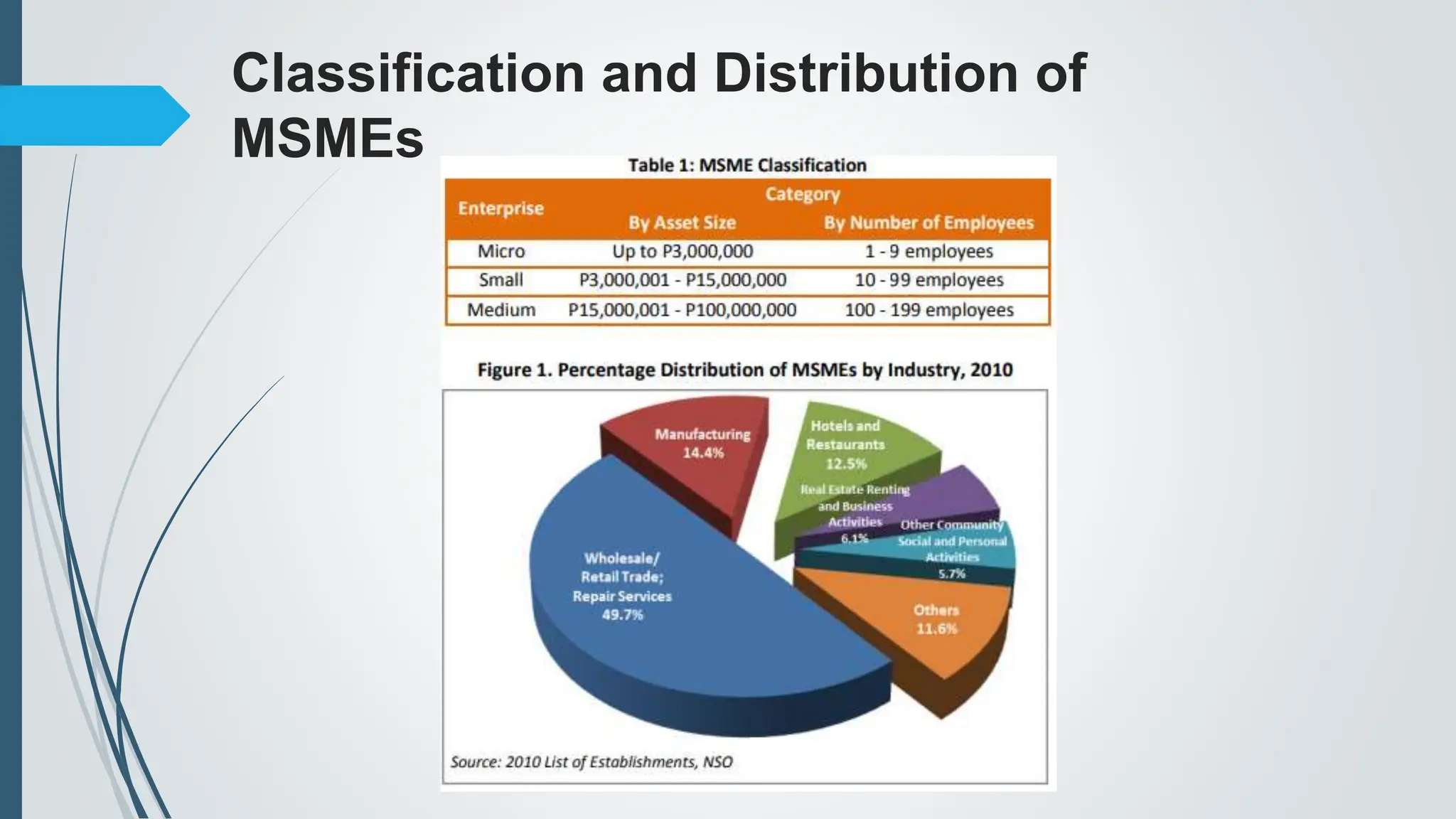
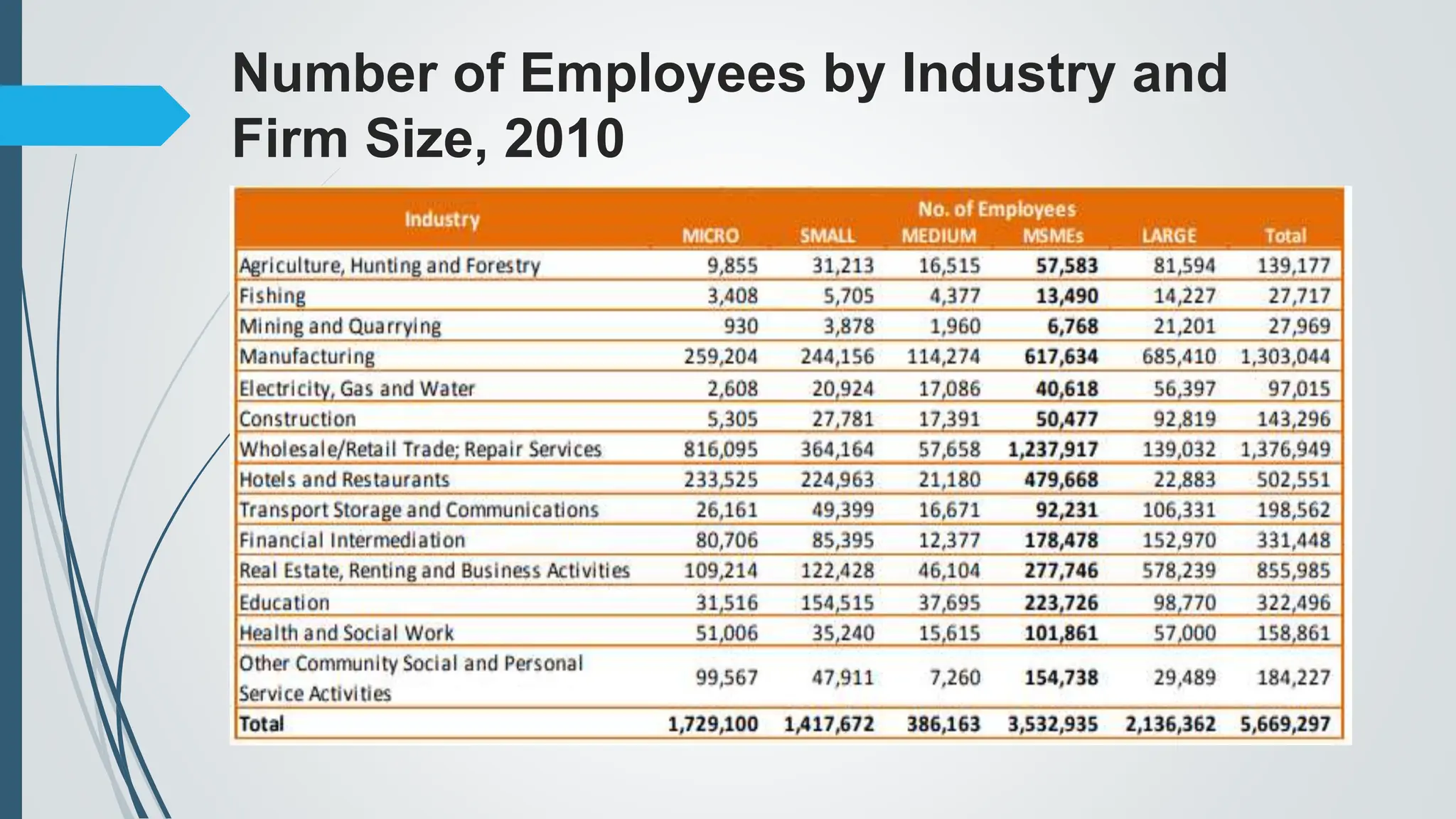
