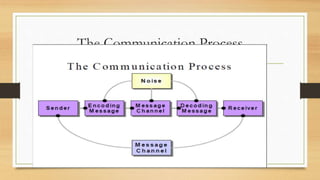
Communication involves the transmission of information from one person to another through both verbal and non-verbal means. It is a two-way process that allows for the sharing of information and understanding between individuals. The key components of the communication process are the message, sender, encoding, channel, decoding, receiver, feedback, and noise. Effective communication relies on clear encoding and decoding of messages between a sender and receiver, with feedback to confirm understanding and address any issues caused by noise in the channel.