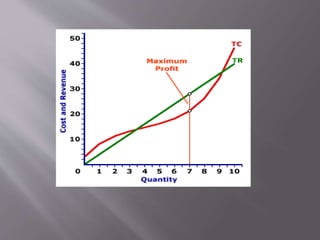
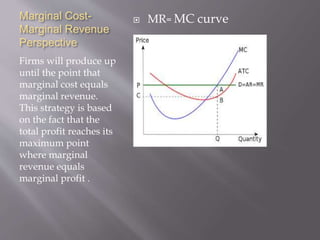
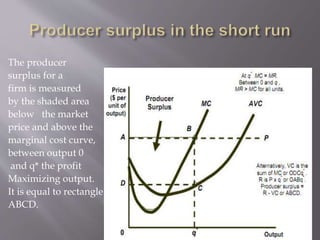
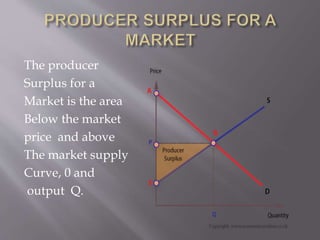
1) A firm produces at the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost to maximize profits. This is the point where additional revenue from producing another unit equals the additional costs.
2) A firm's profit is maximized by producing at the output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. Producing more would mean marginal costs exceed marginal revenues, reducing profits.
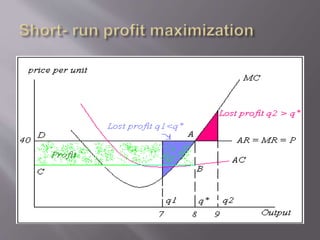
3) In the short run, a competitive firm will produce the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost to maximize profits. The firm's profit is represented by the rectangle between average total cost and marginal cost at the profit-maximizing quantity.