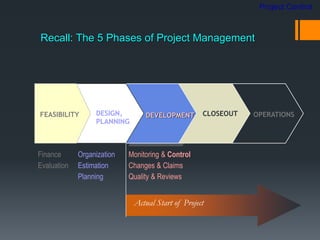
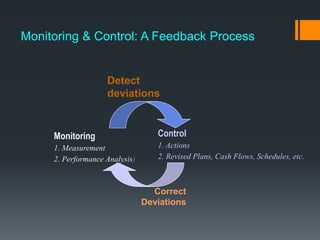
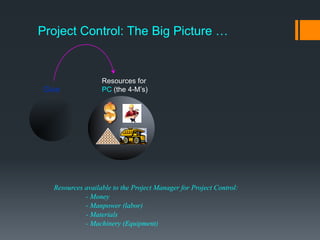
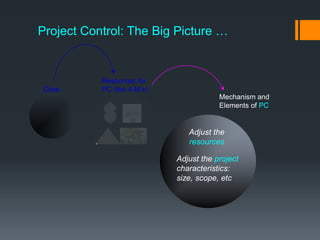
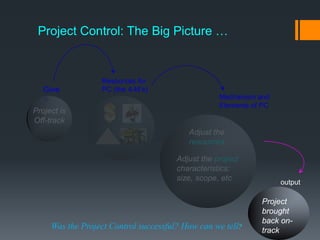
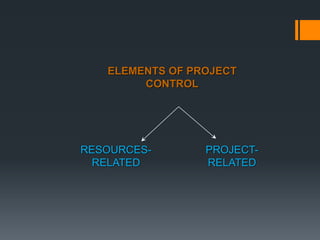
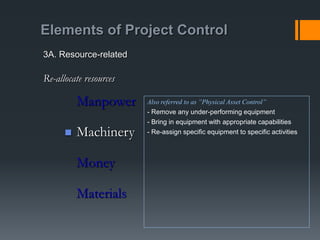
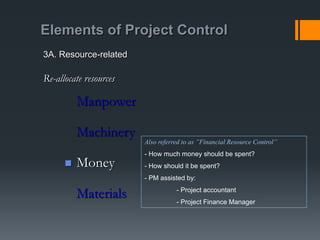
This document discusses project control and monitoring for construction management. It begins with an introduction of the presenter and defines project control as monitoring and controlling processes to track, review, and regulate a project's progress and performance. It then discusses key aspects of project control like what to monitor and control, who is responsible, and documents used. Specific project aspects that are monitored are performance, time/schedule, and cost. Resources available for project control are also outlined as money, manpower, materials, and machinery. The document concludes with discussing elements of project control like re-allocating resources, and mechanisms used like cybernetic, go/no-go, and post-control approaches.