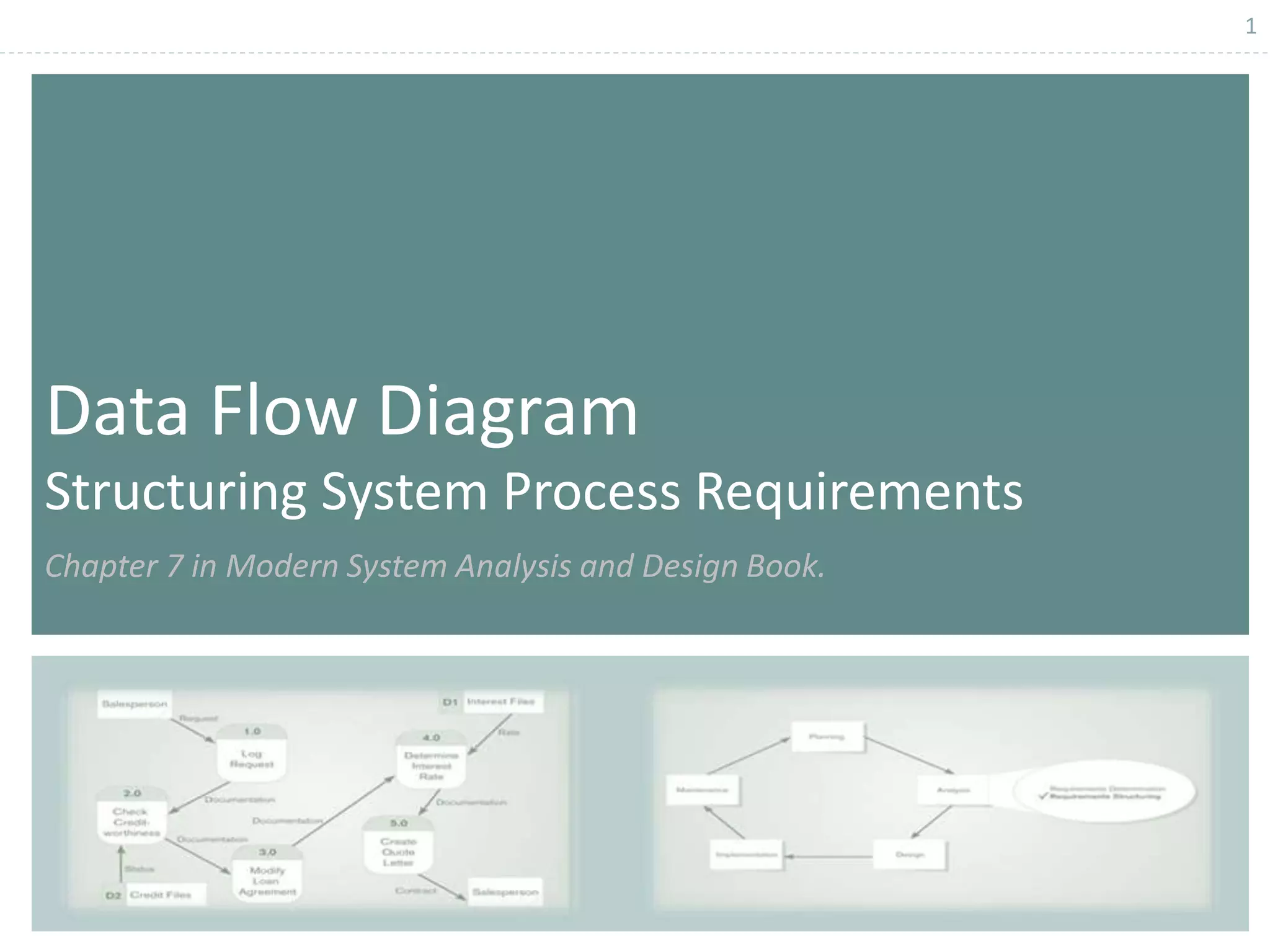
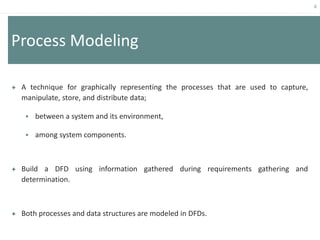
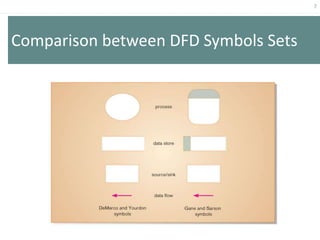
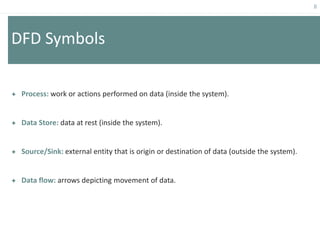
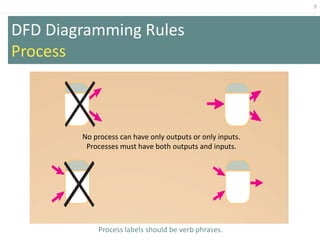
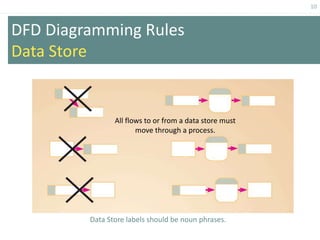
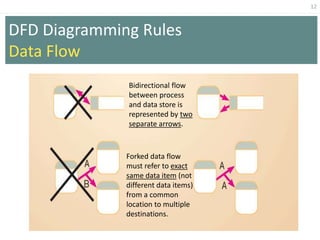
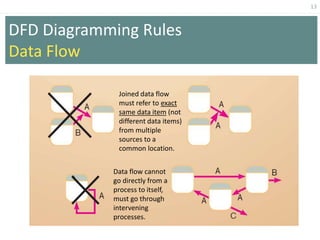
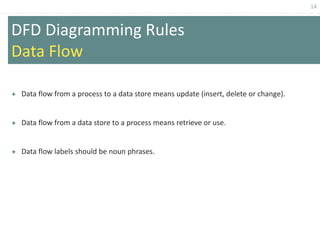
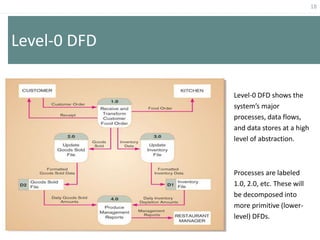
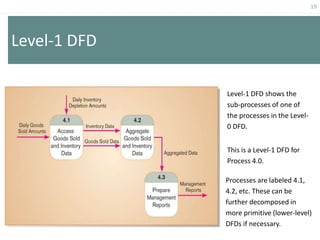
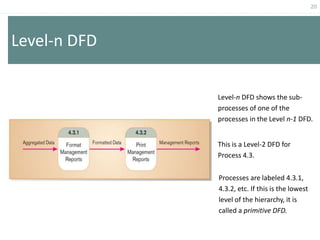
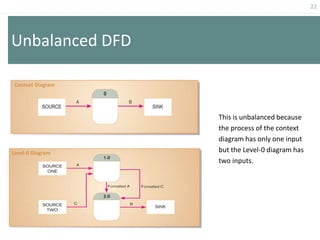
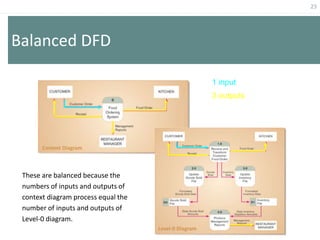
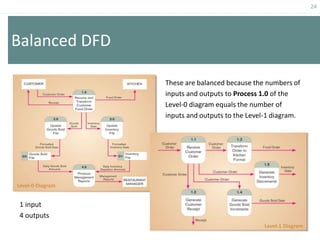
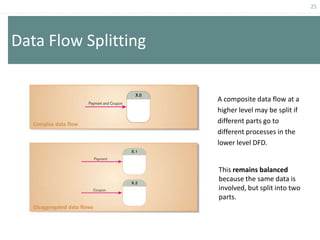
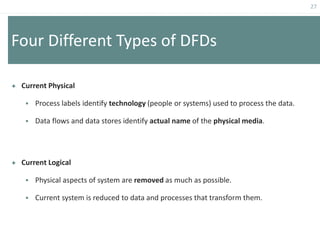
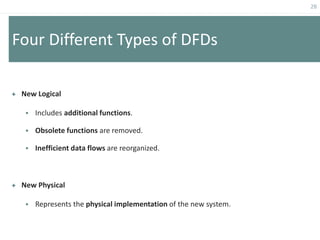
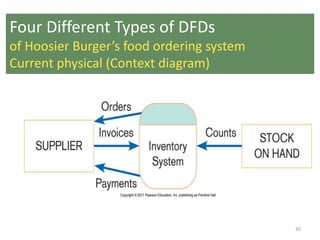
