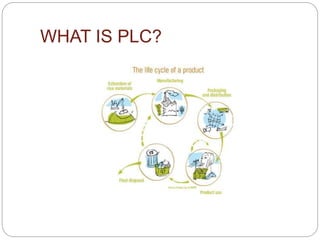
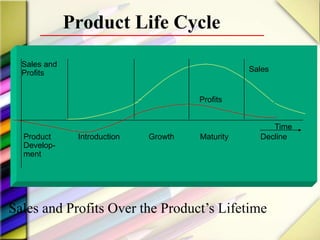
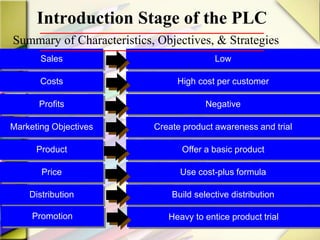
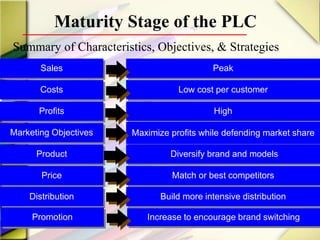
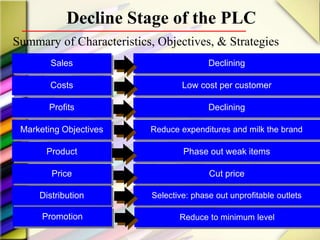
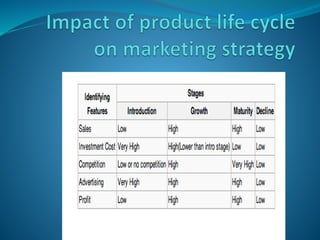
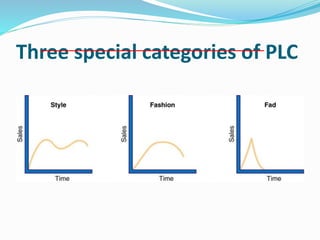
The document discusses the product life cycle (PLC) and strategies companies use at each stage. It notes that products pass through distinct stages of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. During introduction, strategies focus on creating awareness and trial with high promotion at a premium price. Growth focuses on market share gains through distribution expansion, promotions, and price reductions. Maturity aims to maximize profits through diversification while defending market share. Decline entails cost cutting and milking remaining brand value. Strategies may also include market, product, or marketing program modifications to change a brand's course.