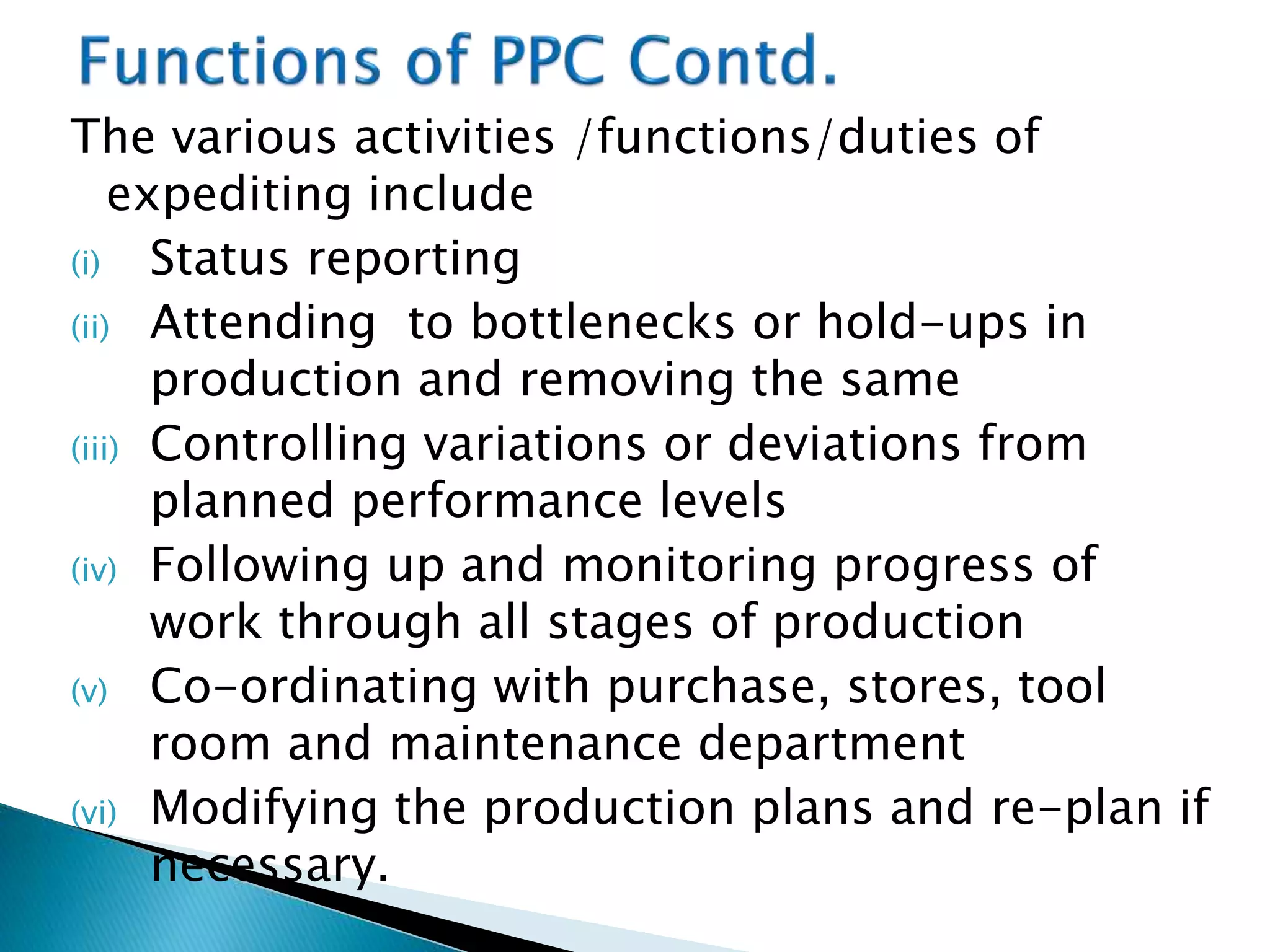
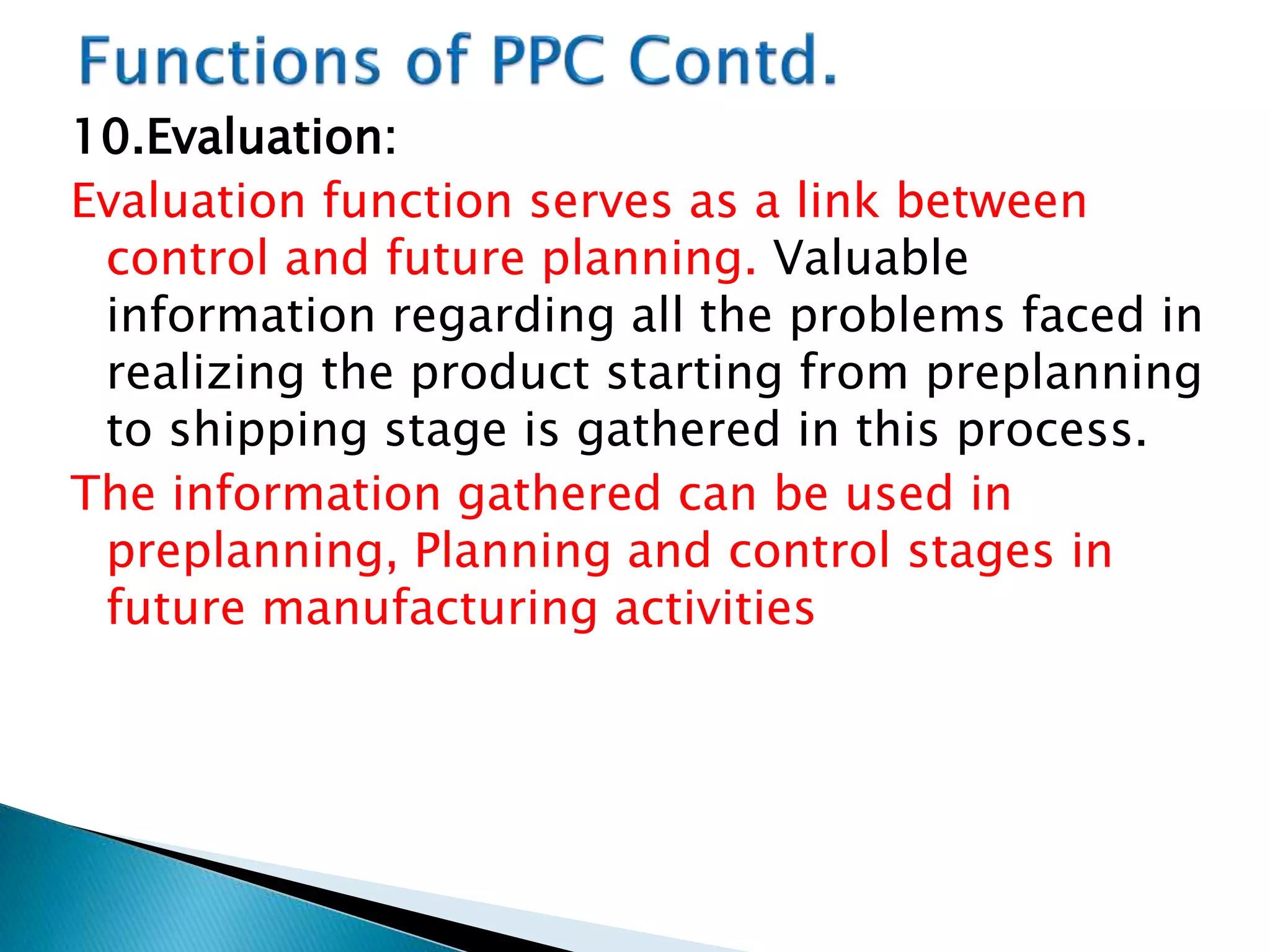
The document discusses production planning and control (PPC). It defines PPC as planning, coordinating, and controlling production activities to transform raw materials into finished products efficiently. PPC consists of production planning and production control. Production planning determines requirements for resources like materials, labor, and equipment. Production control implements production plans and ensures operations occur as planned through monitoring and corrective actions. The key goals of PPC are efficient resource utilization and producing quality products on schedule and budget.