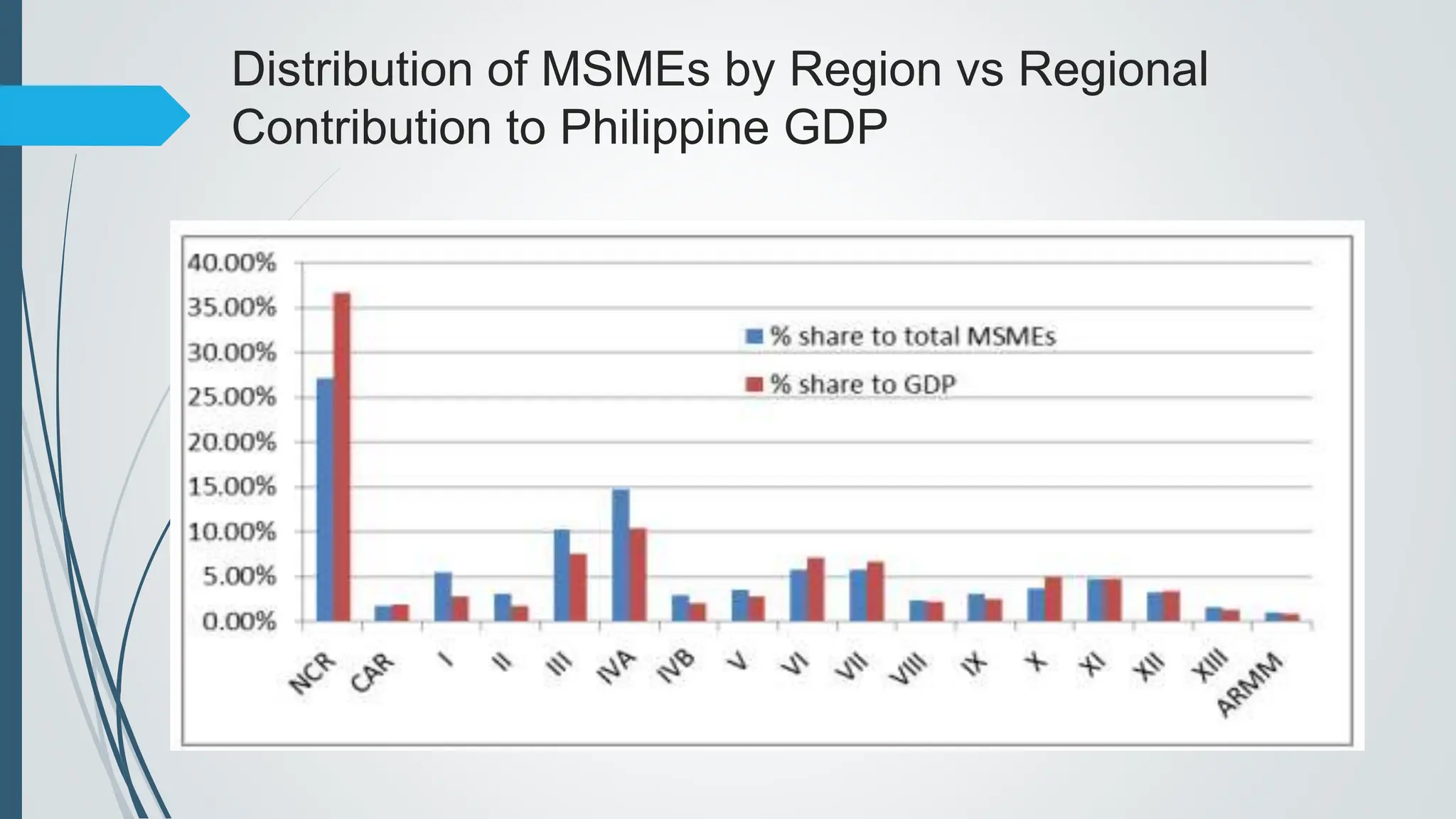
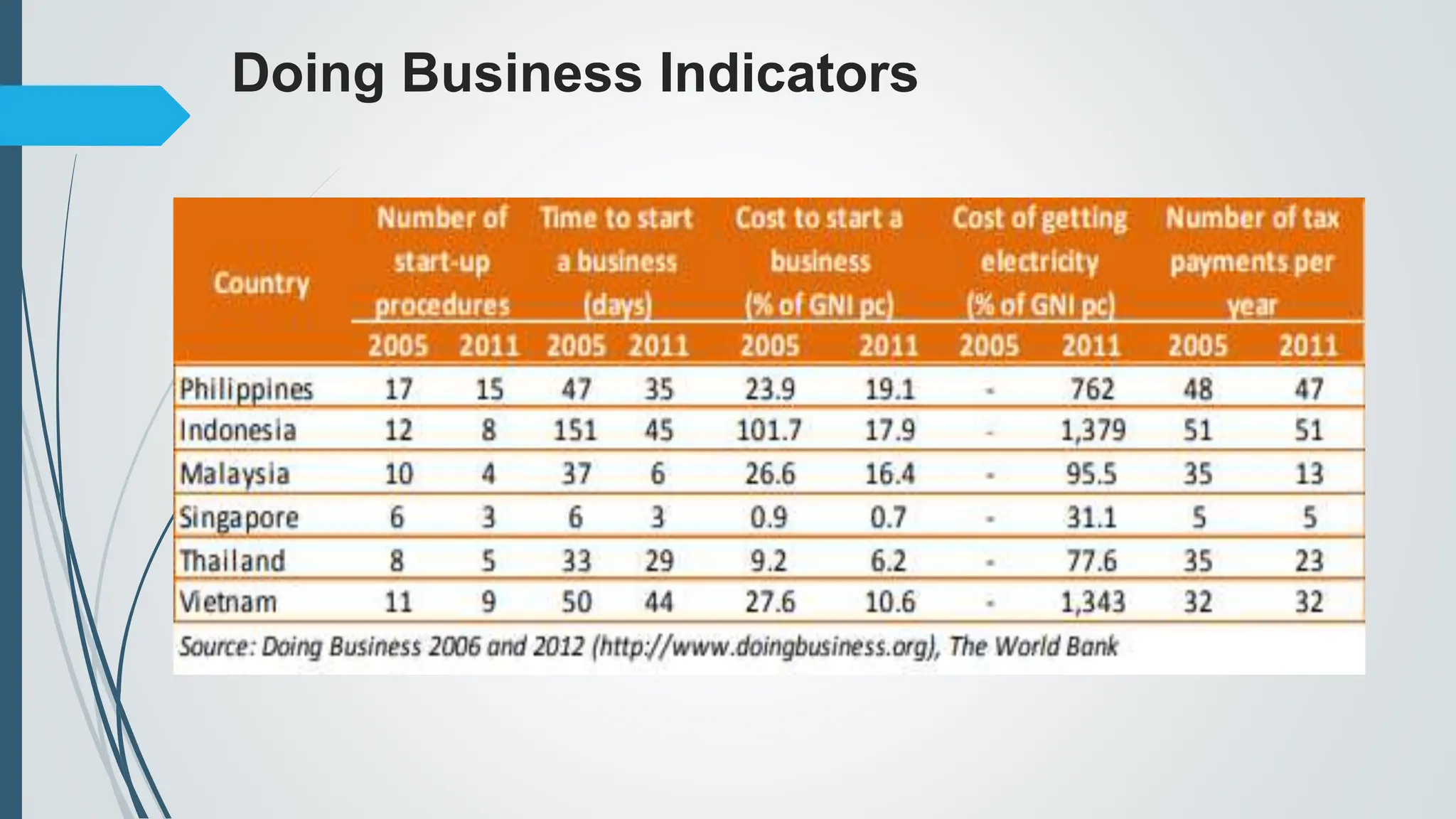
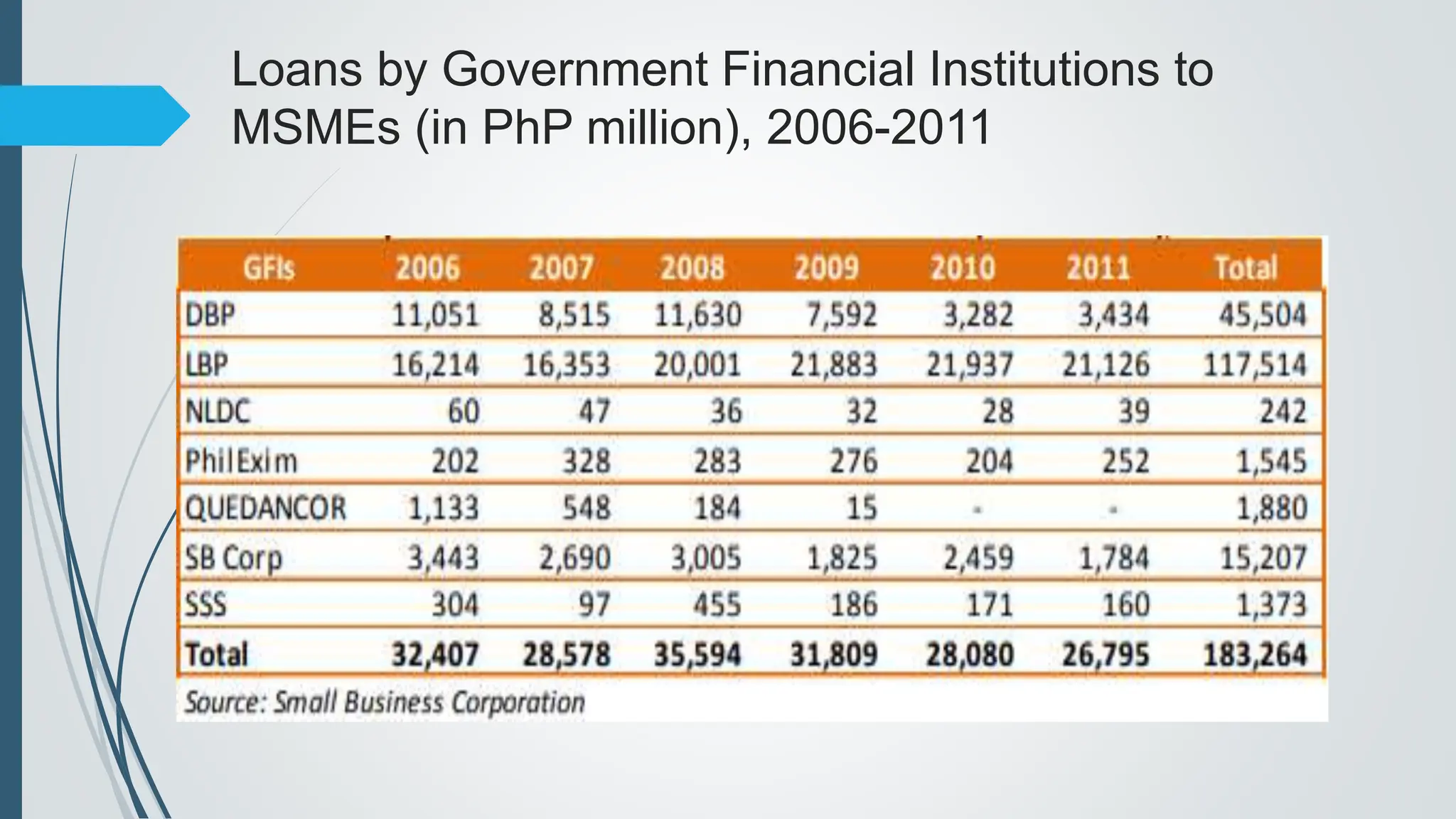
