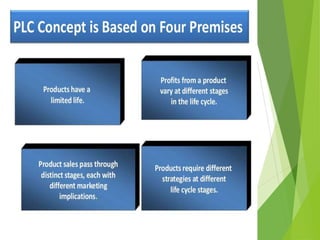
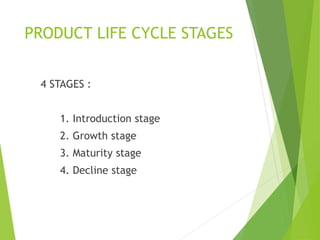
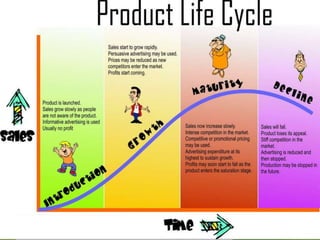
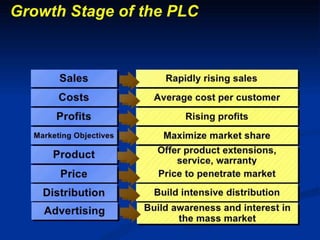
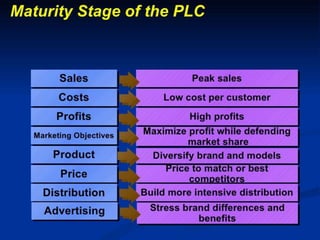
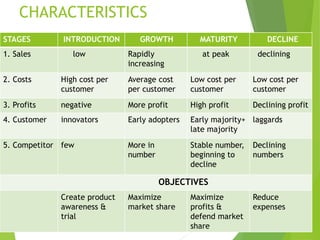
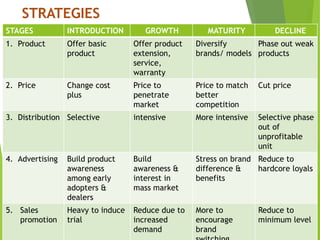
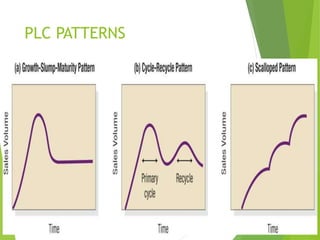
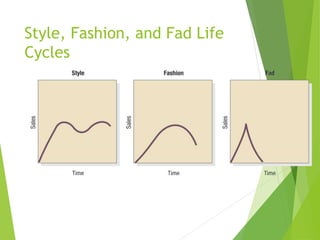
The product life cycle describes the stages a new product goes through from introduction to decline. It includes four main stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. During each stage, sales, costs, profits, customers, competitors, objectives, and marketing strategies differ. For example, during introduction sales are low and costs are high as awareness is built, while during maturity sales peak as profits are maximized and competition stabilizes. However, the product life cycle model has limitations and not all products follow the same pattern or spend equal time in each stage.