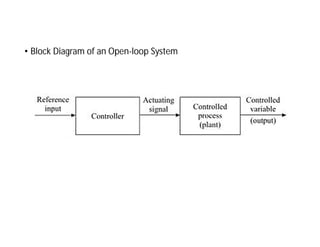
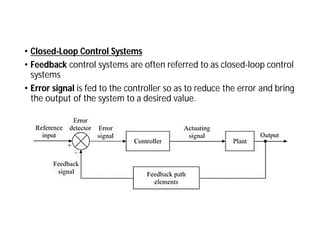
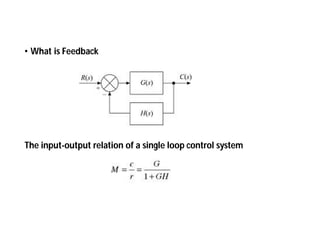
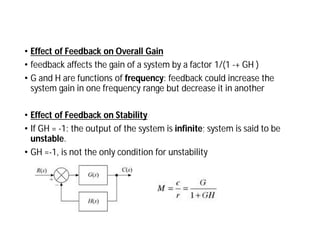
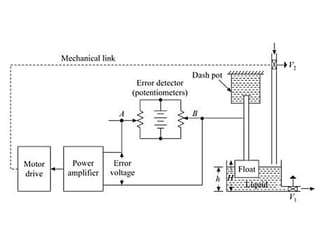
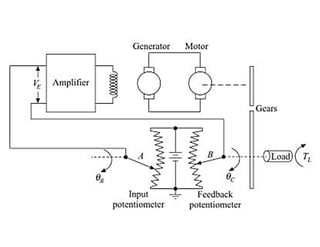
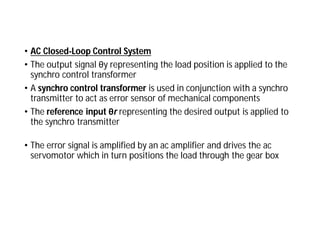
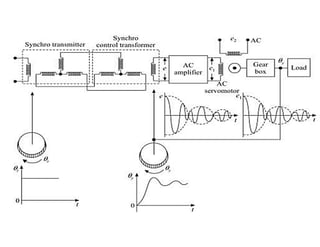
This document discusses control systems. It defines a control system as a means to maintain or alter a quantity of interest in accordance with a desired manner. Control systems can be classified in various ways, including as open-loop or closed-loop depending on whether feedback is present, and as continuous or discrete depending on the type of signals used. Open-loop systems are simple but inaccurate, while closed-loop systems are complex but accurate due to feedback correcting any errors. Feedback affects the stability and overall gain of a system. Common examples of control systems discussed include temperature control, motor position control, and liquid level control in a tank.