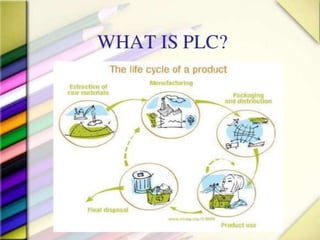
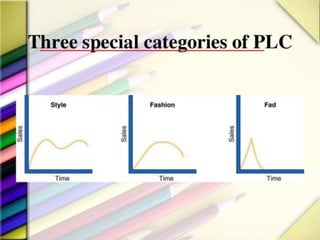
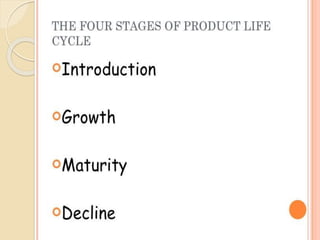
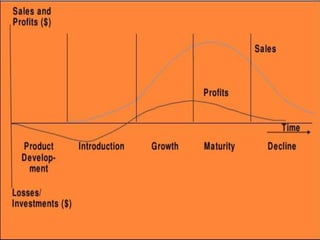
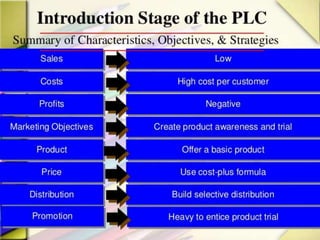
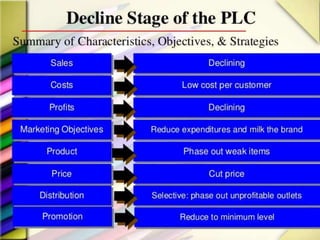
The product life cycle theory describes the typical stages a product goes through from introduction to decline. The stages are introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. During introduction, a product is new to the market and the goal is raising awareness through advertising. In the growth stage, production increases and competition grows as sales momentum builds. The maturity stage sees slower sales growth and increased competition, requiring more promotion to maintain market share. Finally, the decline stage occurs when sales begin decreasing to the point of obsolescence. The goal of life cycle management is to maximize value and profitability at each stage through appropriate marketing strategies.