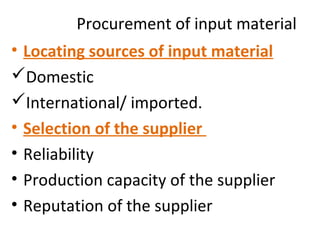
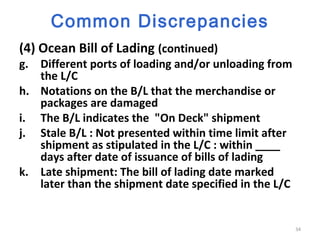
The document discusses the process of an export order from beginning to end. It explains that an export order communicates the importer's decision to purchase items from the exporter, and represents an offer and acceptance between the two parties. The document then outlines each step of securing and processing an export order, including developing logistics, arranging for materials, production, shipment, and negotiating shipping documents.