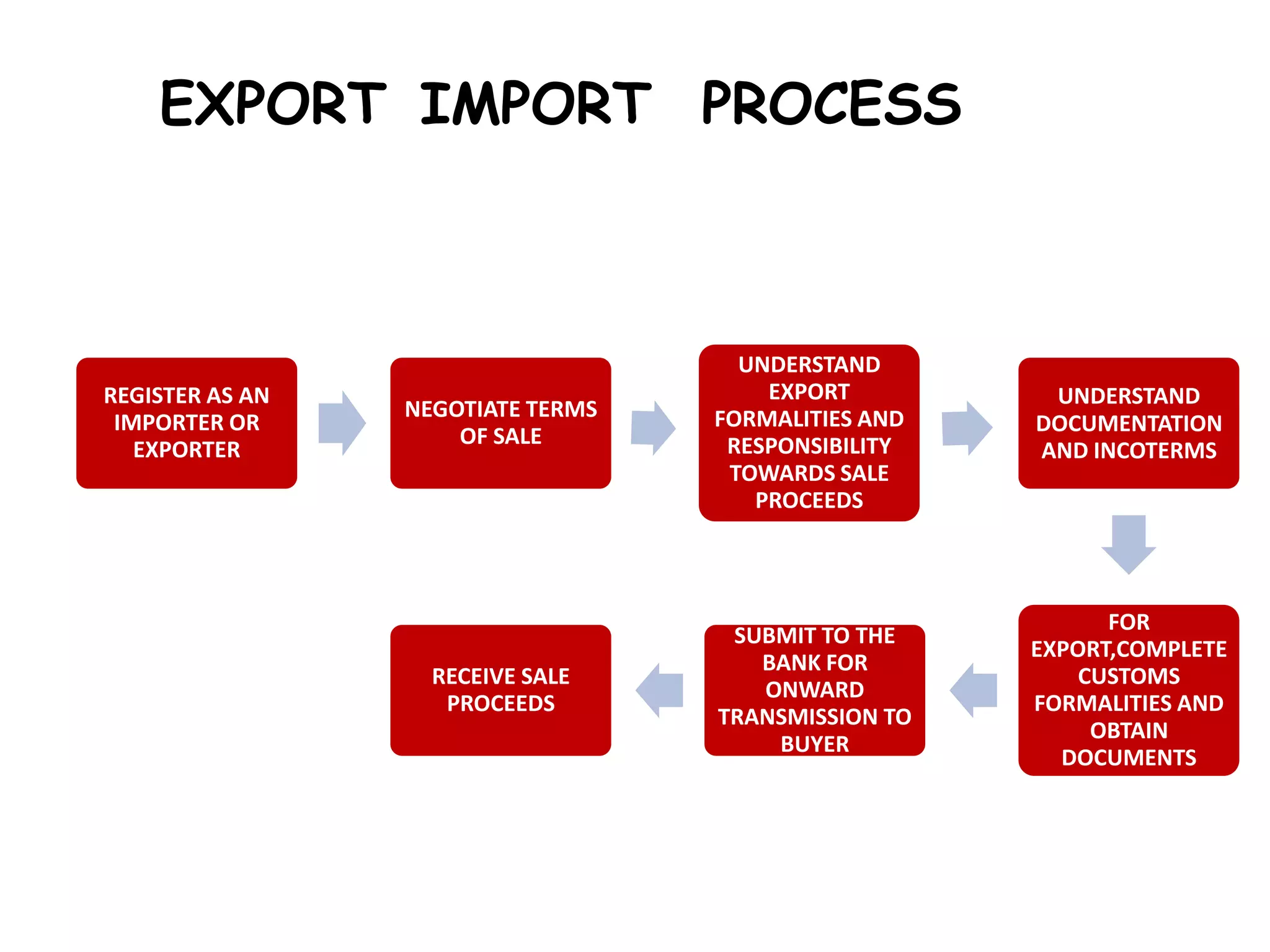
This document provides information about import and export processes. It defines key terms like import, export, importer, exporter and discusses the balance of trade. It outlines the types of imports and exports and explains the steps involved in export like registering, negotiating terms of sale, understanding documentation and customs formalities. It also discusses modes of payment, advantages and disadvantages of import and export, and institutions that support international trade like EXIM Bank, ECGC and provisions in the foreign trade policy regarding excise duty and customs duty.