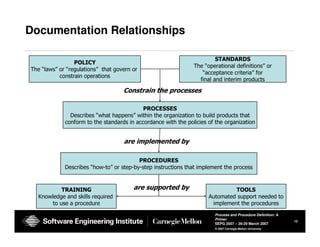
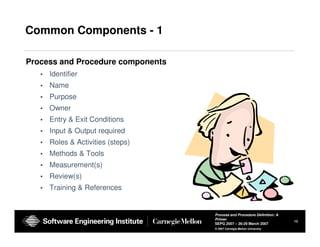
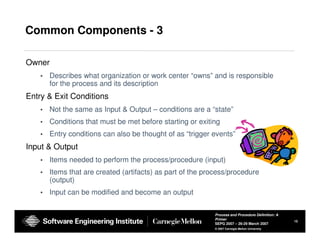
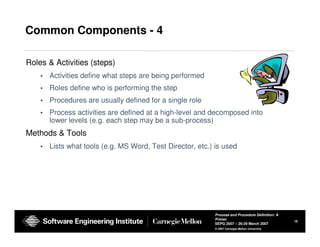
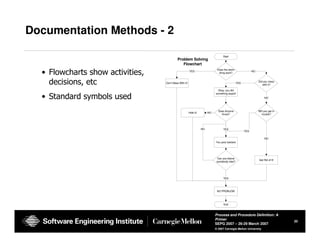
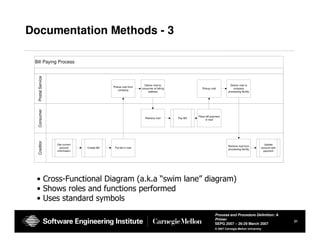
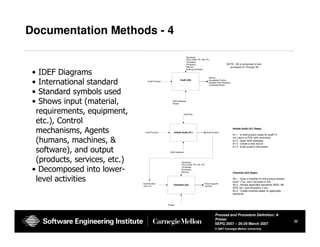
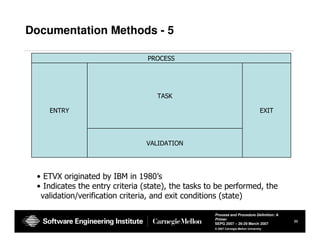
The document provides guidance on defining processes and procedures, including definitions of key terms, components to include in documentation, and examples of different documentation methods such as flowcharts, cross-functional diagrams, and ETVX. It also includes templates for documenting processes and procedures and examples of how to document a process.