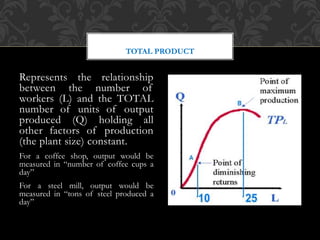
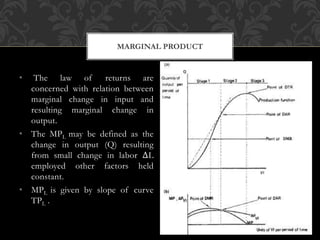
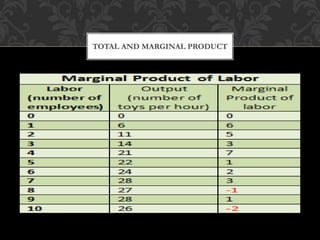
The document discusses the production function, which delineates the relationship between inputs and outputs in production. It emphasizes key concepts such as short run and long run production, detailing how production can be increased with varying inputs, particularly labor and capital. Additionally, it covers ways to measure labor productivity through total, average, and marginal product, along with the laws of production related to variable inputs.