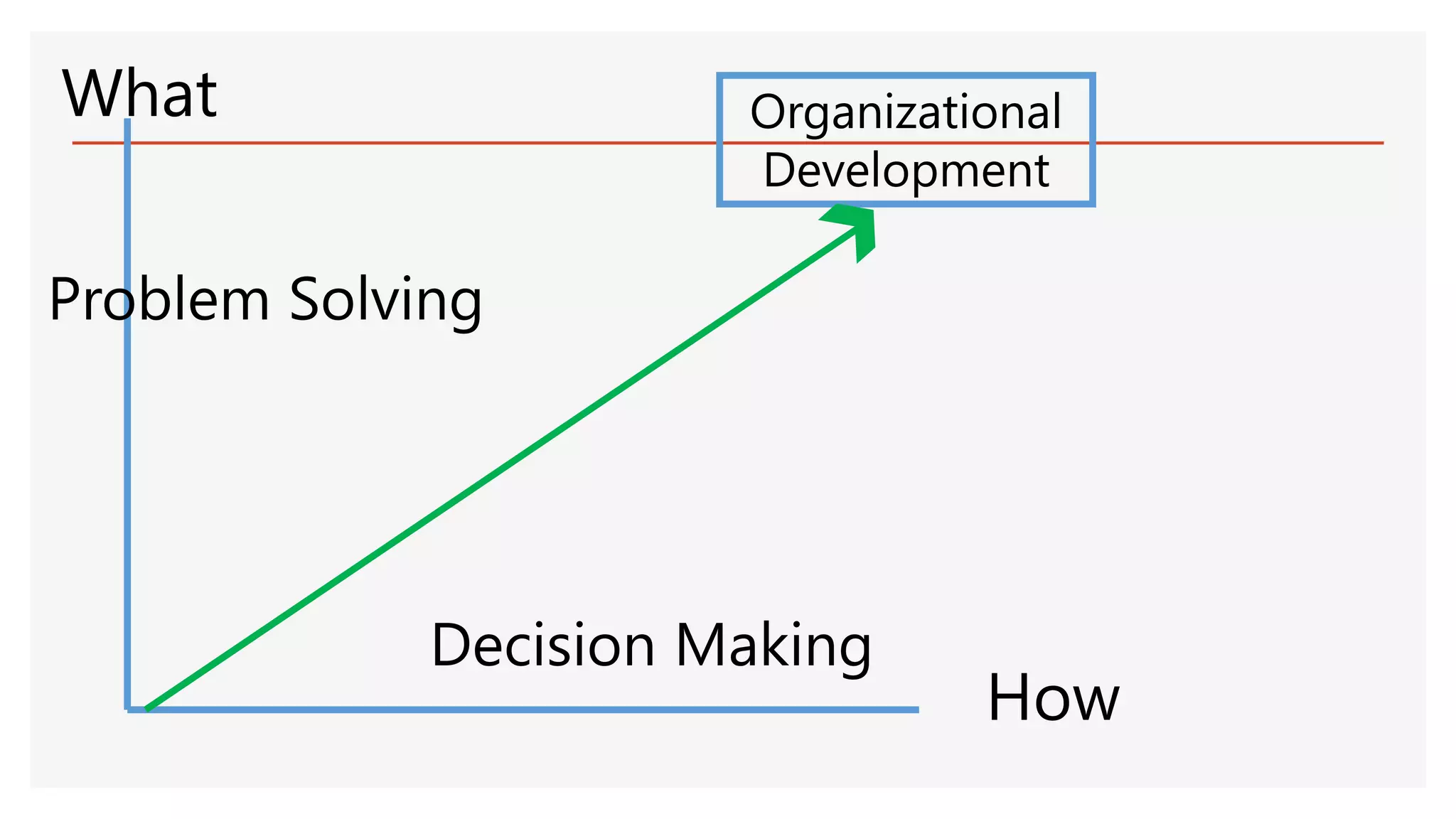
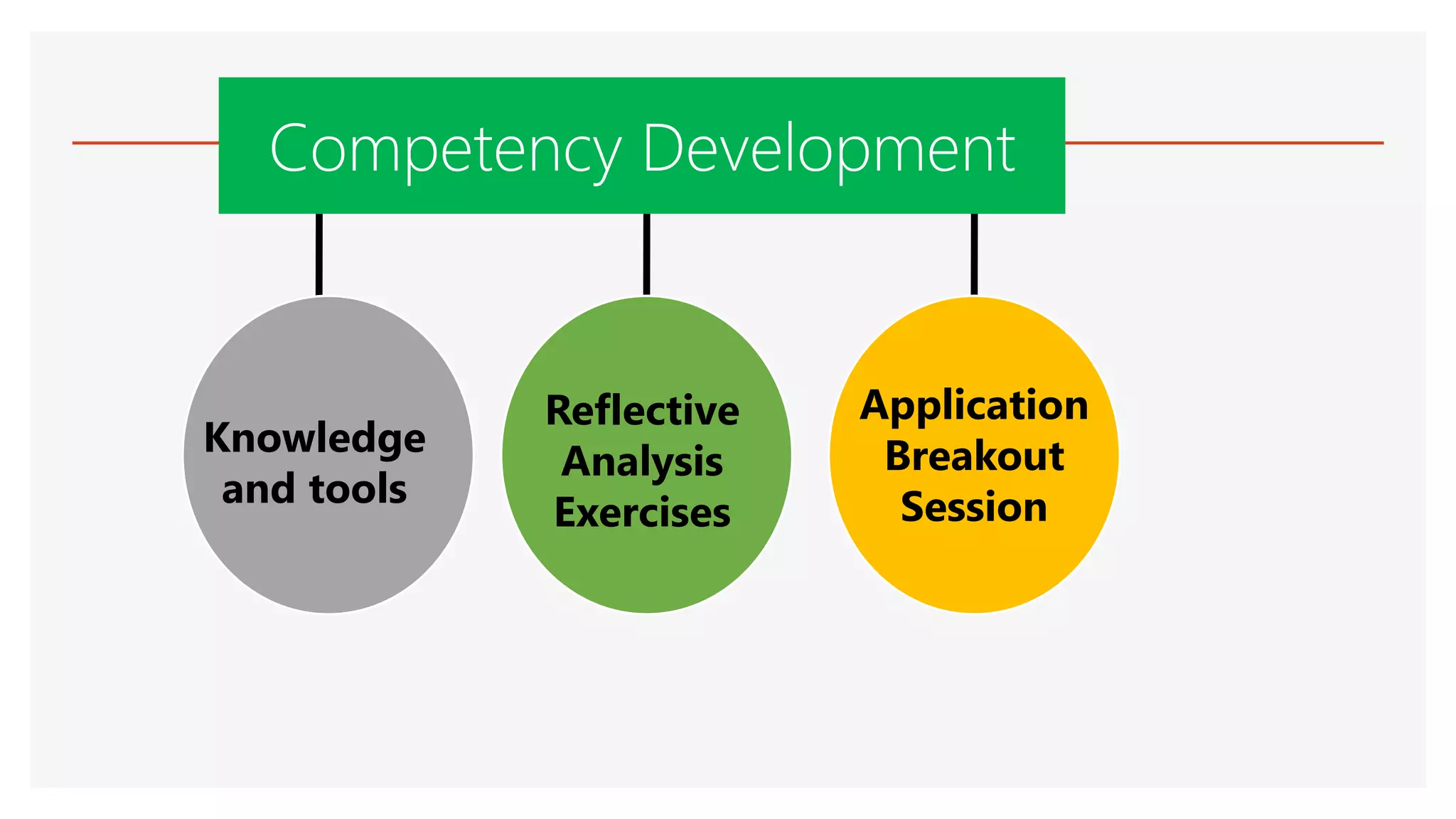
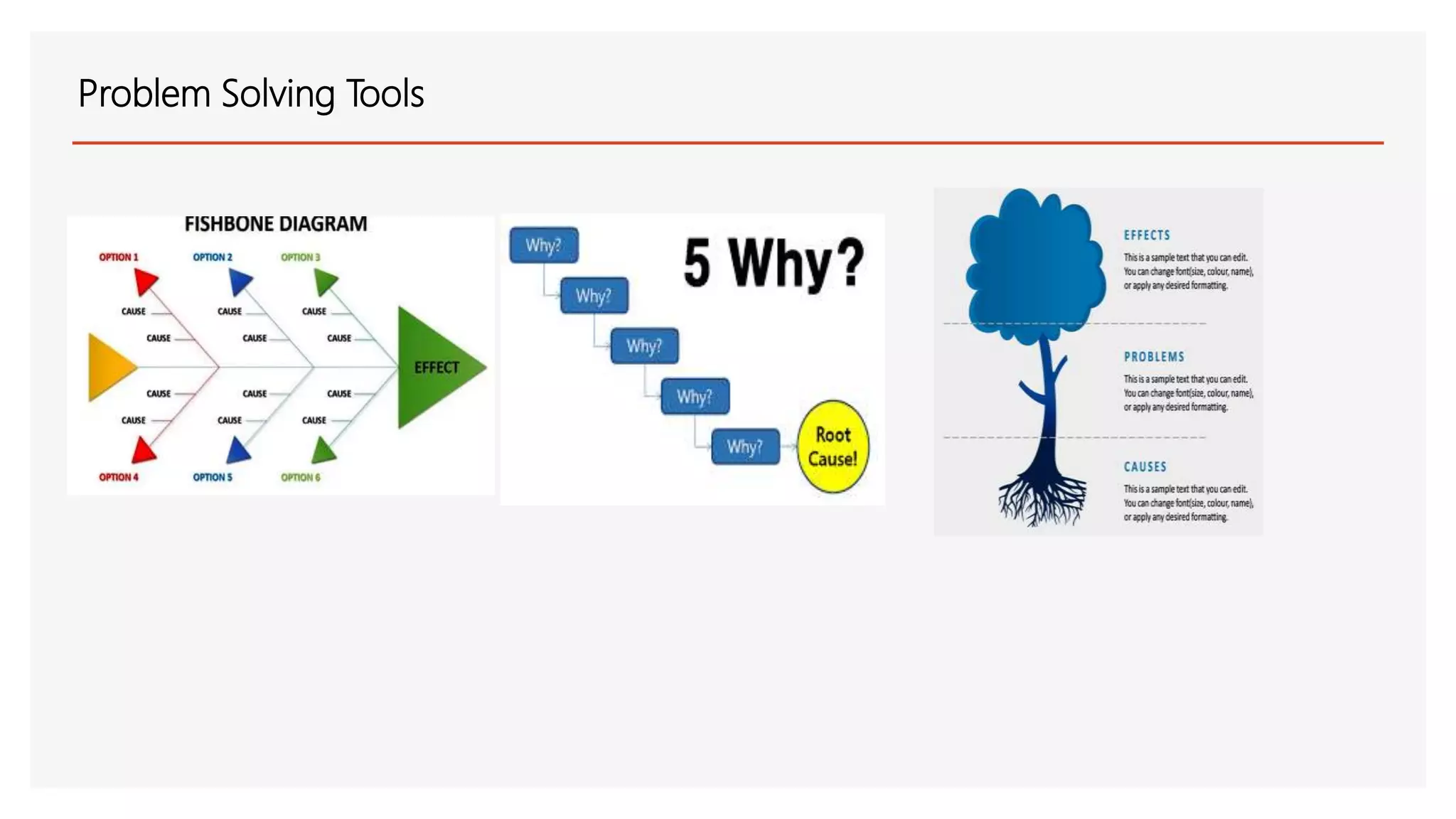
