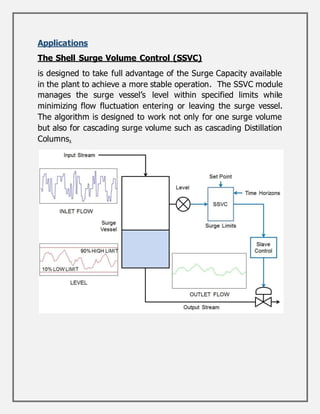
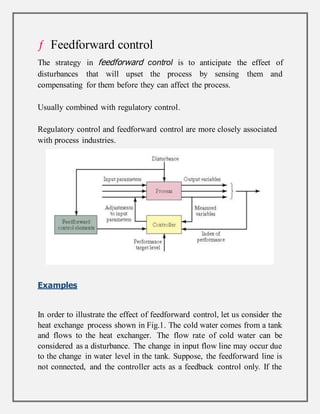
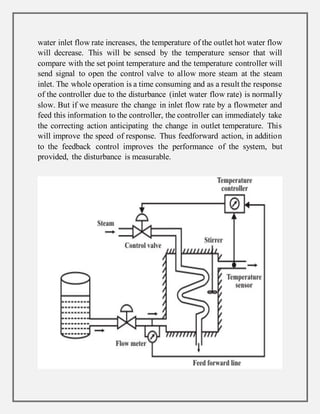
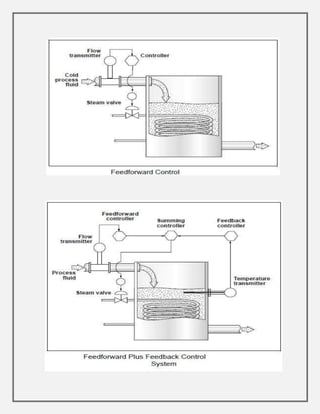
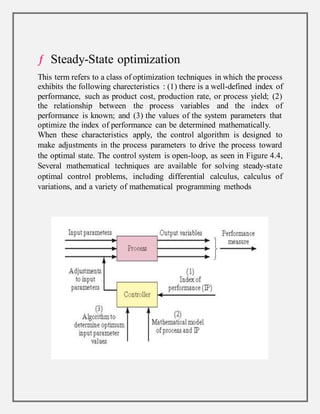
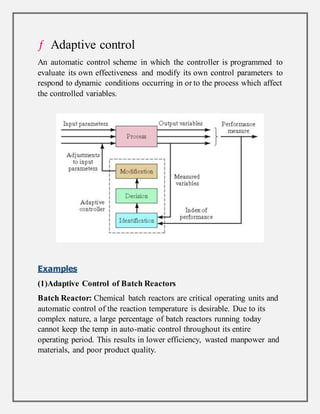
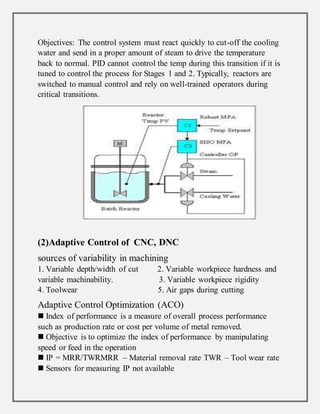
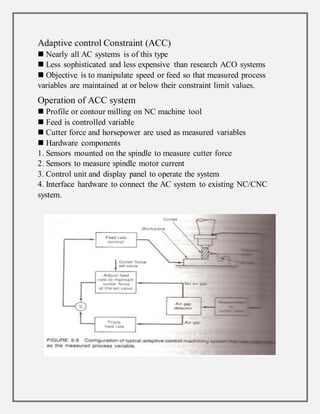
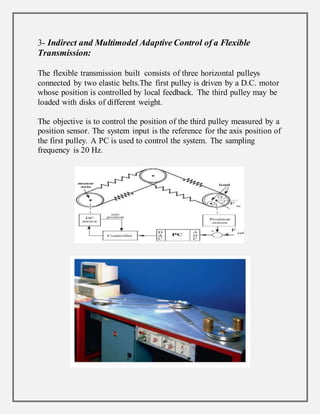
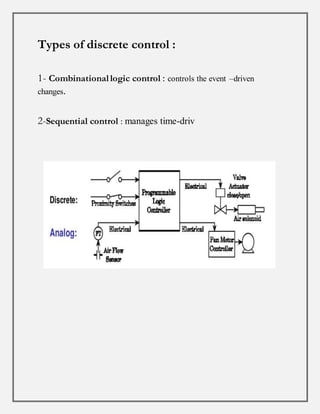
Process control involves maintaining the output of a process within a desired range through mechanisms and algorithms. For example, controlling the temperature of a chemical reactor to maintain consistent product output. There are different types of process control including regulatory control to maintain performance at a certain level, feedforward control which anticipates disturbances to compensate before they affect the process, and adaptive control where the controller modifies its own parameters based on dynamic process conditions. Discrete control systems make event-driven or time-driven changes to processes.