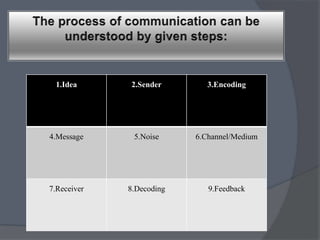
The document outlines the key components of the communication process:
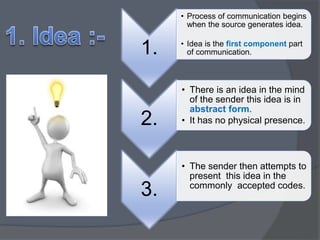
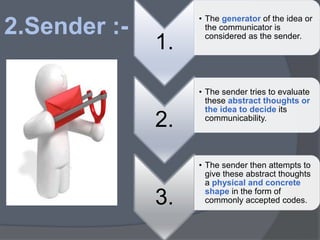
1) An idea is generated by the sender and encoded into a message.
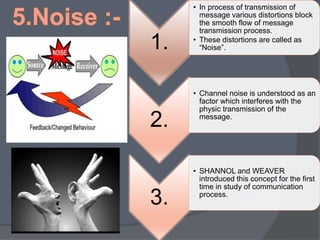
2) The message is transmitted through a channel/medium which can introduce noise.
3) The receiver decodes the message but there may be differences between the intended and received meaning without a shared frame of reference.
4) Feedback from the receiver allows the sender to evaluate and modify their communication strategy.