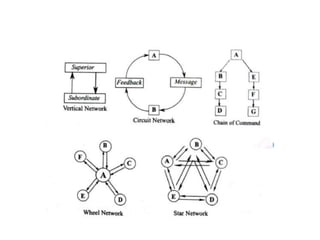
The document discusses the concept of communication, highlighting its origins, elements, levels, channels, and barriers. It emphasizes the importance of effective communication in maintaining social order, harmonious relationships, and effective work culture. Various types of communication, such as intrapersonal, interpersonal, group, public, and mass communication, are examined, along with challenges like physical, psychological, and cultural barriers.