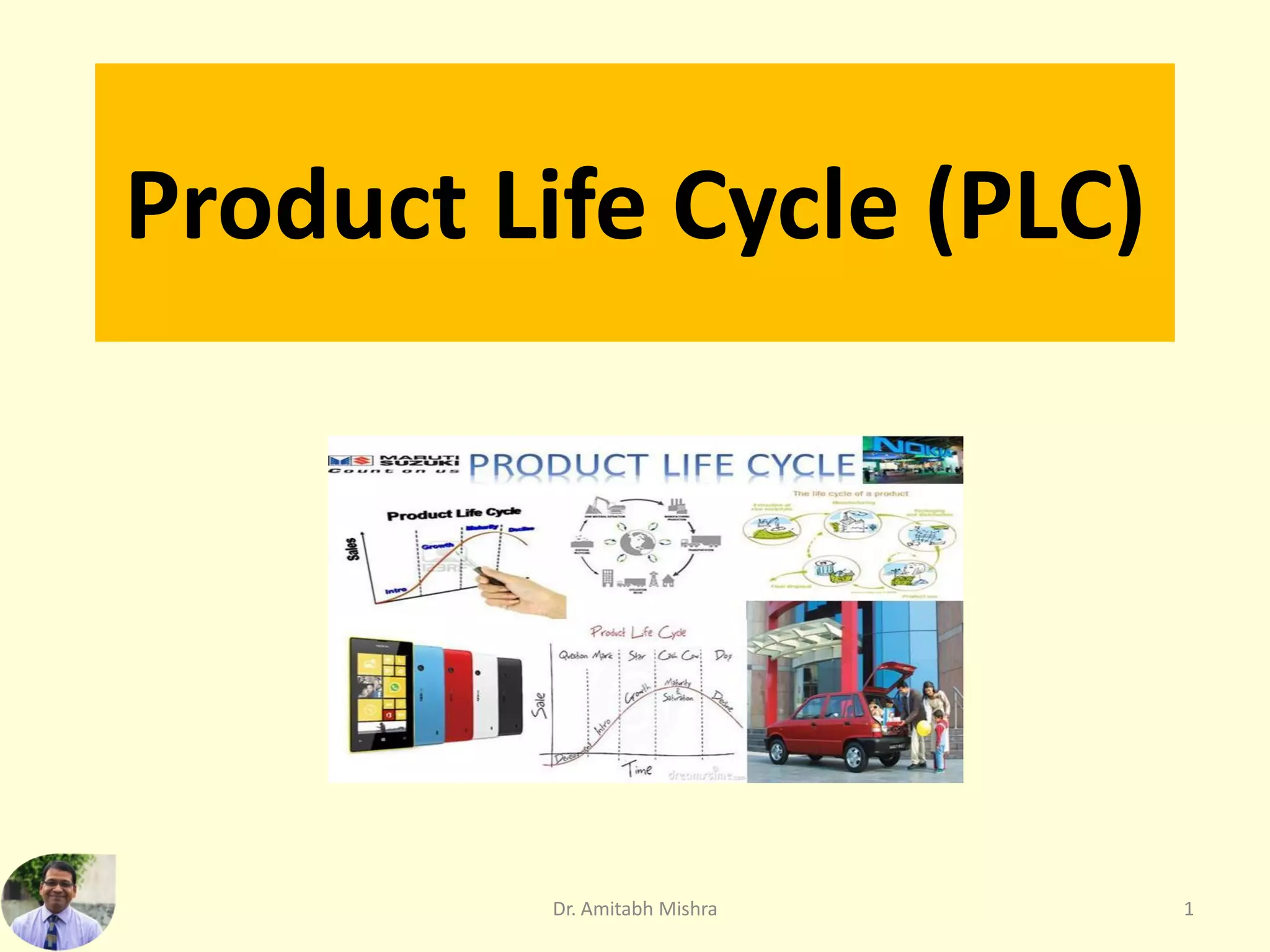
The product life cycle (PLC) outlines the stages products go through, from development to withdrawal, influencing strategies such as marketing and positioning. Key stages include development, introduction, growth, maturity, saturation, decline, and withdrawal, each characterized by specific sales, costs, and marketing objectives. While beneficial for forecasting and strategic planning, the PLC concept has limitations, particularly in predicting product behavior and variations across different products.