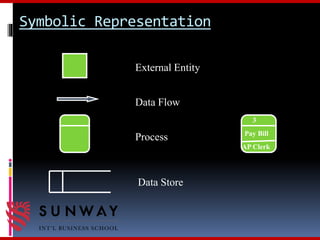
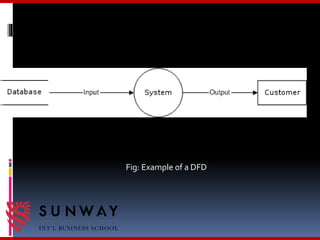
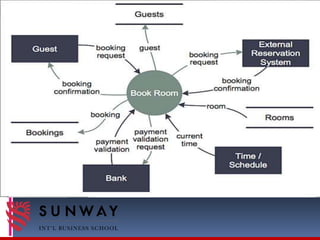
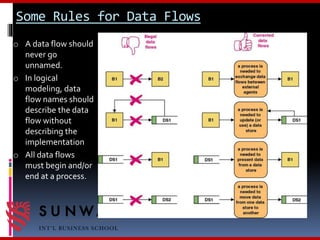
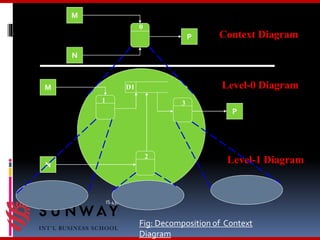
The document discusses process modeling and data flow diagrams (DFDs). It defines process modeling as a technique used to organize and document a system's processes and flow of data through those processes. DFDs are introduced as a type of process model that depict the flow of data through a system using various symbols like processes, data stores, external entities, and data flows. The document outlines the benefits of process modeling and DFDs, provides examples, and describes the basic components, guidelines, and steps for creating DFDs, including drawing a context diagram and decomposing it into level-0 and level-1 DFDs.