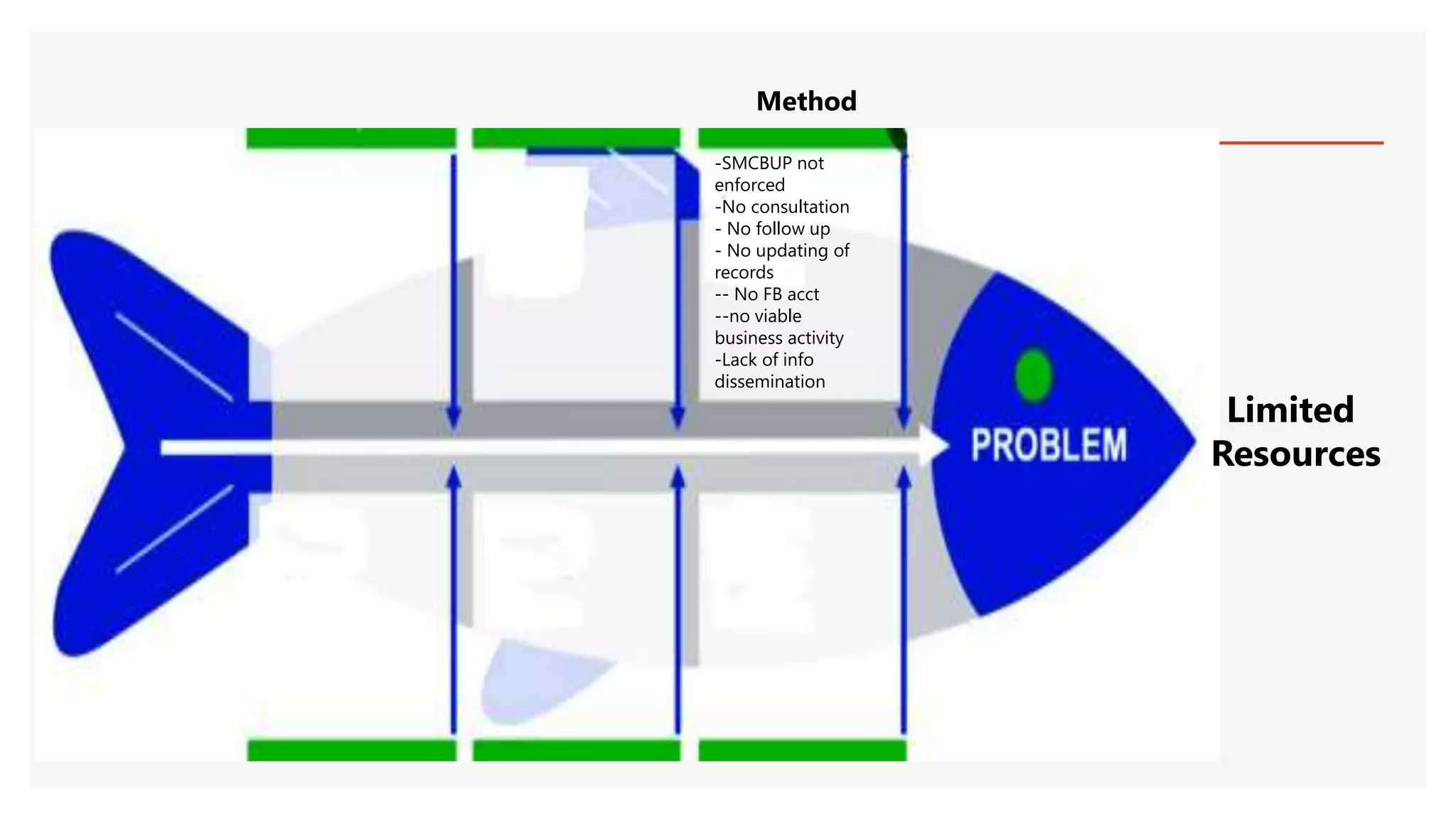
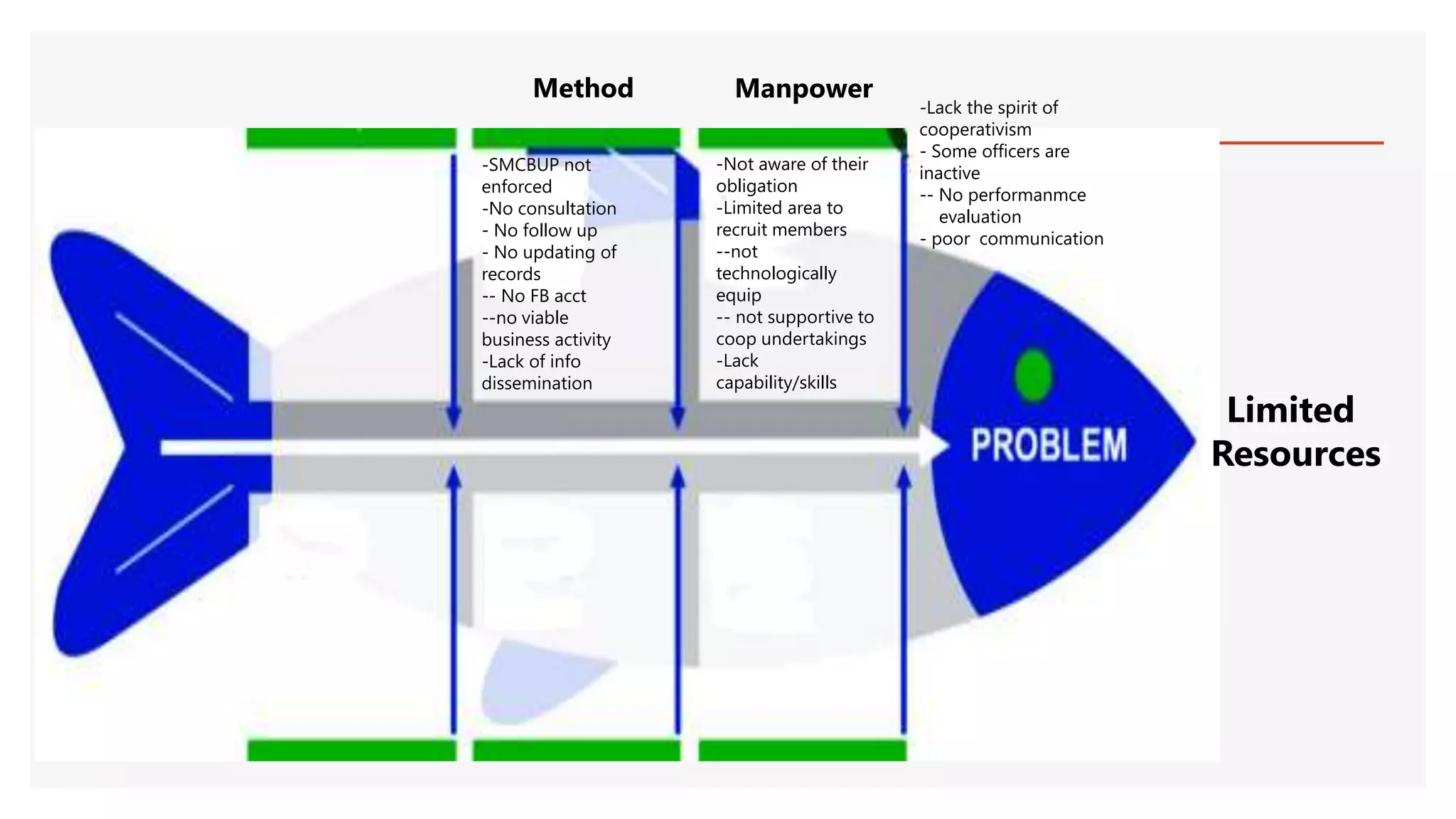
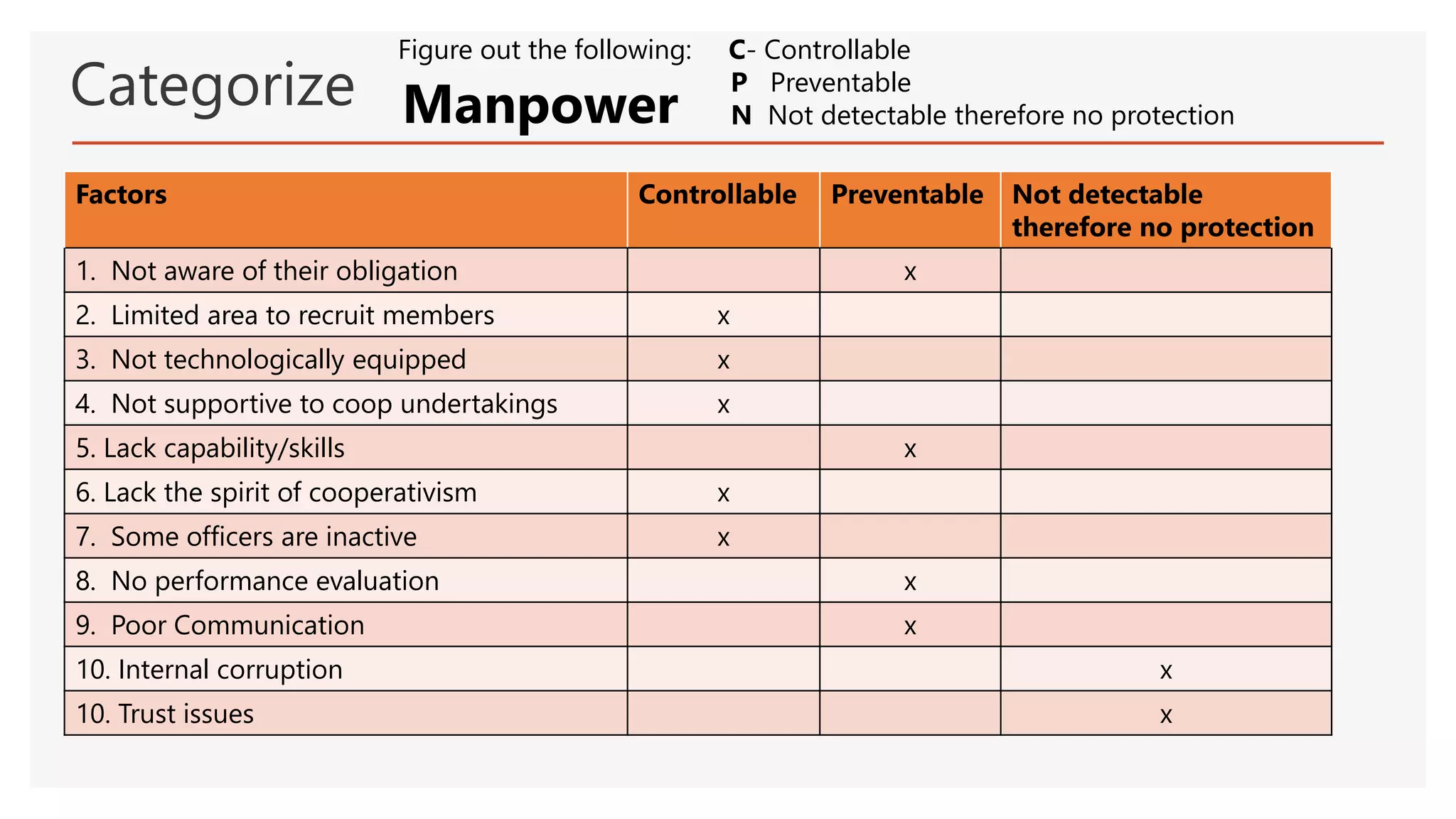
