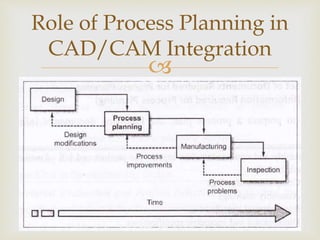
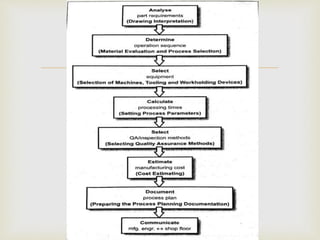
This document discusses computer aided process planning (CAPP). It outlines the key steps in process planning including drawing interpretation, material and process selection, selecting machines and tools, setting process parameters, quality assurance methods, cost estimating, documentation, and communicating the plan to the shop floor. CAPP aims to reduce errors and improve efficiency over manual planning. The benefits of CAPP include process rationalization, productivity gains, cost reductions, faster response to changes, and incorporating other applications. CAPP systems can be either retrieval-based, recalling plans for similar parts, or generative, creating new plans from scratch.