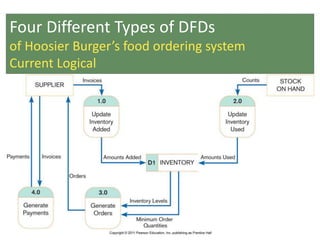
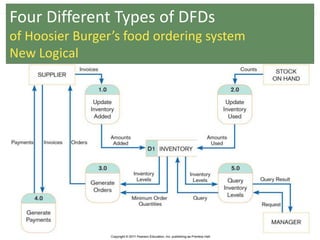
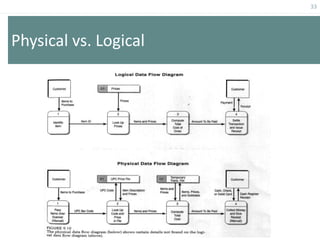
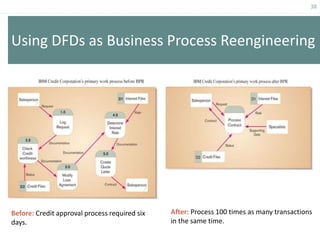
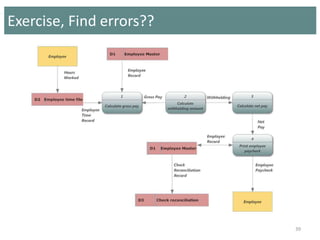
This document provides an overview of data flow diagrams (DFDs) and how they can be used to model system processes and requirements. It discusses how DFDs visually represent the flow of data between external entities, processes, and data stores. DFDs can be decomposed into multiple levels that show both high-level and low-level views of the system. The document also describes guidelines for drawing DFDs, such as using consistent notation and stopping decomposition at the primitive level. Finally, it discusses how DFDs can be used as analysis tools to identify gaps and inefficiencies in systems.