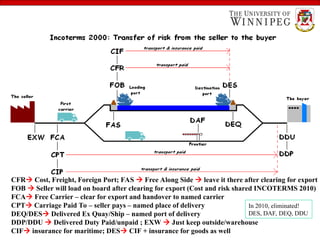
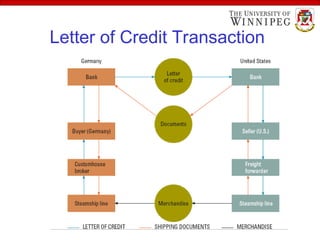
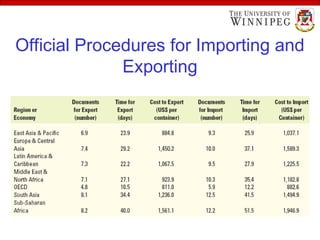
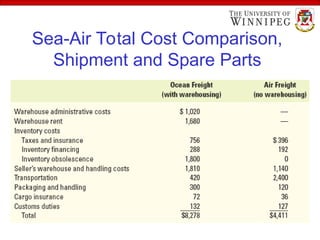
The document outlines various export import practices and payment procedures, including terms like cash in advance, open account, and letter of credit, each presenting different levels of payment risk for sellers. It also discusses export financing through private and public sources, along with the role of foreign freight forwarders in assisting exporters with documentation and logistics. Additionally, it highlights key shipping documents and procedures, including export bills of lading and commercial invoices, while noting methods for efficient transport such as air freight and containers.