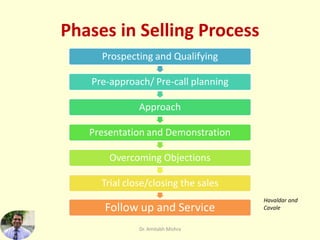
The document outlines the typical phases in a sales process:
1. Prospecting and qualifying potential customers.
2. Pre-call planning to understand customers' needs before meetings.
3. Approaching customers to build rapport.
4. Presenting products and demonstrating how they meet needs.
5. Overcoming objections by asking questions and highlighting benefits.
6. Attempting to close the sale while also leaving room to continue discussions.
7. Following up after sales to ensure customer satisfaction and potential for repeat/referral business.