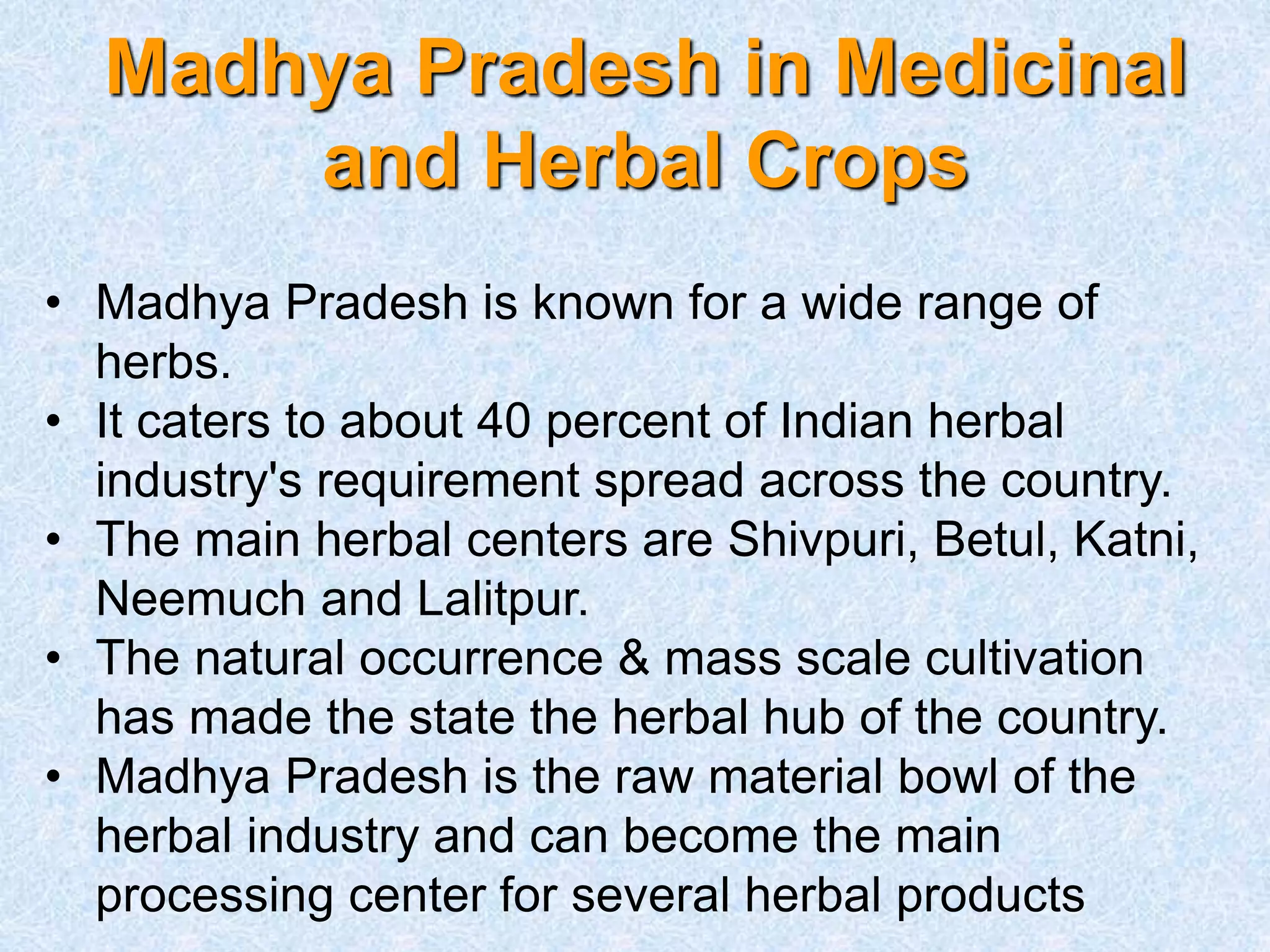
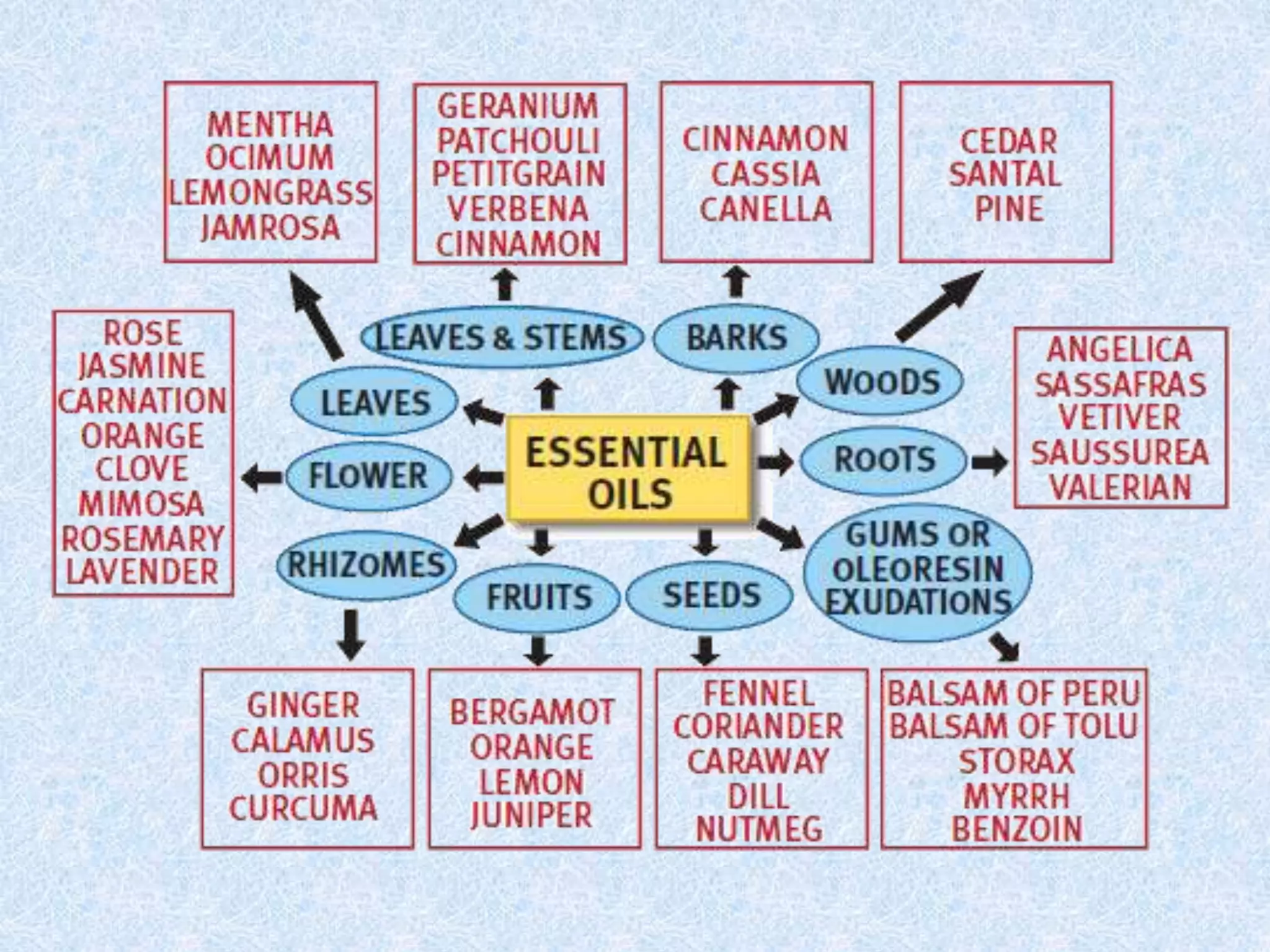
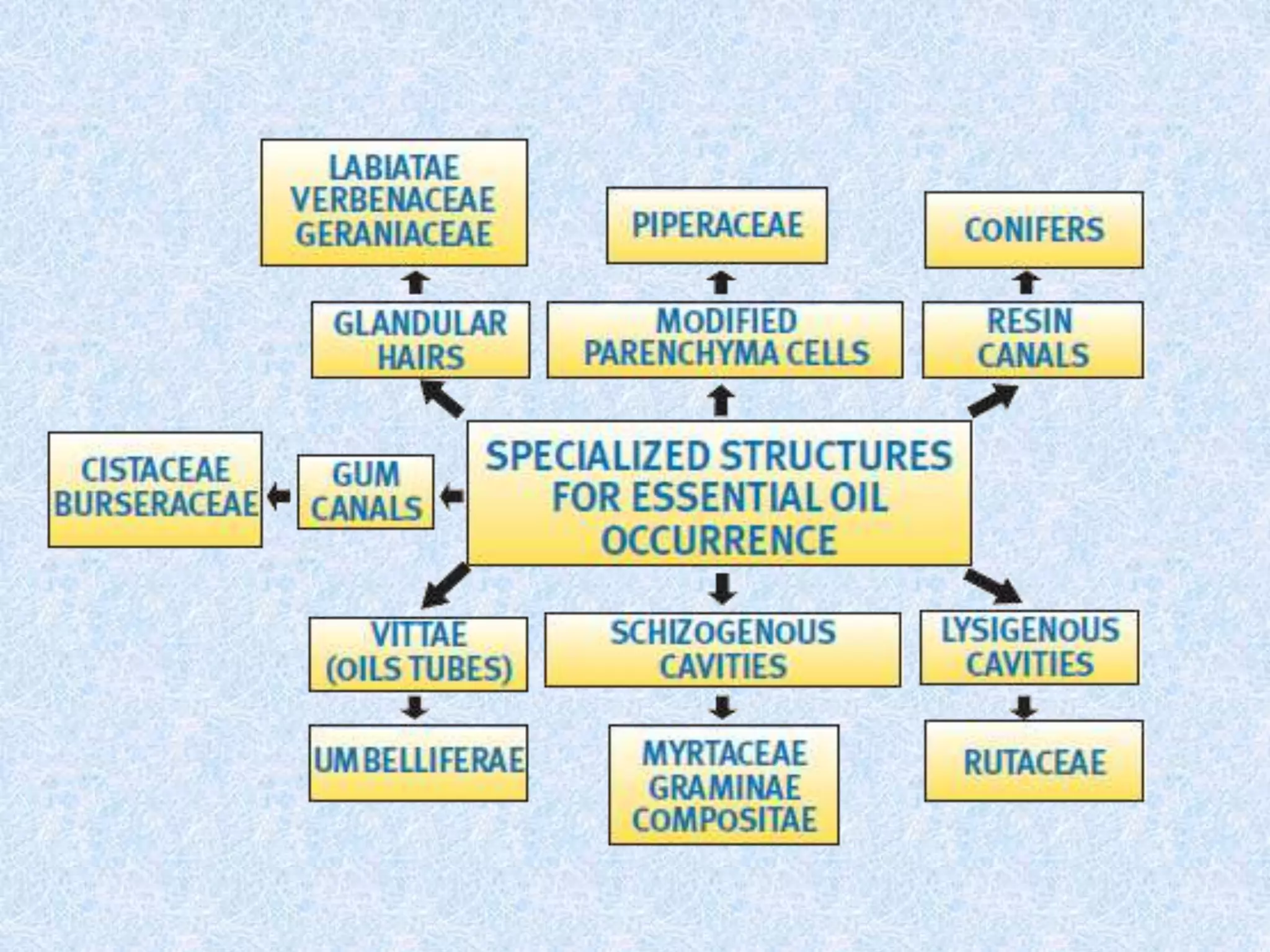
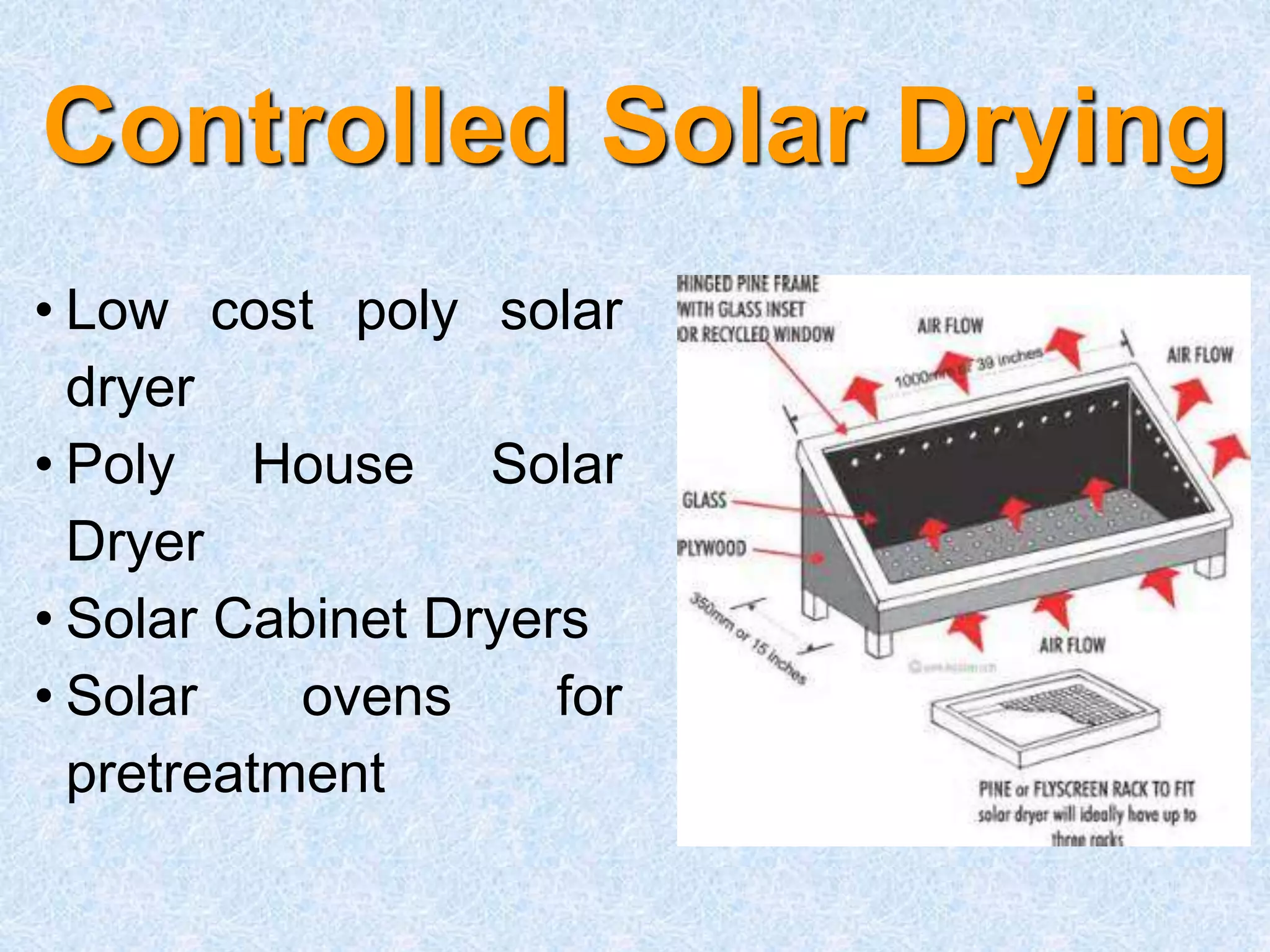
Madhya Pradesh is a major producer of medicinal and herbal crops in India, cultivating over 40% of the country's supply. The state has potential to become a processing hub through establishing facilities and technologies for extraction, drying, size reduction, and producing value-added products from crops. Key recommendations include developing appropriate processing technologies adaptable to rural areas, strengthening R&D institutes with pilot plants, and establishing agro processing centers with custom processing facilities to improve post-harvest handling and increase incomes for tribal collectors.