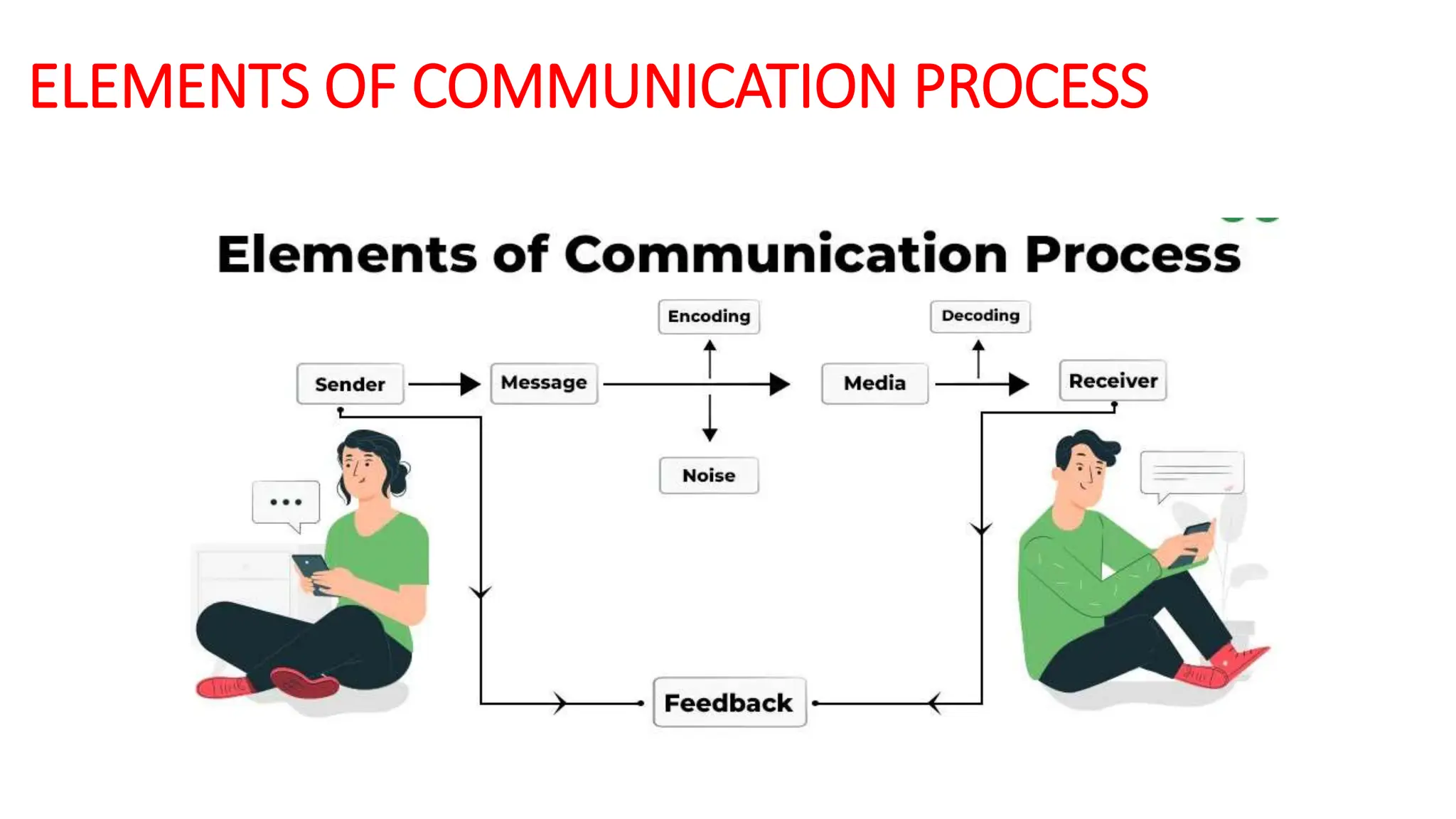
The communication process has eight elements: a sender conveys a message to a receiver through a medium by encoding the message, which the receiver decodes. Feedback from the receiver lets the sender know if the message was understood despite any noise that could interfere with effective communication.