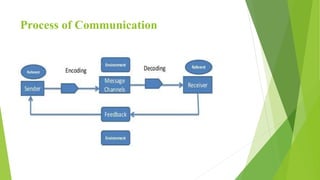
This document outlines the key elements and process of communication. It discusses the main components: the sender who encodes an idea or message; the channel through which the message is sent; the receiver who decodes the message; and feedback from the receiver back to the sender. It describes each part in detail, including that the sender initiates communication, encoding involves giving shape to ideas through symbols, the message is the subject matter, channels are the medium of conveyance, the receiver decodes and interprets, decoding is important for understanding, and feedback shows comprehension and completes the process. Additional factors like noise, environment, and interpersonal variables are noted to influence communication.