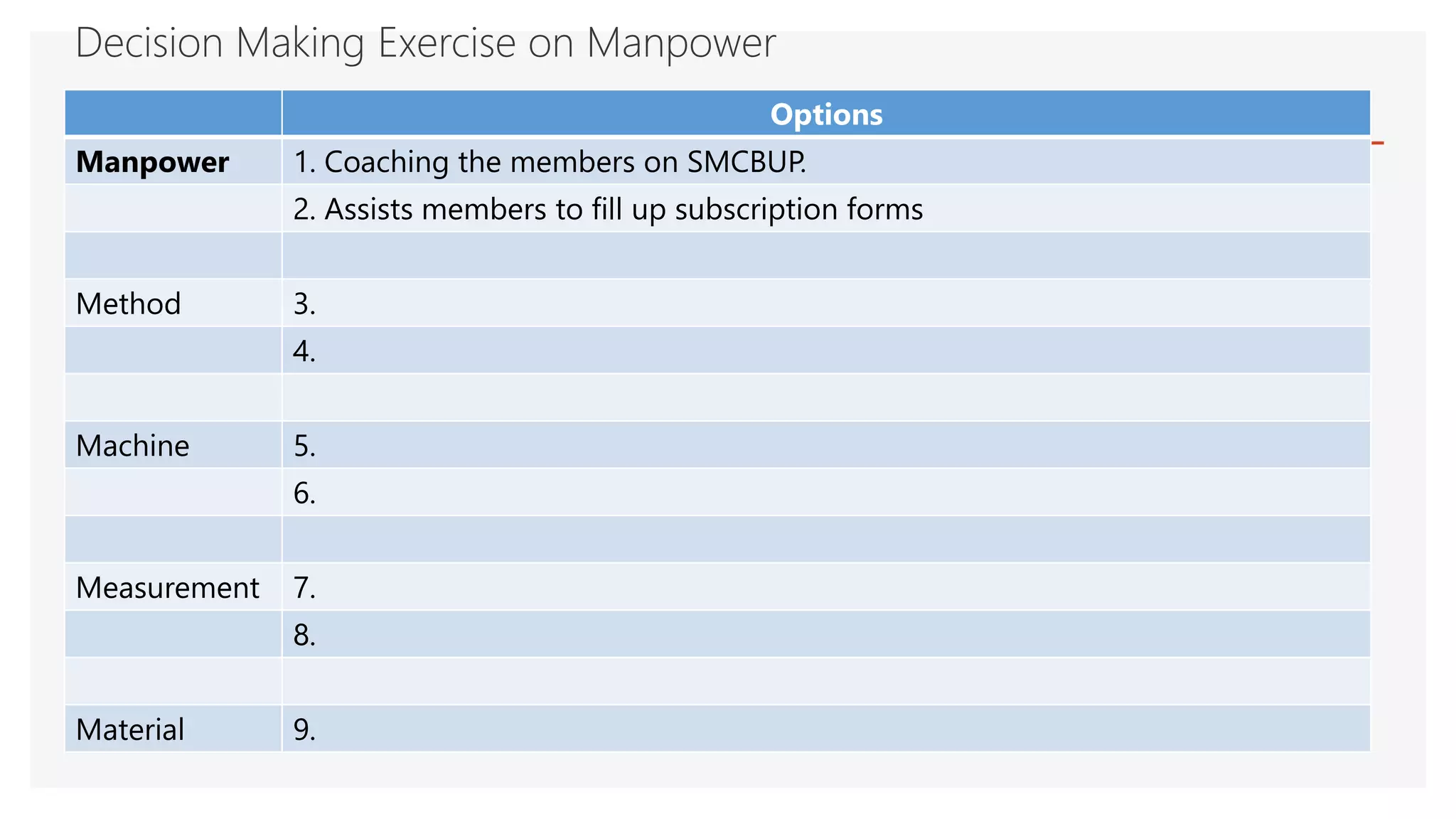
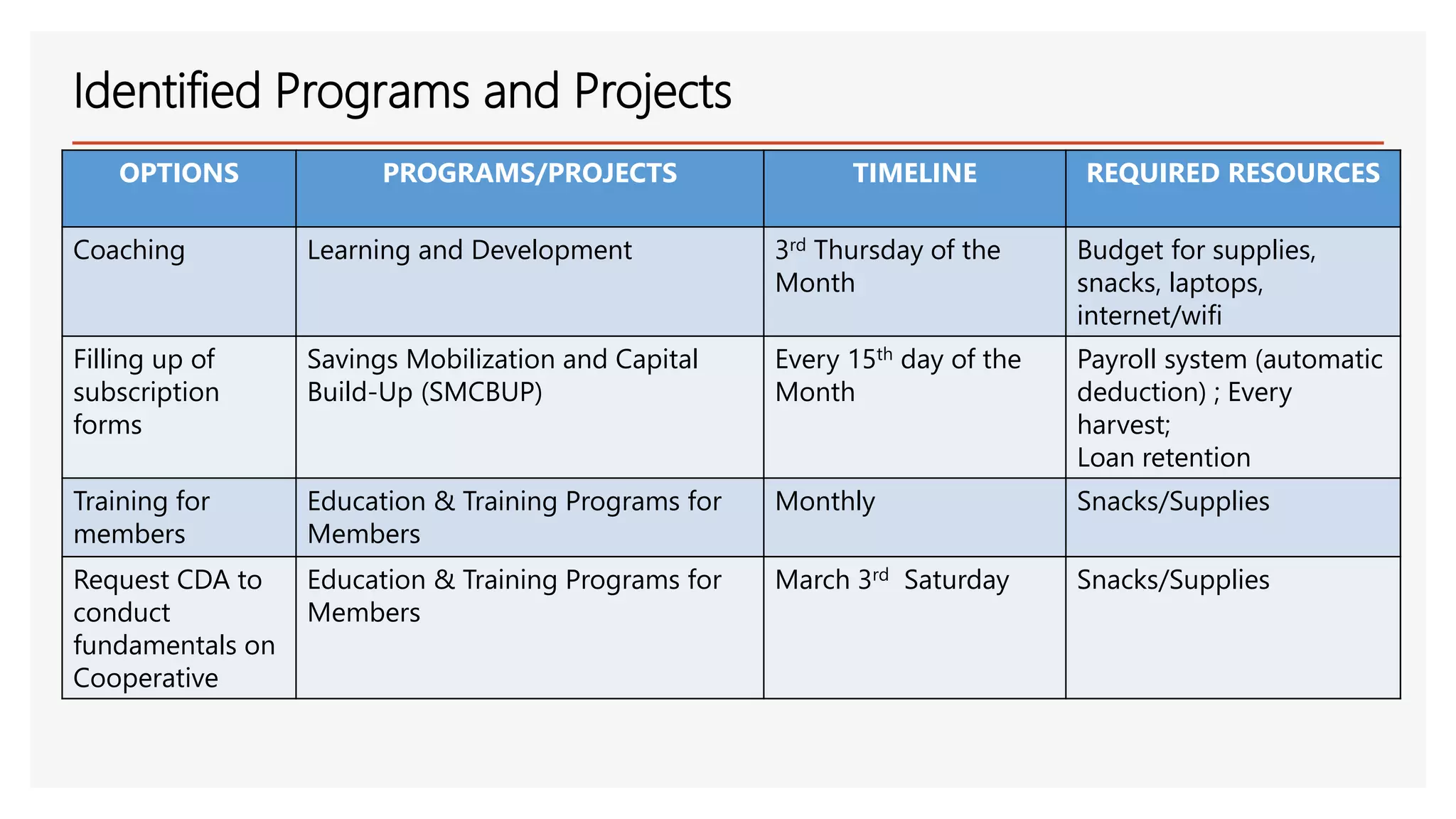
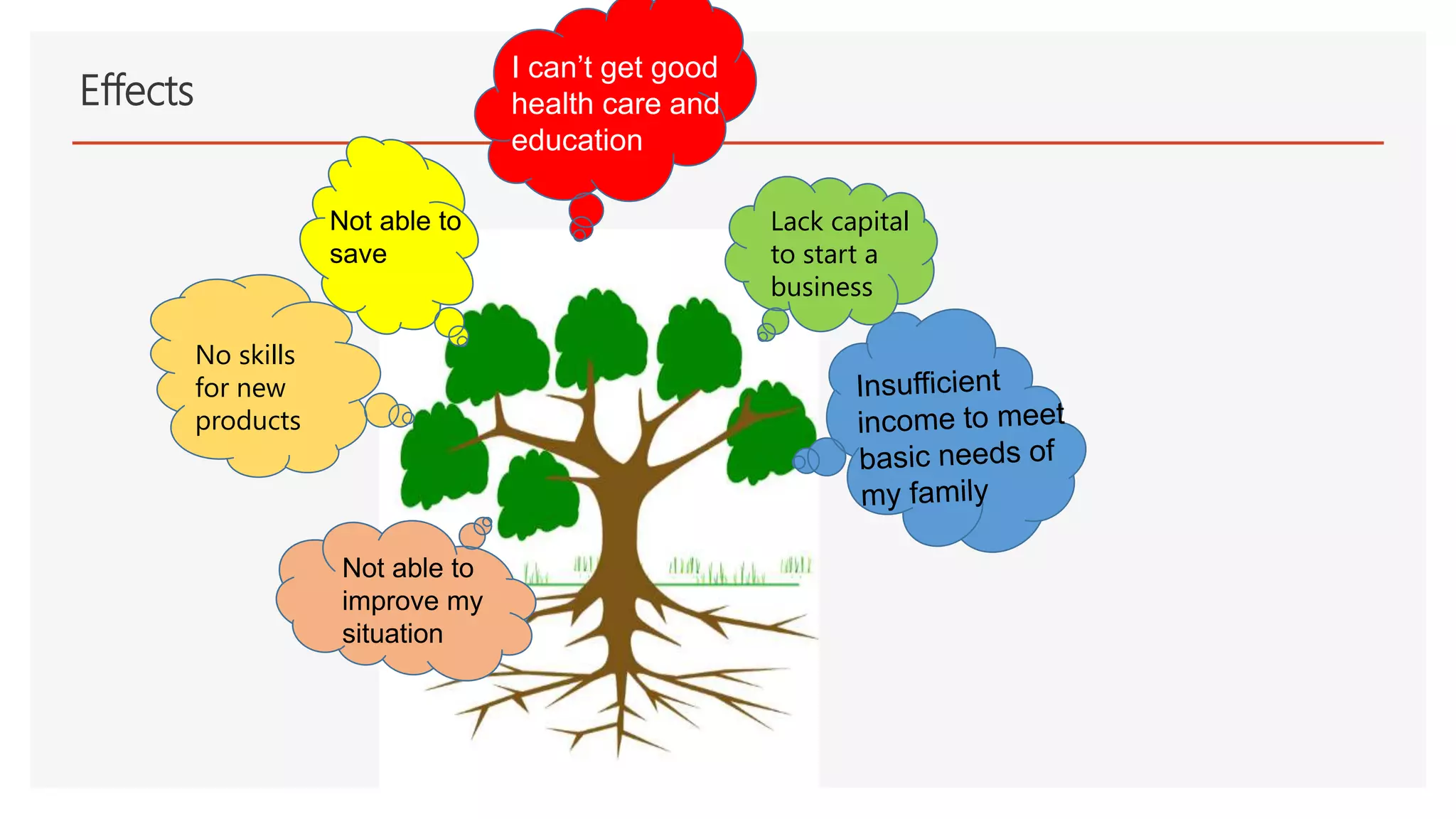
The document provides an overview of a lecture presentation on problem solving and decision making techniques. It discusses differentiating between issues, problems and challenges. It introduces several analytical tools for problem analysis and decision making, including fishbone diagrams and the Five Whys technique. The objectives are to understand frameworks, processes, and problem solving tools. The presentation covers defining issues, problems and challenges; problem solving frameworks; tools for identifying and analyzing problems; and mechanisms for sustaining resolutions. It provides examples of using techniques like fishbone diagrams to analyze organizational and personal problems.