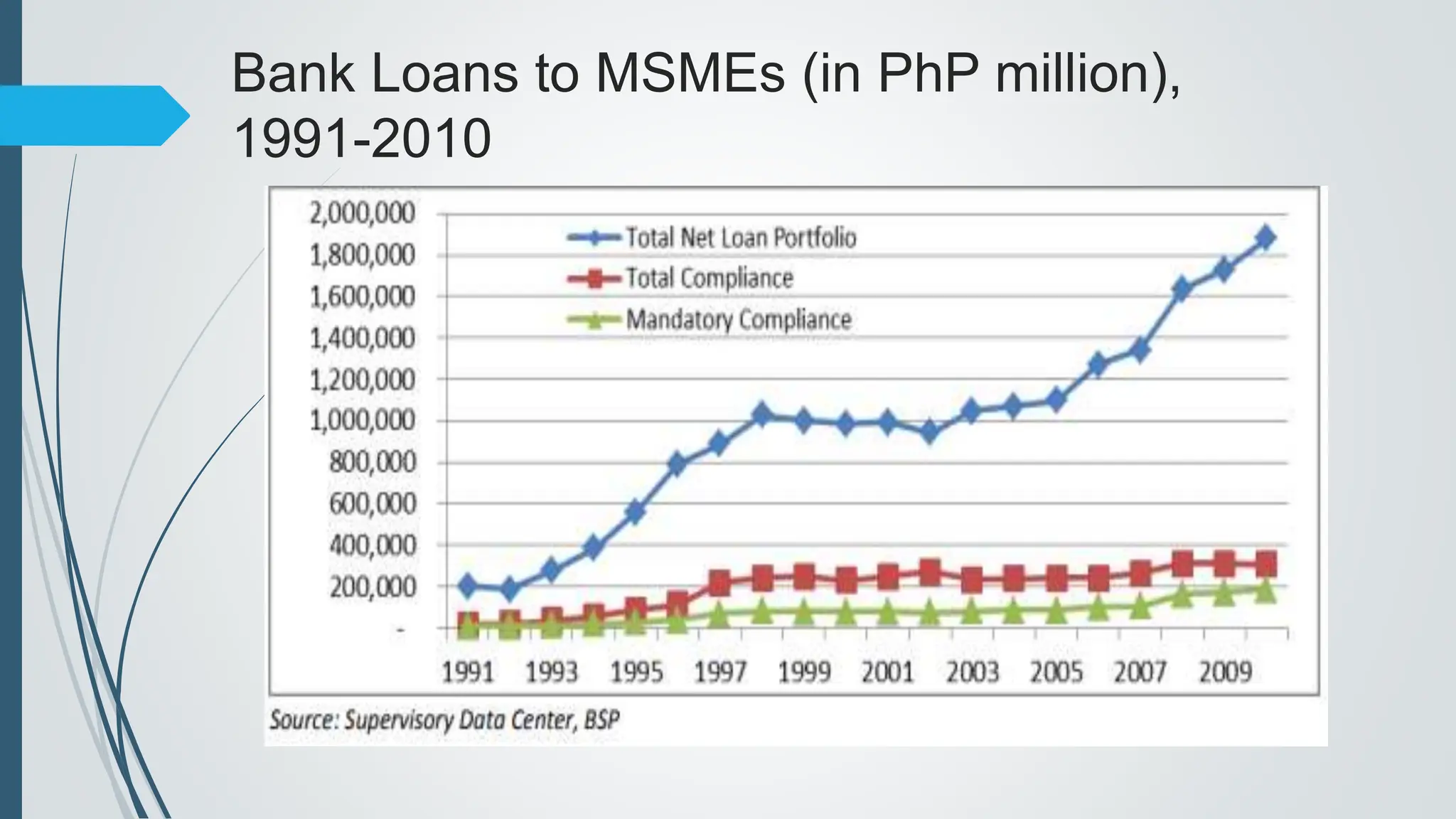
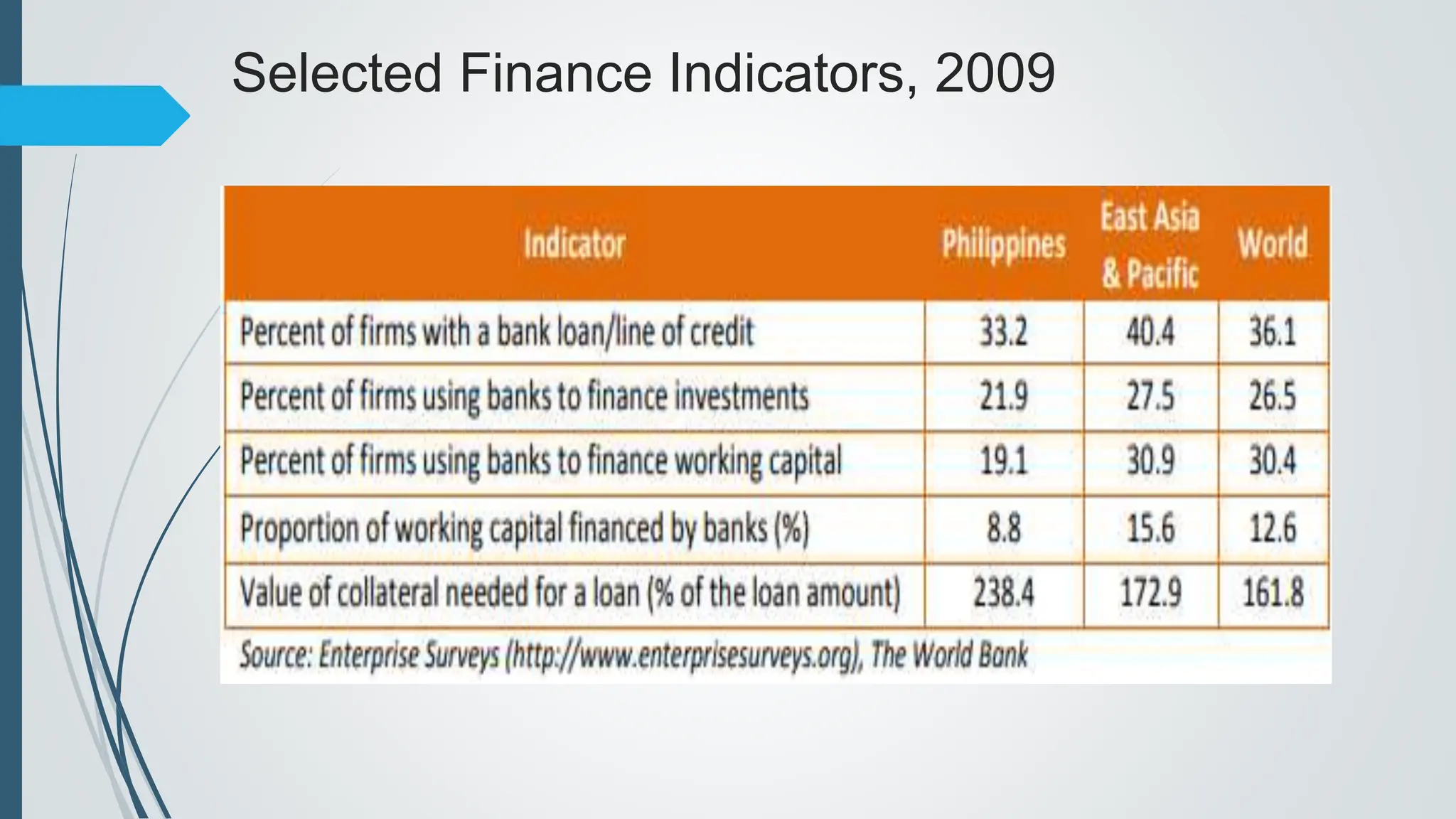
The document outlines the importance of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in the Philippines, highlighting their role in job creation and economic development. It discusses various barriers to MSME growth, including financial constraints, regulatory challenges, and access to financing. Additionally, it presents government programs aimed at supporting MSMEs and enhancing their contributions to the economy.